Ischemic Stroke Causes Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Pathology
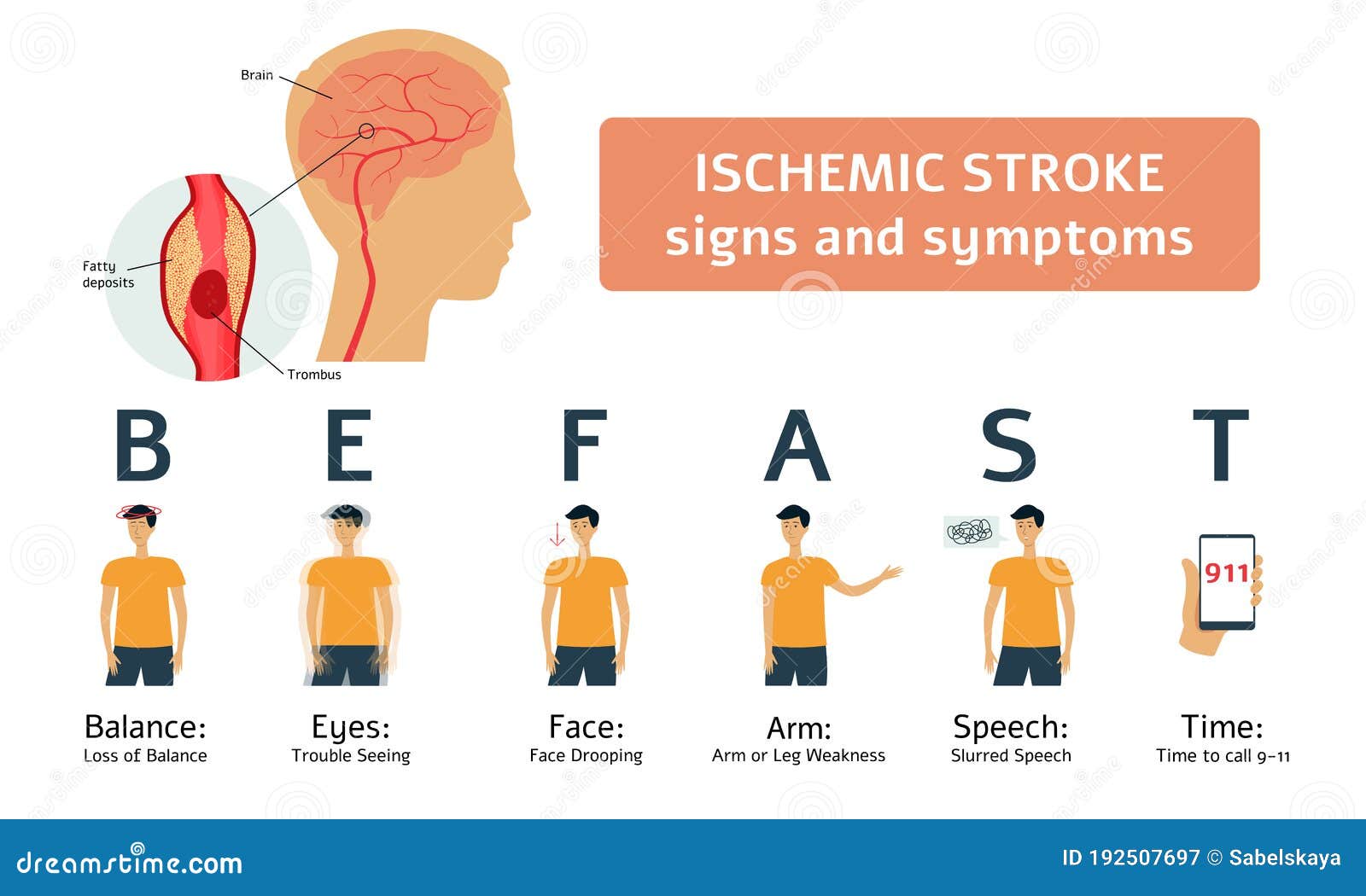
Pathophysiology Of Ischemic Stroke The symptoms of an ischemic stroke can involve one or more of the following: one sided weakness or paralysis. aphasia (difficulty with or loss of speaking ability). slurred or garbled speaking (dysarthria). loss of muscle control on one side of your face or facial droop. Emergency treatment depends on whether you're having an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke. during an ischemic stroke, blood vessels in the brain are blocked or narrowed. during a hemorrhagic stroke, there's bleeding into the brain. ischemic stroke. to treat an ischemic stroke, blood flow must quickly be restored to the brain. this may be done with:.

Acute Ischemic Stroke Signs And Symptoms Stroke Syndromes Causes Acute stroke is the acute onset of focal neurological deficits in a vascular territory affecting the brain, retina, or spinal cord due to underlying cerebrovascular diseases.[1] stroke is prevalent across patient populations and can significantly cause morbidity and mortality. strokes are categorized as ischemic and hemorrhagic. hemorrhagic strokes can further be classified as intracerebral. There are two main causes of stroke. an ischemic stroke is caused by a blocked artery in the brain. a hemorrhagic stroke is caused by leaking or bursting of a blood vessel in the brain. some people may have only a temporary disruption of blood flow to the brain, known as a transient ischemic attack (tia). a tia doesn't cause lasting symptoms. Ischemic stroke is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. approximately 85% of strokes are ischemic, caused by arterial occlusion. a clinical emergency: timely diagnosis, triage, and intervention improves outcomes. care of patients in dedicated stroke units improves survival and function. intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue. Ischemic stroke is sudden neurologic deficits that result from focal cerebral ischemia associated with permanent brain infarction (eg, positive results on diffusion weighted mri). common causes are atherothrombotic occlusion of large arteries; cerebral embolism (embolic infarction); nonthrombotic occlusion of small, deep cerebral arteries.

