Issue Entity Properties

Issue Entity Properties Entity properties enable apps to add key value stores to jira entities, such as issues or projects. you can also add app properties to the connect app itself. this page provides an overview and examples of how entity properties and app properties work: entity properties. app properties. users can access entity and app properties using the rest. To modify, add, or remove the properties, the user who executes the request must have permission to edit the entity. for example, to add new property to issue enpr 4, you need permission to edit the issue. to retrieve a property, the user must have read permissions for the entity.
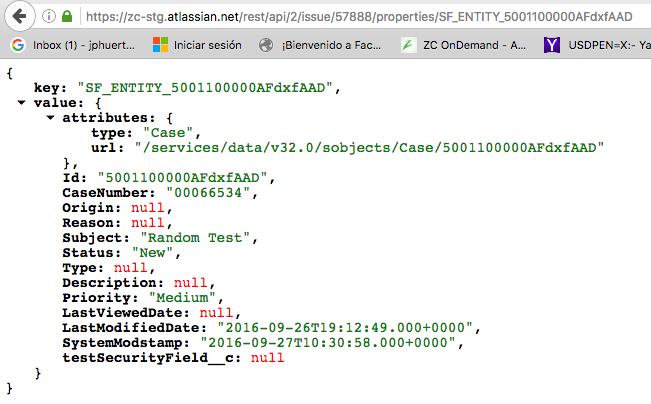
How To Access Case Fields Via Issue Entity Properties In Jira Cloud Using issue.property. rising stars are recognized for providing high quality answers to other users. rising stars receive a certificate of achievement and are on the path to becoming community leaders. hi, we are using jira 7.4.3. i try to understand the usage of the issue.property stuff in jql and rest. first question, is there any doc around. Entity properties allow you to add key value stores to issues, projects, users, and comments. your scripts can use these properties for automations, for example, to store a user's department name on the user object. there are two different mechanisms you can use to create these data stores. check out the table below to compare the two mechanisms:. Issue.property["request.channel.type"].value = portal to retrieve all of the jsd tickets submitted through the portal. some plugins add properties or allow you to add your own properties to an issue. Apps can store data in the form of entity properties in the host application. entity properties are key value pairs where the key is a string used to identify the property in all operations, and the value is a json blob. each host application allows properties to be stored on entities such as jira issues or confluence pages, or on your app.
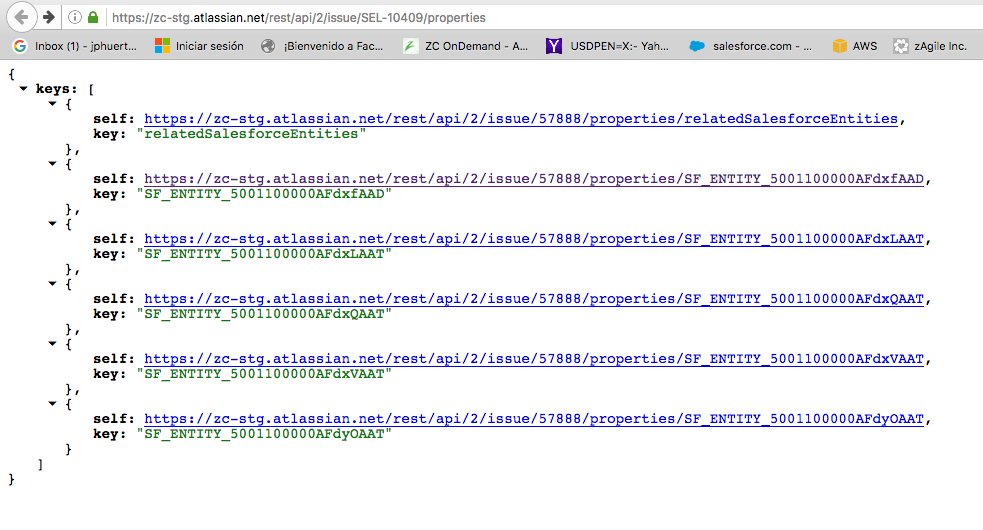
How To Access Case Fields Via Issue Entity Properties In Jira Cloud Issue.property["request.channel.type"].value = portal to retrieve all of the jsd tickets submitted through the portal. some plugins add properties or allow you to add your own properties to an issue. Apps can store data in the form of entity properties in the host application. entity properties are key value pairs where the key is a string used to identify the property in all operations, and the value is a json blob. each host application allows properties to be stored on entities such as jira issues or confluence pages, or on your app. Get entity properties. you can get an issue’s entity properties in the following ways: jira api rest request. open terminal (command line interface) and execute the following curl command, replacing: your domain with your jira url {issuekey} with valid jira issue key. email@example with your email. api token with your api token. The average time to set a storage entity is just 86 ms! surprisingly, this is more than twice as fast as the equivalent “set” operation for entity properties. the “get” operation is even more impressive, with an average time of only 67 ms, again more than twice as fast compared to getting an issue entity property. conclusion.

Get Issue Entity Properties Get entity properties. you can get an issue’s entity properties in the following ways: jira api rest request. open terminal (command line interface) and execute the following curl command, replacing: your domain with your jira url {issuekey} with valid jira issue key. email@example with your email. api token with your api token. The average time to set a storage entity is just 86 ms! surprisingly, this is more than twice as fast as the equivalent “set” operation for entity properties. the “get” operation is even more impressive, with an average time of only 67 ms, again more than twice as fast compared to getting an issue entity property. conclusion.
Entity Property Tool For Jira Atlassian Marketplace
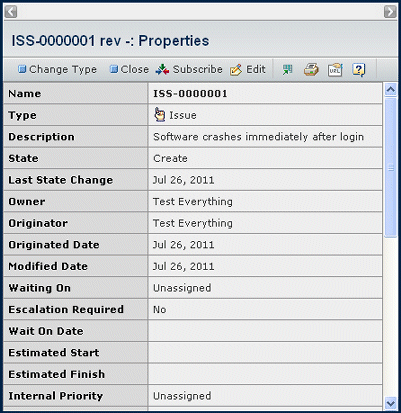
Issue Properties Page

Comments are closed.