Humeral Head Fracture Radiopaedia

Humeral Head Fracture Radiopaedia The majority of proximal humeral fractures occur in the elderly (mean age 65 years) with ~70% occurring in women, presumably due to the greater incidence of osteoporosis 1. most of these (90%) occur at home due to a fall, and in most cases they are isolated injuries 1. Fracture parts. the neer system divides the proximal humerus into four parts and considers not the fracture line, but the displacement as being significant in terms of classification. the four parts are: humeral head. greater tuberosity. lesser tuberosity. humeral shaft.

Humeral Head Fracture Radiopaedia The humerus begins proximally as a rounded head and joins the greater and lesser tubercles via the anatomical neck of the humerus. the surgical neck is found just inferior to the tubercles where the shaft begins. the surgical neck is a common site for fractures (hence its name), while fractures of the anatomical neck are rare. Proximal humerus fractures. proximal humerus fractures are common fractures often seen in older patients with osteoporotic bone following a ground level fall on an outstretched arm. diagnosis is made with orthogonal radiographs of the shoulder. Proximal humerus fractures (phf) account for 5 6% of all adult fractures[1]. there is increasing recognition given in regard to managing these fractures in the setting of elderly, low energy falls as these events are contributing to the global impact of direct and indirect costs of osteoporosis and fragility fractures. moreover, as the general population continues to age and an increasing. Bastian and hertel and hertel et al. measured blood flow to the humeral head of proximal humerus fractures intraoperatively and found that a disrupted medial cortical hinge and short (< 8 mm) metaphyseal extension were correlated with poor perfusion, but even this did not predict the occurrence of avascular necrosis.
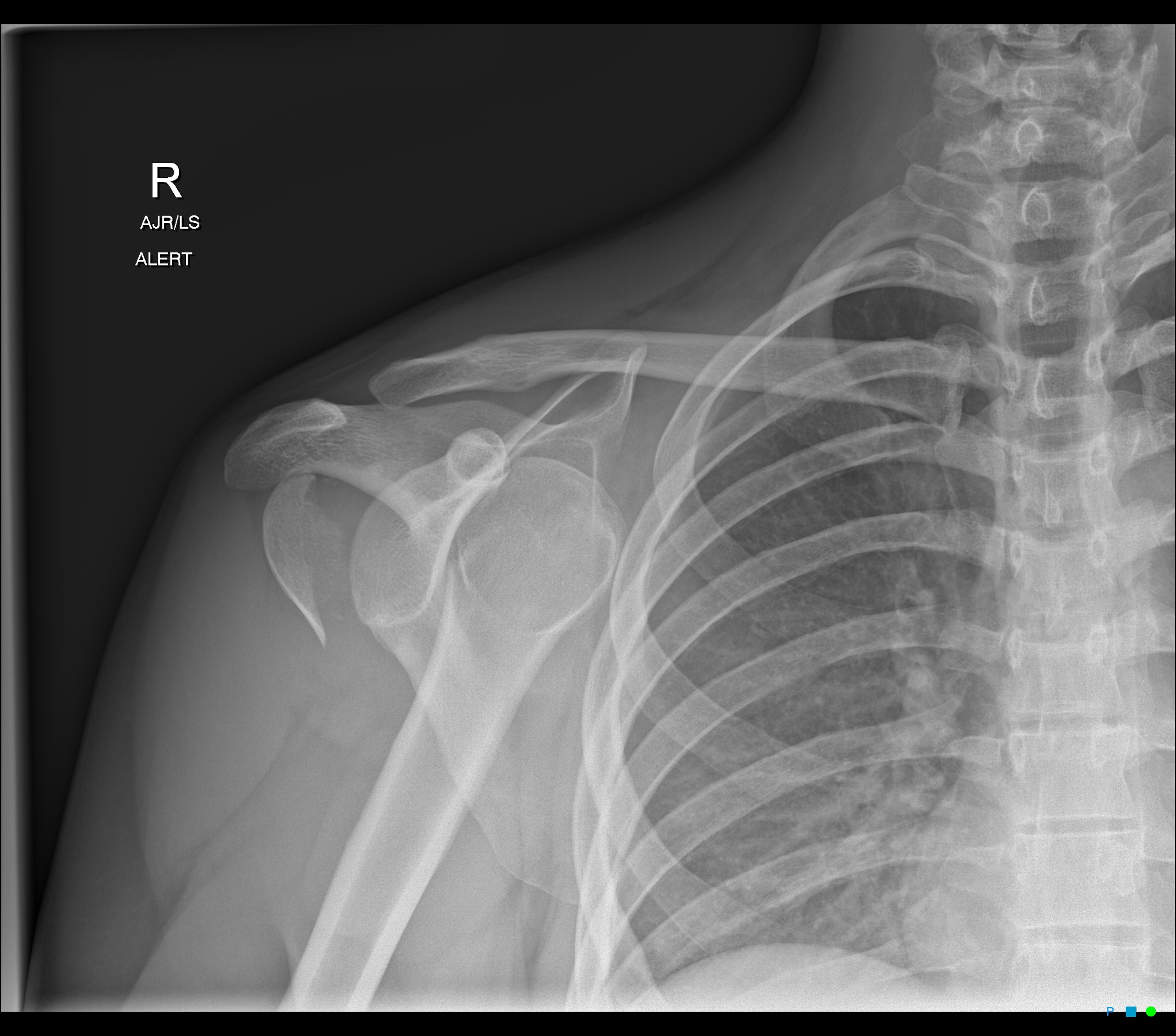
Anterior Shoulder Dislocation And Humeral Head Fracture Image Proximal humerus fractures (phf) account for 5 6% of all adult fractures[1]. there is increasing recognition given in regard to managing these fractures in the setting of elderly, low energy falls as these events are contributing to the global impact of direct and indirect costs of osteoporosis and fragility fractures. moreover, as the general population continues to age and an increasing. Bastian and hertel and hertel et al. measured blood flow to the humeral head of proximal humerus fractures intraoperatively and found that a disrupted medial cortical hinge and short (< 8 mm) metaphyseal extension were correlated with poor perfusion, but even this did not predict the occurrence of avascular necrosis. The proximal humerus comprises four “parts”: the greater tuberosity, the lesser tuberosity, the humeral head and the humeral shaft. fractures in this area are common, especially among older patients. among elderly patients with osteoporotic bone, low energy falls are the most common mechanism of injury; younger individuals sustain fractures. Proximal humeral fractures account for 4–5 % of all fractures, with the higher incidence in women. the ao asif system and the neer’s four segment classification are used to record the fracture anatomy. the neer’s classification is more appropriate to provide an anatomic basis for guiding treatment regimens. generally, conservative.

Humeral Head Fracture Radiopaedia The proximal humerus comprises four “parts”: the greater tuberosity, the lesser tuberosity, the humeral head and the humeral shaft. fractures in this area are common, especially among older patients. among elderly patients with osteoporotic bone, low energy falls are the most common mechanism of injury; younger individuals sustain fractures. Proximal humeral fractures account for 4–5 % of all fractures, with the higher incidence in women. the ao asif system and the neer’s four segment classification are used to record the fracture anatomy. the neer’s classification is more appropriate to provide an anatomic basis for guiding treatment regimens. generally, conservative.

Humeral Head Fracture Radiopaedia

Comments are closed.