Information About Food Chains And Food Webs
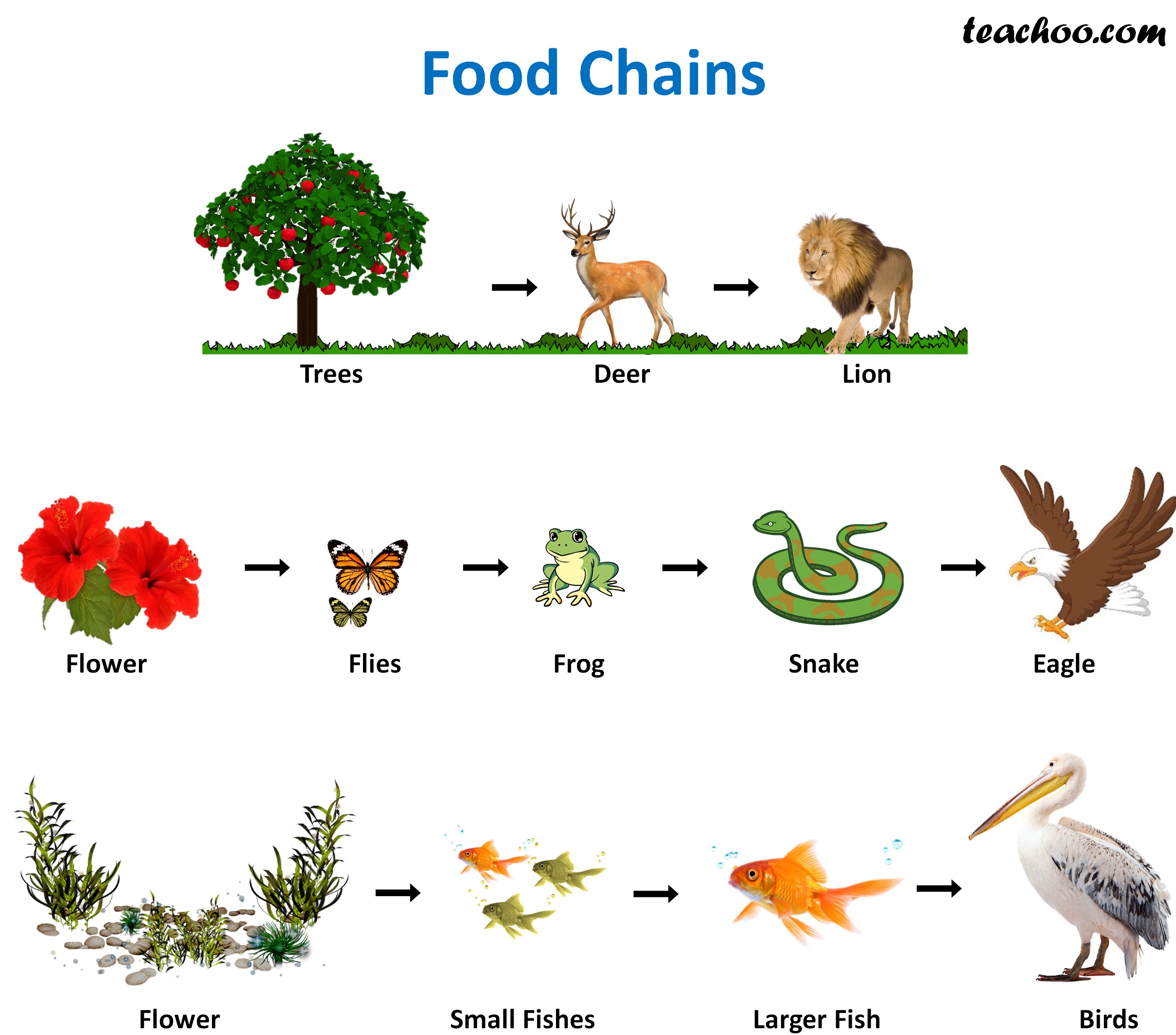
Food Chain And Food Web Meaning Diagrams Examples Teachoo Food chain. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. food webs also demonstrate that most. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.
