How To Calculate Theoretical Yield Definition And Example

How To Calculate Theoretical Yield Definition And Example Chemical Steps to calculate theoretical yield. write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction. identify the limiting reactant. convert grams of limiting reactant to moles. use the mole ratio between the limiting reactant and the product and find the theoretical number of moles of product. convert the number of moles of product to grams. 5. convert the result to grams. this is the reverse of your earlier step of calculating the number of moles or reactant. when you know the number of moles that you expect, you will multiply by the molar mass of the product to find the theoretical yield in grams.
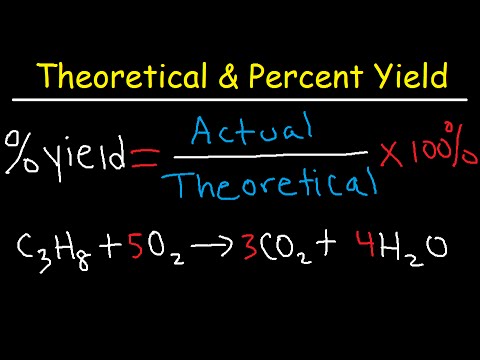
How To Calculate Theoretical Yield And Percent Yield Youtube The percent yield of a reaction is the ratio of the actual yield to the theoretical yield, multiplied by 100 to give a percentage: percent yield = actual yield (g) theoretical yield(g) × 100%. the method used to calculate the percent yield of a reaction is illustrated in example 4.3.4. Theoretical yield formula quick review . balance your equations. find the mole ratio between the reactant and the product. calculate using the following strategy: convert grams to moles, use the mole ratio to bridge products and reactants, and then convert moles back to grams. Now, the theoretical yield formula may seem challenging to understand, so we will show you a quick guide on how to calculate the theoretical yield. the measurements you need are the mass of the reagents, their molecular weights, the stoichiometry of the reaction (found from the balanced equation), and the molecular weight of the desired product. This concept has been illustrated for the reaction: 2na cl2 → 2nacl 2 n a c l 2 → 2 n a c l. amounts of products calculated from the complete reaction of the limiting reagent are called theoretical yields, whereas the amount actually produced of a product is the actual yield. the ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield expressed in.
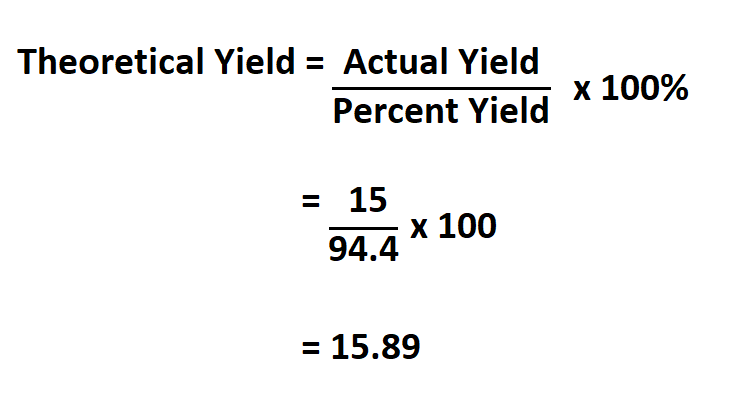
How To Calculate Theoretical Yield Now, the theoretical yield formula may seem challenging to understand, so we will show you a quick guide on how to calculate the theoretical yield. the measurements you need are the mass of the reagents, their molecular weights, the stoichiometry of the reaction (found from the balanced equation), and the molecular weight of the desired product. This concept has been illustrated for the reaction: 2na cl2 → 2nacl 2 n a c l 2 → 2 n a c l. amounts of products calculated from the complete reaction of the limiting reagent are called theoretical yields, whereas the amount actually produced of a product is the actual yield. the ratio of actual yield to theoretical yield expressed in. The percent yield is a comparison between the actual yield and the theoretical yield and is defined as. percent yield = actual yield theoretical yield × 100% (8.10.1) (8.10.1) percent yield = actual yield theoretical yield × 100 %. it does not matter whether the actual and theoretical yields are expressed in moles or grams, as long as they. How to calculate percent yield understanding the percent yield formula. percent yield is a crucial concept in chemistry, representing the efficiency of a reaction. the formula for this is: \text{percent yield} = \frac{\text{actual yield}}{\text{theoretical yield}} \times 100\% actual yield: the quantity of product actually produced in the reaction.

Comments are closed.