Invasion And Metastasis Simplified

Chapter 32 Invasion And Metastasis Metastasis is one of the most enigmatic features of cancer biology, and is a complex sequential and interrelated process leading to the formation of distant secondary tumors, collectively termed. In vivo studies show that autophagy is involved in modulating tumor cell motility and invasion, cancer stem cell viability and differentiation, resistance to anoikis, emt, metastatic cell dormancy.

Key Steps Of Invasion And Metastasis Download Scientific Diagram Metastasis is the leading reason for the resultant mortality of patients with cancer. the past few decades have witnessed remarkable progress in understanding the molecular and cellular basis of this lethal process in cancer. the current article summarizes some of the key progress in this area and discusses the role of cell junctions, cell adhesions, epithelial mesenchymal transition, angio. Abstract. metastasis is the primary cause of cancer morbidity and mortality. the process involves a complex interplay between intrinsic tumor cell properties as well as interactions between cancer cells and multiple microenvironments. the outcome is the development of a nearby or distant discontiguous secondary mass. to successfully disseminate, metastatic cells acquire properties in addition. Cell motility is a fundamental and ancient cellular behaviour that contributes to metastasis and is conserved in simple organisms. to human cancer invasion and metastasis that have come from. Invasion and metastasis are complex processes, particularly in carcinomas, since normal epithelia are composed of strongly adherent cells and are confined by a basement membrane. before or during invasion, carcinomas activate the surrounding connective tissue, eliciting inflammation and angiogenesis.
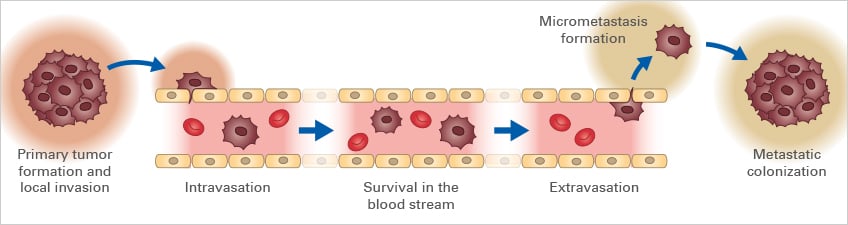
Cancer Research Invasion And Metastasis Ibidi Cell motility is a fundamental and ancient cellular behaviour that contributes to metastasis and is conserved in simple organisms. to human cancer invasion and metastasis that have come from. Invasion and metastasis are complex processes, particularly in carcinomas, since normal epithelia are composed of strongly adherent cells and are confined by a basement membrane. before or during invasion, carcinomas activate the surrounding connective tissue, eliciting inflammation and angiogenesis. Cancer associated metastasis is the primary cause of morbidity and mortality. yet, its underlying biological mechanism remains poorly understood. efforts to prevent or delay metastasis require a deep understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms. however, continued advancement in cancer biology research has improved the comprehensive understanding of some of the molecular keystones of. Simple model organisms can be used to investigate aspects of tumour invasion and metastasis. open in a new tab metastasis is a multistep process during which tumour cells breach tissue borders (1); migrate in sheets, strands, streams and clusters (2); cross into and out of blood vessels (3) and form colonies at distant sites (4).
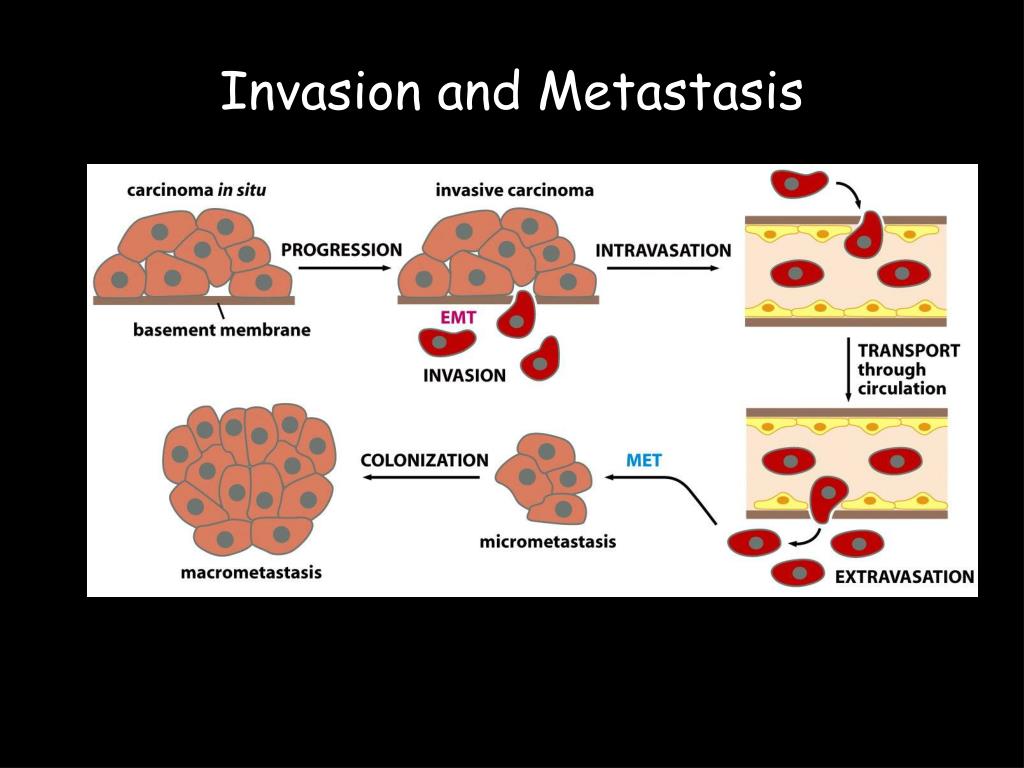
Ppt Mechanisms Of Cell Invasion Powerpoint Presentation Free Cancer associated metastasis is the primary cause of morbidity and mortality. yet, its underlying biological mechanism remains poorly understood. efforts to prevent or delay metastasis require a deep understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms. however, continued advancement in cancer biology research has improved the comprehensive understanding of some of the molecular keystones of. Simple model organisms can be used to investigate aspects of tumour invasion and metastasis. open in a new tab metastasis is a multistep process during which tumour cells breach tissue borders (1); migrate in sheets, strands, streams and clusters (2); cross into and out of blood vessels (3) and form colonies at distant sites (4).
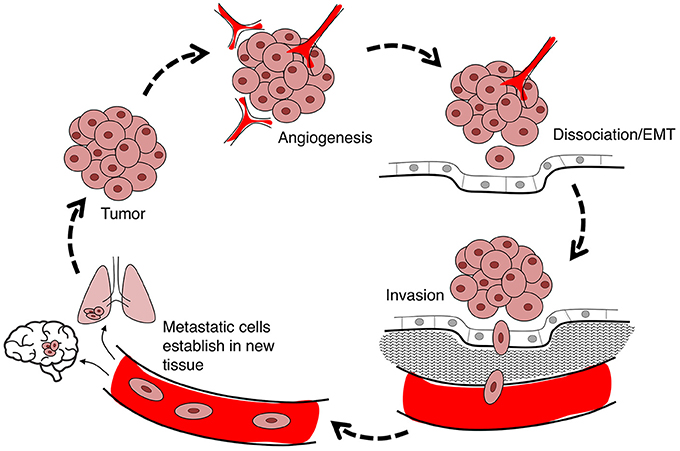
Frontiers Mechanisms Of Aquaporin Facilitated Cancer Invasion And

Comments are closed.