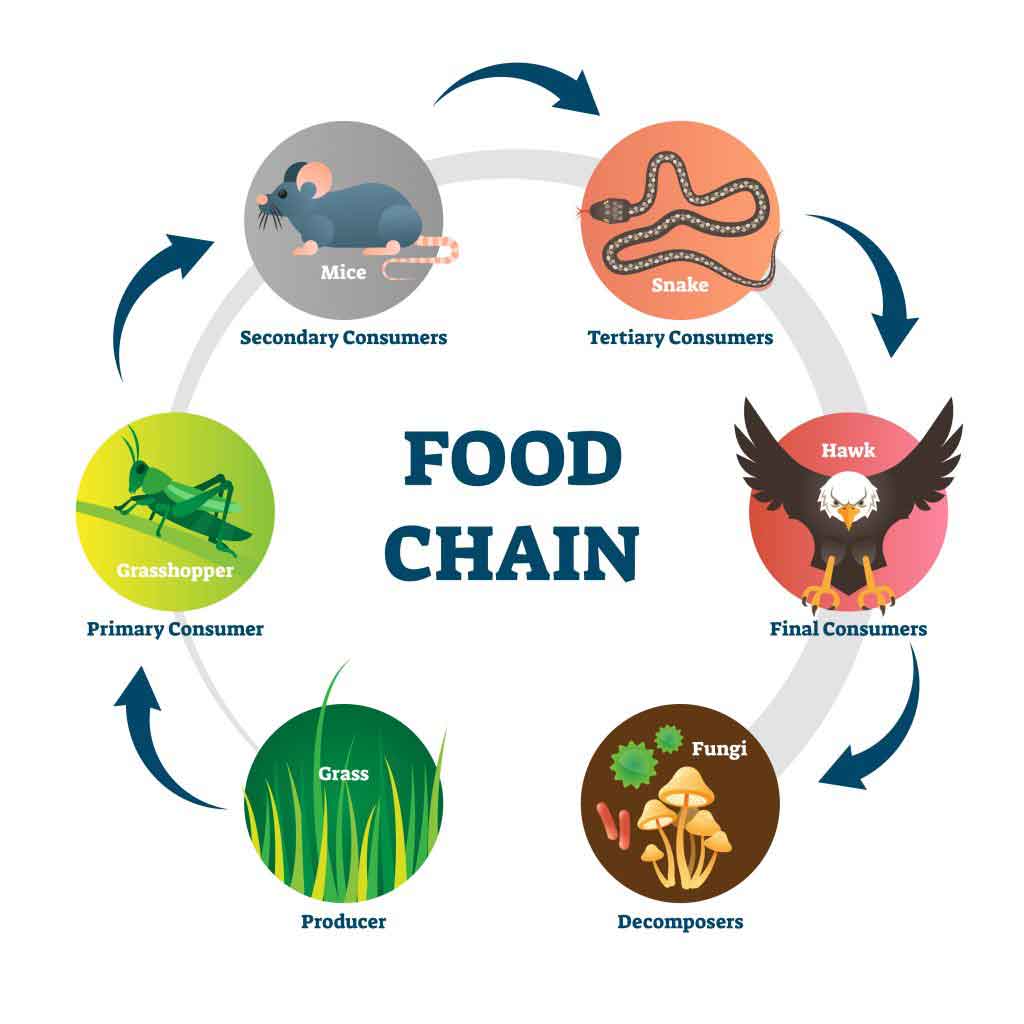
Explain The Difference Between Food Chain And Food Web Bitwise Academy Grazing food chain. food chain, in ecology, the sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. plants, which convert solar energy to food by photosynthesis, are the primary food source. The mean chain length of an entire web is the arithmetic average of the lengths of all chains in a food web. [ 42 ] [ 14 ] in a simple predator prey example, a deer is one step removed from the plants it eats (chain length = 1) and a wolf that eats the deer is two steps removed from the plants (chain length = 2). Summary. food chains and food webs model feeding relationships in ecosystems. they show how energy and materials are transferred between trophic levels when consumers eat producers or other organisms. a food web is a diagram of feeding relationships that includes multiple intersecting food chains. energy is passed up the food chain from one. A simple food chain with three trophic levels. food chains always start with a producer. this is usually a green plant or algae that completes. to store energy from sunlight as glucose. grass is.
