Human Circulatory System Gcse Biology Revision Notes
Biology B3 The Circulatory System And Blood Revision Notes In Gcse The circulatory system (ccea) functions blood is pumped away from the heart at high pressure in arteries, and returns to the heart at low pressure in veins. the human circulatory system is a. The human circulatory system which is also known as blood vascular system comprises muscular chambered heart, a network of closed branching blood vessels and fluid in the form of blood. blood vessels – arteries, capillaries, and veins. arteries can carry blood from the heart to the of the parts of the body. veins can carry blood from organs.

Human Circulatory System Diagram Labeled Basic The human heart is part of a double circulatory system. the circulatory system is a system of: blood vessels. a pump (the heart) valves that maintain a one way flow of blood around the body. the heart has four chambers separated into two halves: the right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs for gas exchange (this is the pulmonary circuit). The circulatory system. the circulatory system consists of a closed network of blood vessels connected to the heart. oxygenated blood is carried away from the heart and towards organs in arteries. these narrow to arterioles and then capillaries as they pass through the organ. in the organs, respiring cells use up the oxygen from the blood. Question 1: humans have a double circulatory system. explain what this means. [3 marks] gcse combined science foundation combined science higher biology foundation biology higher aqa. in the second loop the heart pumps blood all around the body to supply the cells so they are able to exchange substances with blood before returning to the heart. The circulatory system (ccea) the heart blood is pumped away from the heart at high pressure in arteries, and returns to the heart at low pressure in veins. the human circulatory system is a.
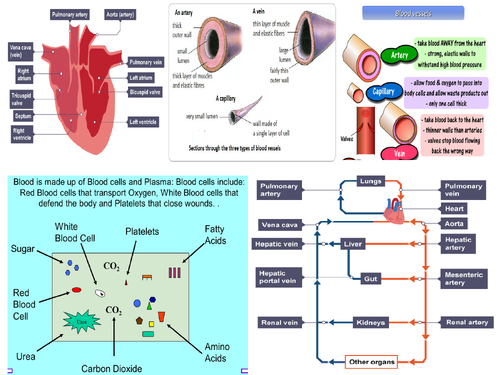
Aqa Gcse Biology Circulatory System And Blood Revision Mat Teaching Question 1: humans have a double circulatory system. explain what this means. [3 marks] gcse combined science foundation combined science higher biology foundation biology higher aqa. in the second loop the heart pumps blood all around the body to supply the cells so they are able to exchange substances with blood before returning to the heart. The circulatory system (ccea) the heart blood is pumped away from the heart at high pressure in arteries, and returns to the heart at low pressure in veins. the human circulatory system is a. The heart has four chambers. blood is pumped between the following four chambers: the circulatory system – heart: structure and function. the right and left sides of the heart are divided by a wall called the septum. this ensures that deoxygenated and oxygenated blood don’t mix. it is the muscular walls of the chambers that contract to. Valves. describe how the heart works. 1. diastole atria fill with blood from the vena cava and the pulmonary vein. as pressure in the aorta and pulmonary artery is greater than the pressure in the ventricles, the semi lunar valves close.2. atrial systole blood moves from the atria into the ventricles. as pressure in the atria is greater.

Comments are closed.