Increasing Motivation Readiness For Change Precontemplation Addiction And Mental Health Recovery

Increasing Motivation Readiness For Change Precontemplation Chapter 4 discusses strategies you can use to help clients raise doubt and concern about their substance use and related health, social, emotional, mental, financial, and legal problems. it highlights areas of focus and key counseling strategies that will help clients move from the precontemplation stage to contemplation. this chapter also addresses issues that may arise for clients mandated. Enhancing motivation for change in substance use disorder treatment intended audience the primary audiences for this tip are: • drug and alcohol treatment service providers. • mental health service providers, such as psychologists, licensed clinical social workers, and psychiatric mental health nurses. • peer recovery support specialists. •.

Tony Nichols Addiction Recovery Stages Of Change The following factors define motivation and its ability to help people change health risk behaviors. • motivation is a key to substance use behavior change. change, like motivation, is a complex construct with evolving meanings. one framework for understanding motivation and how it relates to behavior changes is the self determination theory. Chapter 5 describes strategies to increase clients' commitment to change by normalizing and resolving ambivalence about change and enhancing clients' decision making capabilities. central to most strategies is the process of evoking and exploring reasons to change through asking open question and reflective listening. the chapter begins with a discussion of ambivalence, extrinsic (external. Tip 35: enhancing motivation for change in substance abuse treatment. this guide helps clinicians influence the change process in their clients by incorporating motivational interventions into substance use disorder treatment programs. authoring agency. substance abuse and mental health services administration (samhsa) view resource. Abstract. motivation plays an important role in alcoholism treatment by influencing patients to seek, complete, and comply with treatment as well as make successful long term changes in their drinking. both alcohol abusing and alcohol dependent people can be classified into different “stages of change” in terms of their readiness to alter.
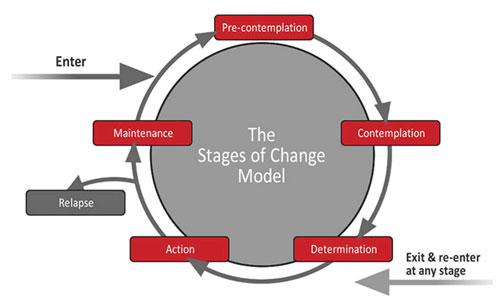
Motivation St Joseph Institute For Addiction Tip 35: enhancing motivation for change in substance abuse treatment. this guide helps clinicians influence the change process in their clients by incorporating motivational interventions into substance use disorder treatment programs. authoring agency. substance abuse and mental health services administration (samhsa) view resource. Abstract. motivation plays an important role in alcoholism treatment by influencing patients to seek, complete, and comply with treatment as well as make successful long term changes in their drinking. both alcohol abusing and alcohol dependent people can be classified into different “stages of change” in terms of their readiness to alter. Enhancing motivation for change in substance abuse treatment, number 35 in the treatment improvement protocol (tip) series published by the center for substance abuse treatment (csat), substance abuse and mental health services administration. this quick guide is based entirely on tip 35 and is designed to meet the needs of. Stages of change. the stages of change is a model of the behavioural change process. it helps people to understand that change takes place incrementally, and that changes in a person's thoughts often take place before changes in action. breaking down change into a series of stages often makes it easier to intervene appropriately.

Comments are closed.