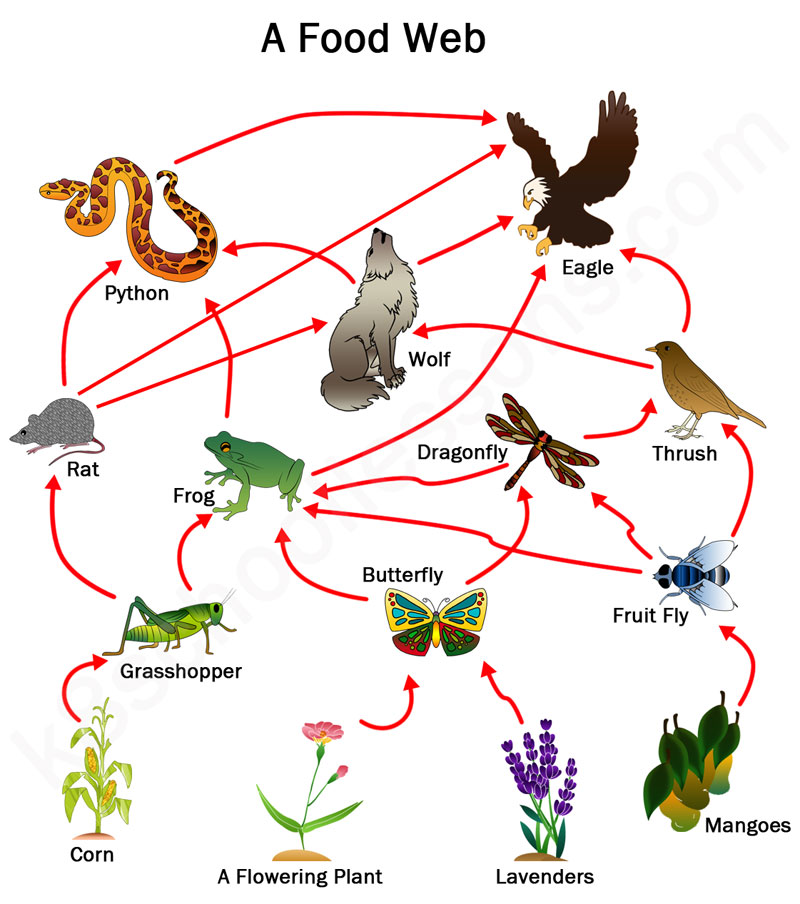
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs Summary. food chains and food webs model feeding relationships in ecosystems. they show how energy and materials are transferred between trophic levels when consumers eat producers or other organisms. a food web is a diagram of feeding relationships that includes multiple intersecting food chains. energy is passed up the food chain from one. A simple food chain with three trophic levels. food chains always start with a producer. this is usually a green plant or algae that completes. to store energy from sunlight as glucose. grass is. There are two types of food chains: the grazing food chain, beginning with autotrophs, and the detrital food chain, beginning with dead organic matter (smith & smith 2009). A food web is a diagram showing an ecosystem's complex feeding relationships. learn about types of food webs and how they differ from a food chain.
