Hrct Vs X Ray For Ild Evaluation Suspect Ild
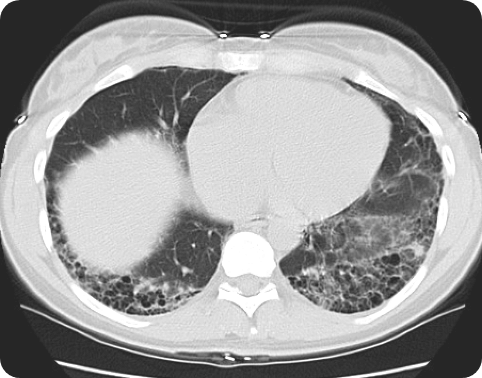
Hrct Vs X Ray For Ild Evaluation Suspect Ild Hrct scan reveals extensive lower lung abnormalities, including honeycombing cysts. case study used with permission from the american thoracic society. images courtesy of and used with permission from robert suh, md. view a comparison of a hrct scan compared to an x ray when evaluating for interstitial lung disease (ild). Six ild experts were provided the deidentified hrcts. they were all instructed to independently provide two reads of each hrct, based on the old and the new guidelines. results: the kappa statistic for concordance for hrct reads under old guidelines was 0.5, while for the new guidelines it was 0.38. under the framework of the old guidelines.
Hrct Vs X Ray For Ild Evaluation Suspect Ild Interstitial lung diseases (ilds) may present a diagnostic dilemma due to their many classifications and overlapping imaging findings. in this review, we present an algorithmic approach for assessing ilds based on identifying and understanding key imaging features to aid in narrowing a differential diagnosis or reaching a specific diagnosis. we use the recently introduced interstitial lung. 4.1. the hrct technique. in the era of multi detector row ct machines, a brief reminder of the hrct technique is pertinent. the two technical features that differentiate hrct imaging from conventional ct are, first, the narrow x ray beam collimation that significantly improves spatial resolution and, second, the use of a dedicated reconstruction algorithm []. When ila is identified, a clinical evaluation should ensue to determine the presence of clinical symptoms, and an hrct scan should be obtained if the initial ct scan is incomplete, equivocal, or if there is clinically significant disease. 62 ilas share common risk factors with ild and in some cases may represent a precursor to ild. 57, 58, 63. Interstitial lung diseases (ilds) are challenging to diagnose, requiring integration of multiple complex features that are often difficult to interpret. this article reviews a pragmatic approach to ild diagnosis and classification, focusing on diagnostic tools and strategies that are used to separate different subtypes and identify the most appropriate management. we discuss the evolution of.
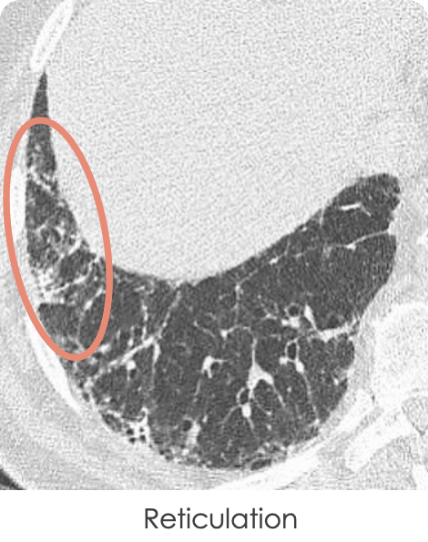
Hrct Vs X Ray For Ild Evaluation Suspect Ild When ila is identified, a clinical evaluation should ensue to determine the presence of clinical symptoms, and an hrct scan should be obtained if the initial ct scan is incomplete, equivocal, or if there is clinically significant disease. 62 ilas share common risk factors with ild and in some cases may represent a precursor to ild. 57, 58, 63. Interstitial lung diseases (ilds) are challenging to diagnose, requiring integration of multiple complex features that are often difficult to interpret. this article reviews a pragmatic approach to ild diagnosis and classification, focusing on diagnostic tools and strategies that are used to separate different subtypes and identify the most appropriate management. we discuss the evolution of. Optimal hrct technique for evaluation of ild. the advent of hrct and the development of advanced reconstruction algorithms has allowed confident diagnoses of interstitial lung disease without surgical lung biopsy, a significant advancement as lung biopsy confers additional risk. 5 a definitive usual interstitial pneumonia pattern on hrct as. The diffuse parenchymal lung diseases, often collectively referred to as the interstitial lung diseases (ilds), are a heterogeneous group of disorders that are classified together because of similar clinical, radiographic, physiologic, or pathologic manifestations (algorithm 1) [1 7]. the descriptive term "interstitial" reflects the pathologic.

Comments are closed.