Humeral Intraosseous Keep Em In And Keep Em Straight

Humeral Intraosseous Keep Em In And Keep Em Straight Youtube Demonstrating the mechanism of dislodgement & deformation of humeral io needles. More recent studies in both swine models and humans, however, have shown higher flow rates in the humeral io compared to the proximal tibial insertion site. 9,10,11,12 a 2010 study showed that the humeral mean flow rate was 5,093 ml hr ± 2,632 ml hr (range 828 9,000 ml hr) and the tibial mean flow rate was 1,048 ml hr ± 831 ml hr (range 336.
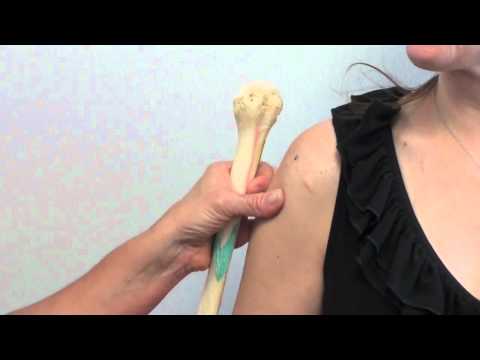
Intraosseous Line Placement Curbside Procedure: 1. palpate the greater tubercle of the proximal humerus and then the surgical neck below that landmark. the ideal insertion site is 1 cm above surgical neck. 2. io drill should be placed at a 45 degree angle with the humeral head. ensure that you have at least 5 mm left of needle length or the needle will not be long enough. Procedure. identify landmarks. clean skin. place appropriate needle on drill and remove safety cap. advance needle through skin to bone. 5 mm of the catheter (at least one black line) must be visible outside the skin. drill needle perpendicular into bone at site with gentle, constant pressure. when needle tip contacts bone there should be 5mm. Budach nm, niehues sm. ct angiography of the chest and abdomen in an emergency patient via humeral intraosseous access. emergency radiology 2017;:1–4. schindler p, helfen a, wildgruber m, heindel w, schülke c, masthoff m. intraosseous contrast administration for emergency computed tomography: a case control study. plos one 2019;14(5. This video shows the mechanism for dislodgement and deformation of humeral intraosseous needles and how to avoid this. in summary, if you need to abduct the arm (eg. for thoracostomy), keep the thumbs down (ie. have the arm internally rotated at the shoulder). otherwise the io catheter may bend or fall out. humeral intraosseous keep 'em in.

Demonstration Of The Humeral Head Intraosseous Procedure On The Partial Budach nm, niehues sm. ct angiography of the chest and abdomen in an emergency patient via humeral intraosseous access. emergency radiology 2017;:1–4. schindler p, helfen a, wildgruber m, heindel w, schülke c, masthoff m. intraosseous contrast administration for emergency computed tomography: a case control study. plos one 2019;14(5. This video shows the mechanism for dislodgement and deformation of humeral intraosseous needles and how to avoid this. in summary, if you need to abduct the arm (eg. for thoracostomy), keep the thumbs down (ie. have the arm internally rotated at the shoulder). otherwise the io catheter may bend or fall out. humeral intraosseous keep 'em in. Humeral ios should be our go to location and the key is to keep the arm in internal rotation to prevent dislodgement. expand to view reference list resus.me: humeral intraosseous – stay in & stay straight. Placement of an intraosseous (io) device. io placement is a safe and rapid method for obtaining parenteral access in patients with difficult venous access. the io route is the fastest way to infuse fluids, medications, and blood products in emergency situations including cardiac resuscitation. bones are better:.
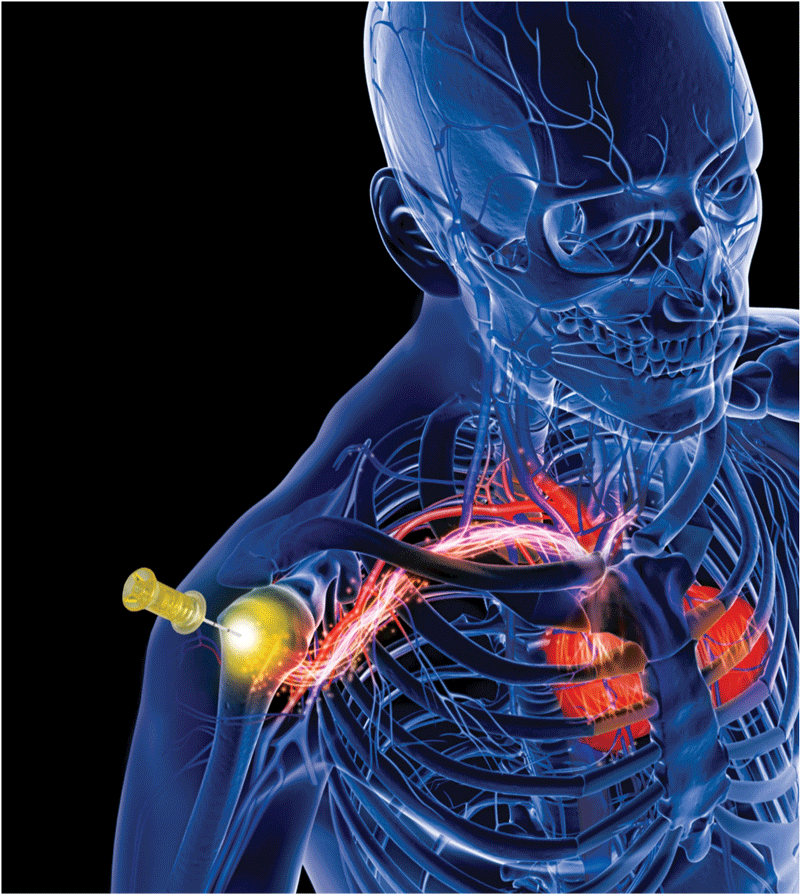
Resuscitation And The Humeral Intraosseous Line Emra Humeral ios should be our go to location and the key is to keep the arm in internal rotation to prevent dislodgement. expand to view reference list resus.me: humeral intraosseous – stay in & stay straight. Placement of an intraosseous (io) device. io placement is a safe and rapid method for obtaining parenteral access in patients with difficult venous access. the io route is the fastest way to infuse fluids, medications, and blood products in emergency situations including cardiac resuscitation. bones are better:.

Understanding And Establishing Intraosseous Access Wfsa Resources

An Observational Prospective Study Comparing Tibial And Humeral

Comments are closed.