Ib Economics Hl Section 1 Microeconomics 1 3 Government Intervention
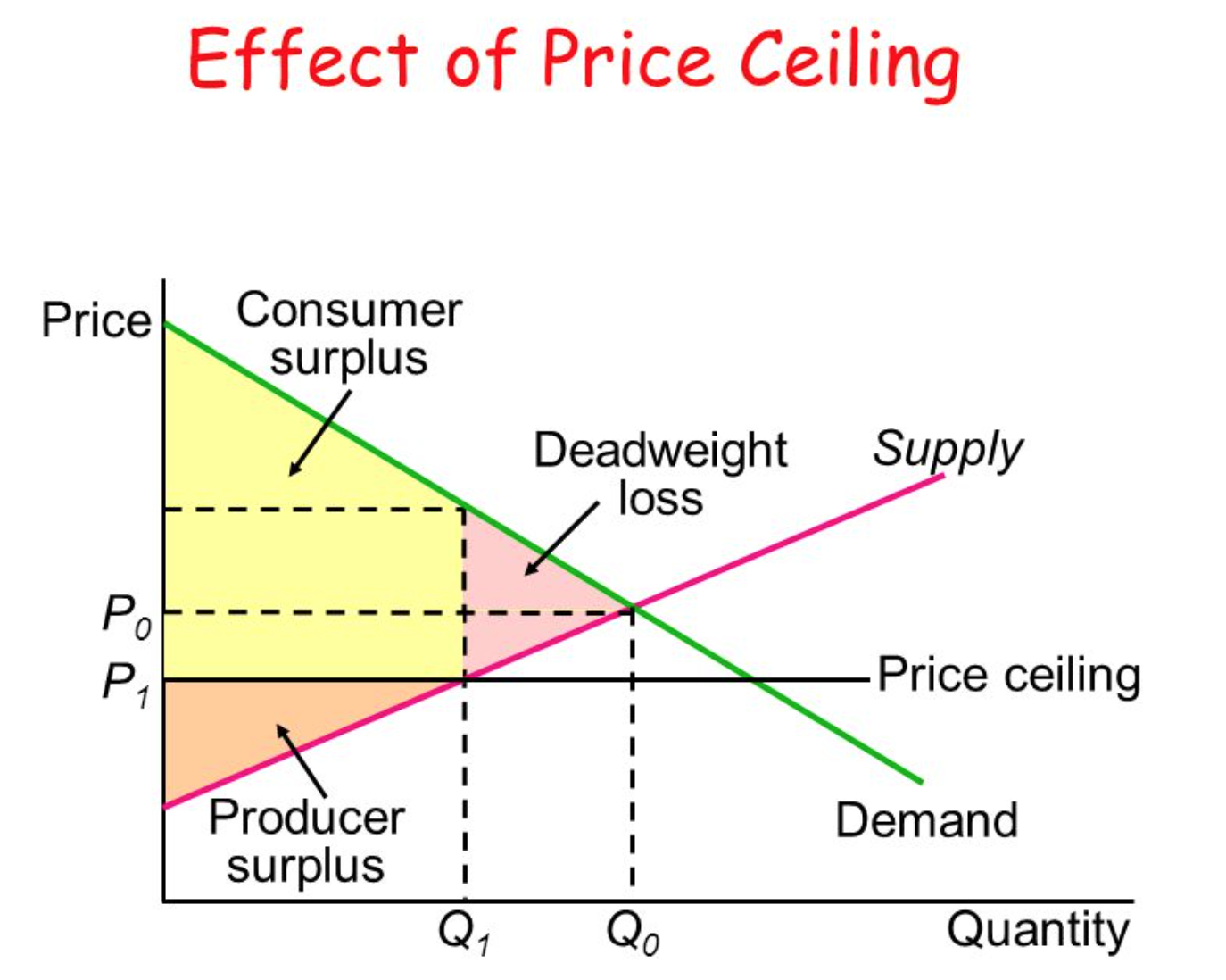
Ib Economics Hl Section 1 Microeconomics 1 3 Government Intervention 4.10 economic growth & development strategies. trade strategies, diversification & social enterprise. evaluating market orientated approaches versus government intervention. revision notes for the dp ib economics: hl syllabus, written by the economics experts at save my exams. 1.3 government intervention – maximum price. definition: price ceiling (maximum price) – the highest possible price that producers are allowed to charge consumers for the good service produced provided set by the government. it must be set below the equilibrium price to have any effect. governments will usually impose price ceilings when.
Ib Economics Hl Section 1 Microeconomics 1 3 Government Intervention 1.3. government intervention. indirect taxes. indirect taxes are those imposed by a government on goods and services, in contrast to direct taxes, such as income and corporation tax, which are levied on incomes of households and firms. indirect taxes are also called expenditure taxes. Paper 1 extended response paper on microeconomics and macroeconomics 1.5 30 paper 2 data response paper on international and develop ment economics 1.5 30 paper 3 hl extension paper on all syllabus content 1 20 internal portfolio three commentaries based on different sections of the syllabus and on published extracts from the news media. 20 20 iv. 1.3 government intervention – minimum price. definition: price floor (minimum price) – the lowest possible price set by the government that producers are allowed to charge consumers for the good service produced provided. it must be set above the equilibrium price to have any effect on the market. price floors are mostly introduced to. Past papers. ib economics hl (higher level) => government intervention. revision village best ib economics hl resource!.
Ib Economics Hl Section 1 Microeconomics 1 3 Government Intervention 1.3 government intervention – minimum price. definition: price floor (minimum price) – the lowest possible price set by the government that producers are allowed to charge consumers for the good service produced provided. it must be set above the equilibrium price to have any effect on the market. price floors are mostly introduced to. Past papers. ib economics hl (higher level) => government intervention. revision village best ib economics hl resource!. Definition: this is when the government sets a minimum price on a product which all producers must legally set their price above. this is done to protect producers as it forces the price of the product to go up. now hardworking producers, who normally very little, can now get a more ethical price. this encourages more producers to produce this. Step 1: calculate the consumer surplus before the policy. (1 mark) step 2: calculate the consumer surplus after the policy. remember! theory states that suppliers do not supply past the intersection of pmax and qty. (1 mark) step 3: calculate the difference between old and new consumer surplus.

Comments are closed.