Ischemic Stroke Causes Signs Symptoms Ischemic Stroke Treatment Ischemic stroke is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality. approximately 85% of strokes are ischemic, caused by arterial occlusion. a clinical emergency: timely diagnosis, triage, and intervention improves outcomes. care of patients in dedicated stroke units improves survival and function. intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue. Ischemic stroke is sudden neurologic deficits that result from focal cerebral ischemia associated with permanent brain infarction (eg, positive results on diffusion weighted mri). common causes are atherothrombotic occlusion of large arteries; cerebral embolism (embolic infarction); nonthrombotic occlusion of small, deep cerebral arteries. Acute ischemic stroke (ais) is among the leading causes of death and long term disability. intravenous tissue plasminogen activator has been the mainstay of acute therapy. recently, several prospective randomized trials documented the value of endovascular revascularization in selected patients with large vessel occlusion within the anterior circulation. this finding has led to a paradigm. Stroke (including ischaemic stroke and haemorrhagic stroke) affects 13.7 million people globally per year and is the second leading cause of death, with 5.5 million deaths per year 14, 15. an.
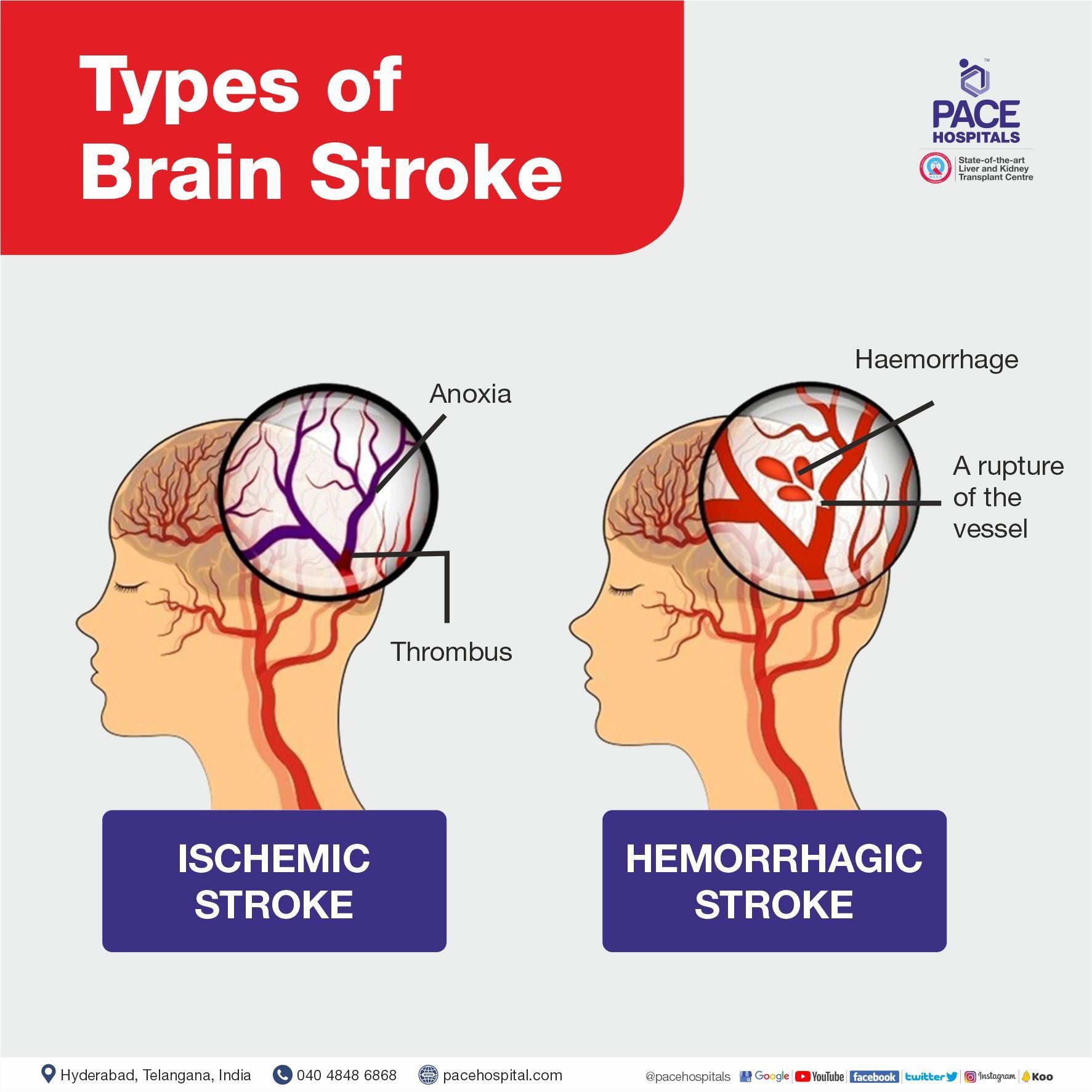
Brain Stroke Types Causes Symptoms Prevention And Treatment Acute ischemic stroke (ais) is among the leading causes of death and long term disability. intravenous tissue plasminogen activator has been the mainstay of acute therapy. recently, several prospective randomized trials documented the value of endovascular revascularization in selected patients with large vessel occlusion within the anterior circulation. this finding has led to a paradigm. Stroke (including ischaemic stroke and haemorrhagic stroke) affects 13.7 million people globally per year and is the second leading cause of death, with 5.5 million deaths per year 14, 15. an.

Comments are closed.