Interpretation Of Graphs
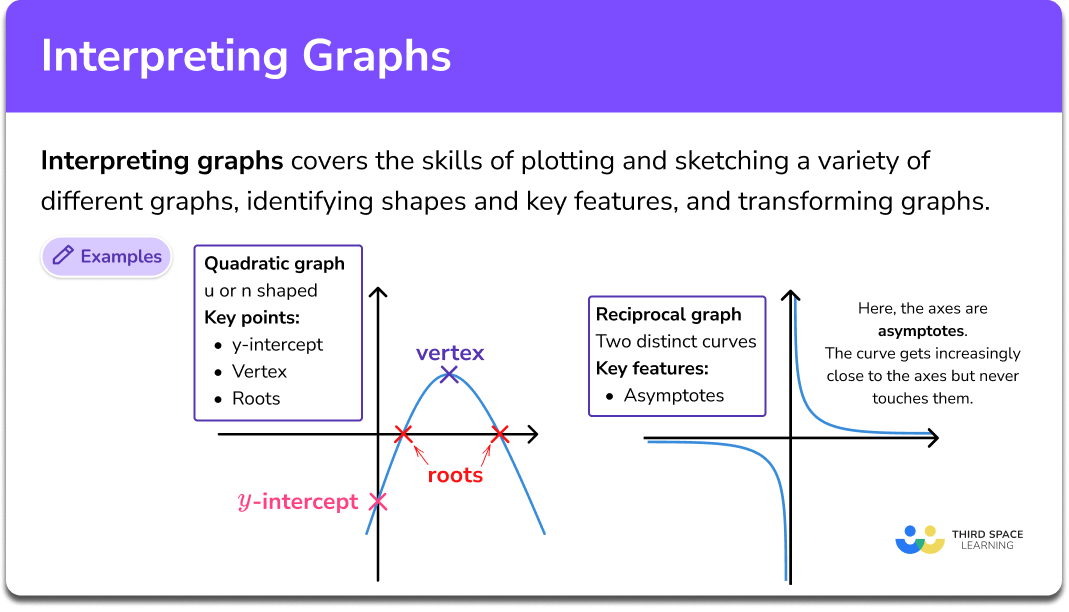
Interpreting Graphs Gcse Maths Steps Examples Worksheet Learn the basics of chart and graph interpretation with examples and tips. find out how to use chartexpo, a data visualization tool, to create and customize easy to interpret charts and graphs. Useful phrases to interpret a graph. as every graph tells a story, the creator has to be a good story teller. she or he needs basic knowledge in creating and interpreting the graphs produced. also the person trying to understand the story, needs some basic knowledge about graphs. otherwise reading a graph is like reading a text in a foreign.

Interpretation Of Graphs And Charts Example 1: find the slope (rate of change) use the graph to find the rate of change. identify two points on the graph. 2 count the vertical movement and horizontal movement from one point to the second point. 3 write the slope. the slope is the ratio, slope = change in y change in x. Graph types and terminology: understanding different types of graphs, such as bar graphs, line graphs, scatter plots, and pie charts, is essential in graph interpretation. familiarity with graph terminology, such as axes, legends, data points, and scales, enables individuals to effectively analyze and interpret visual representations of data. Use scatterplots to show relationships between pairs of continuous variables. these graphs display symbols at the x, y coordinates of the data points for the paired variables. scatterplots are also known as scattergrams and scatter charts. the pattern of dots on a scatterplot allows you to determine whether a relationship or correlation exists. This guide has been created because a ll data visualizations, whether a chart, graph, infographic, etc, should be read with a grain of salt. data is misinterpreted more than you may think. even with the best of intentions, visualization creators may omit, over simplify, or over complicate important variables. as a reader of data visualizations.
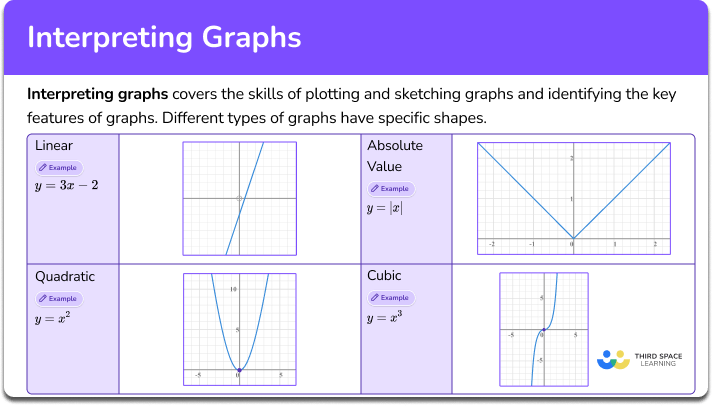
Interpreting Graphs Math Steps Examples Questions Use scatterplots to show relationships between pairs of continuous variables. these graphs display symbols at the x, y coordinates of the data points for the paired variables. scatterplots are also known as scattergrams and scatter charts. the pattern of dots on a scatterplot allows you to determine whether a relationship or correlation exists. This guide has been created because a ll data visualizations, whether a chart, graph, infographic, etc, should be read with a grain of salt. data is misinterpreted more than you may think. even with the best of intentions, visualization creators may omit, over simplify, or over complicate important variables. as a reader of data visualizations. Graphs that are used to depict qualitative data are pie charts and bar graphs. a pie chart looks exactly like what you might expect: a pie! a circle, representing 100% of a particular variable of interest, is divided into categories. segments of the pie represent a percentage of the whole. Line charts: using, examples, and interpreting. by jim frost 3 comments. use line charts to display a series of data points that are connected by lines. analysts use line charts to emphasize changes in a metric on the vertical y axis by another variable on the horizontal x axis. often, the x axis reflects time, but not always.

Example Of Graph Interpretation Graphs that are used to depict qualitative data are pie charts and bar graphs. a pie chart looks exactly like what you might expect: a pie! a circle, representing 100% of a particular variable of interest, is divided into categories. segments of the pie represent a percentage of the whole. Line charts: using, examples, and interpreting. by jim frost 3 comments. use line charts to display a series of data points that are connected by lines. analysts use line charts to emphasize changes in a metric on the vertical y axis by another variable on the horizontal x axis. often, the x axis reflects time, but not always.

Interpreting Graphs Youtube

Comments are closed.