Ijms Free Full Text Dna Damage Response In The Adaptive Arm Of The
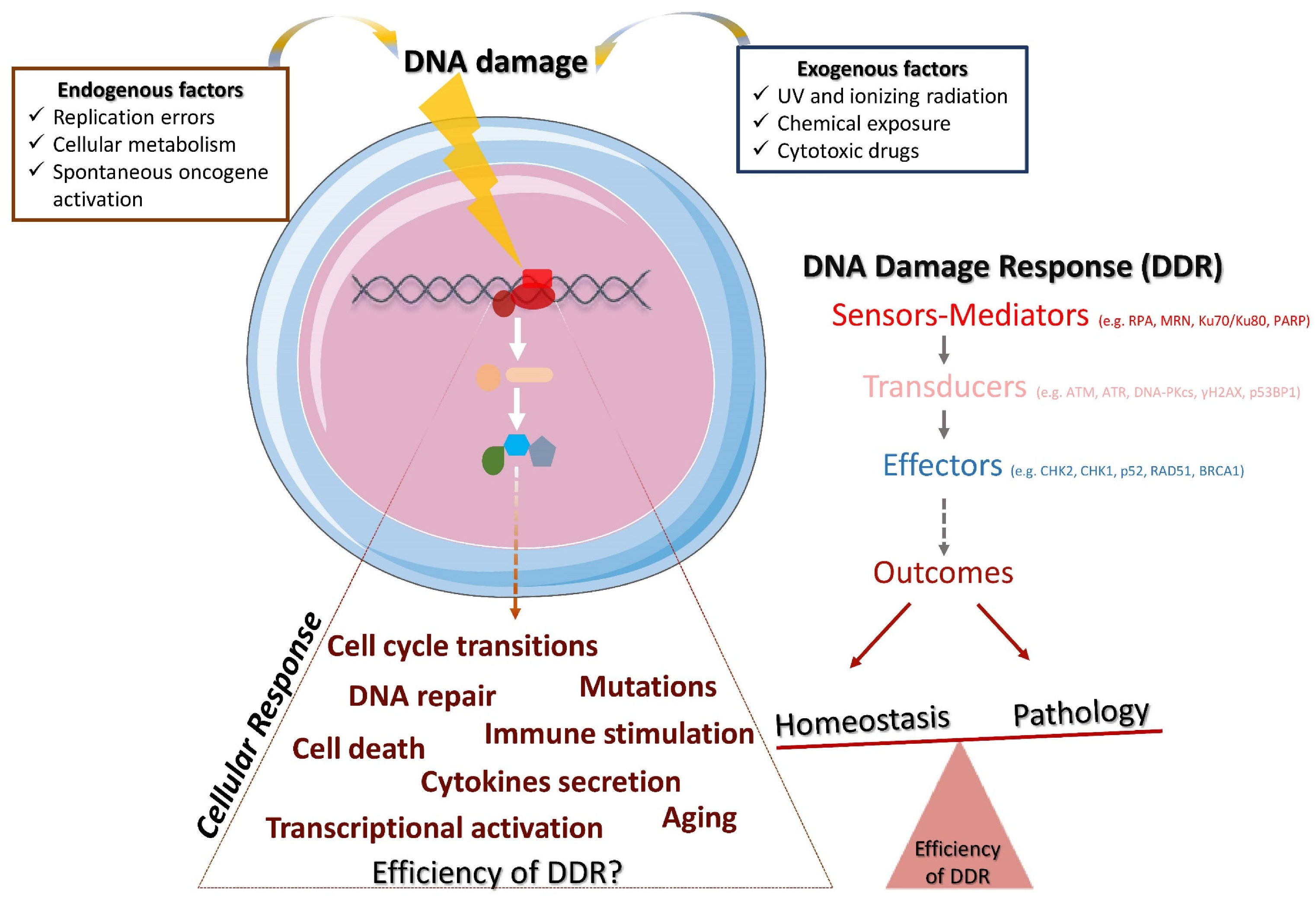
Ijms Free Full Text Dna Damage Response In The Adaptive Arm Of The In complex environments, cells have developed molecular responses to confront threats against the genome and achieve the maintenance of genomic stability assuring the transfer of undamaged dna to their progeny. dna damage response (ddr) mechanisms may be activated upon genotoxic or environmental agents, such as cytotoxic drugs or ultraviolet (uv) light, and during physiological processes. Search text. search type . add circle outline ijms. volume 22. issue 11. 10.3390 ijms22115842. version notes. d.t. dna damage response in the adaptive arm of.

Ijms Free Full Text Dna Damage Response In The Adaptive Arm Of The The dna damage response (ddr) is a mechanism th at consists of multiple signal transduction pathways required to meet th e challenge of passing do wn undamaged dna to subsequent generations and. As a result of various stresses, lesions caused by dna damaging agents occur constantly in each cell of the human body. generally, dna damage is recognized and repaired by the dna damage response (ddr) machinery, and the cells survive. when repair fails, the genomic integrity of the cell is disrupted—a hallmark of cancer. in addition, the ddr plays a dual role in cancer development and. Dna damage is the cause of numerous human pathologies including cancer, premature aging, and chronic inflammatory conditions. the dna damage response (ddr), in turn, coordinates dna damage checkpoint activation and promotes the removal of dna lesions. in recent years, several studies have shown how the ddr and the immune system are tightly. They are required for generation of the large repertoire of antigen specific cells that are the main components of the adaptive arm of the immune system. dna damage responses to dsbs have.
Ijms Free Full Text The Adaptive Mechanisms And Checkpoint Dna damage is the cause of numerous human pathologies including cancer, premature aging, and chronic inflammatory conditions. the dna damage response (ddr), in turn, coordinates dna damage checkpoint activation and promotes the removal of dna lesions. in recent years, several studies have shown how the ddr and the immune system are tightly. They are required for generation of the large repertoire of antigen specific cells that are the main components of the adaptive arm of the immune system. dna damage responses to dsbs have. As a severe detrimental process, dna damage also systematically impacts immune cell function and surveillance, further influencing the adaptive immune response. the activation and maturation of antigen presenting cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells (dcs), initiate the systematic adaptive immune response. Ape cleaves the dna to generate a nick at the ung initiated abasic site. the nick is further processed to generate a gap, which is filled by dna polymerase β and sealed by dna ligase 1 3. mmr repairs the aid initiated du from the recognition of the mismatch by msh2 6, which further recruits mlh1 and pms2.

Ijms Free Full Text Dna Damage Response Regulation By Histone As a severe detrimental process, dna damage also systematically impacts immune cell function and surveillance, further influencing the adaptive immune response. the activation and maturation of antigen presenting cells, such as macrophages and dendritic cells (dcs), initiate the systematic adaptive immune response. Ape cleaves the dna to generate a nick at the ung initiated abasic site. the nick is further processed to generate a gap, which is filled by dna polymerase β and sealed by dna ligase 1 3. mmr repairs the aid initiated du from the recognition of the mismatch by msh2 6, which further recruits mlh1 and pms2.

Comments are closed.