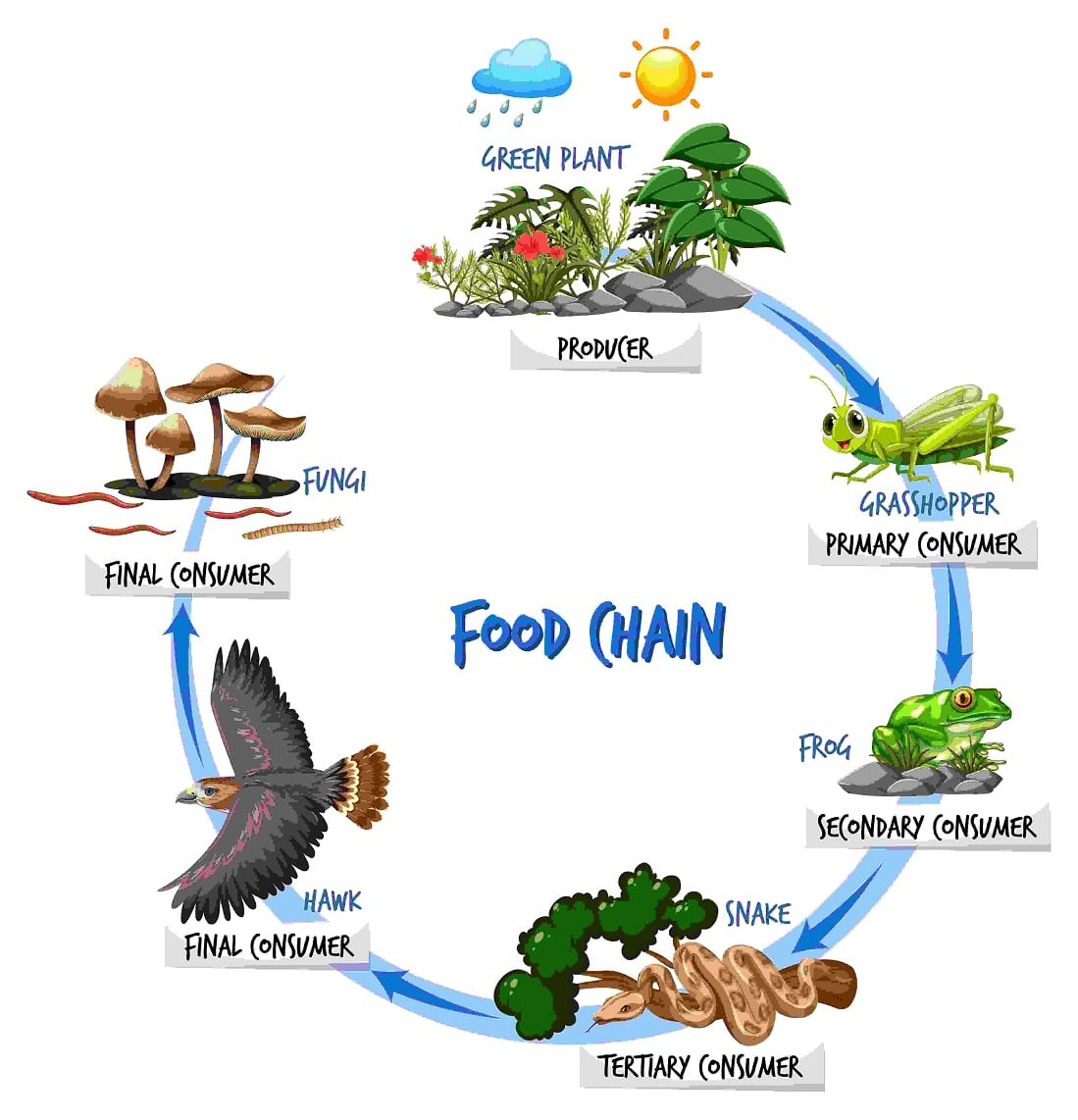
Food Chains And Food Webs Geeksforgeeks There are two types of food chains: the grazing food chain, beginning with autotrophs, and the detrital food chain, beginning with dead organic matter (smith & smith 2009). A food web is a diagram showing an ecosystem's complex feeding relationships. learn about types of food webs and how they differ from a food chain.

Comments are closed.