How To Calculate Fault Current Using Percent Impedance
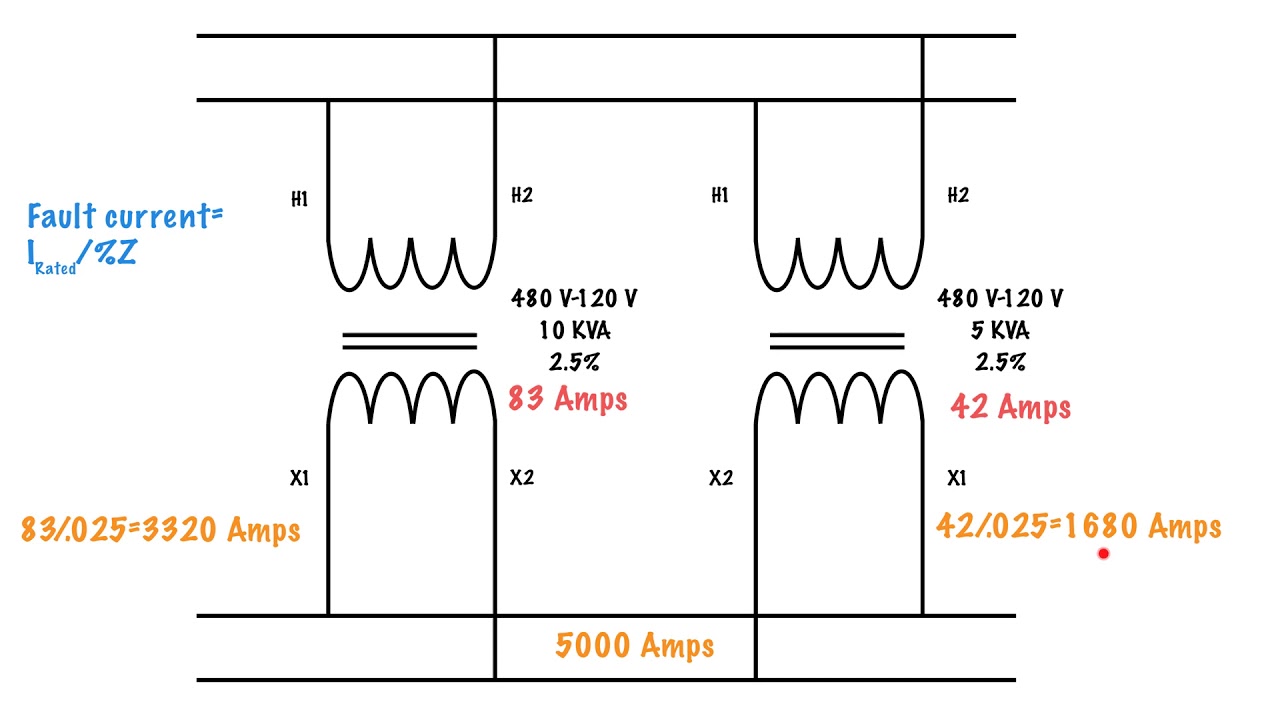
How To Calculate Fault Current Using Percent Impedance Youtube 3. the impedance of the cable and two pole switches on the system must be considered “both ways” since the current flows to the fault and then returns to the source. for instance, if a line to line fault occurs 50 feet from a transformer, then 100 feet of cable impedance must be included in the calculation. This video describes how to calculate the fault current using a transformers rated percent impedance.

Percentage Impedance Of Transformer Its Calculation Fault current calculations. to calculate the fault current available from a transformer if a dead short occurs across the secondary terminals, use the formula: i rated (secondary) %z = fault current. remember to use the percentage as a decimal not the full number. for example, 2.5% is actually .025. video alert! how to calculate fault current. Example calculation. for example, if a 2400 240 volt transformer has a measured impedance voltage of 72 volts on the high voltage windings, its impedance (z), expressed as a percent, is: z% = (impedance voltage rated voltage) x 100. percent z = (72 2400)*100 = 3 percent. Role of percentage impedance in short circuit calculations. the impedance of the transformer limits the fault current. the higher the percentage impedance lower will be the fault current magnitude. the fault current of the system can be expressed with the following mathematical expression. a 132 6.6 kv, 30 mva transformer has an impedance of 9 %. A transformer’s nameplate details are 25 kva, 440v secondary voltage, 5% of percentage impedance, calculate the short circuit fault current. i (fault) = 25 x 100 (1.732 x 440 x 5) i (fault) = 0.66 ka. notes: we have assumed the transformer is connected with the infinity bus to get the worse case fault level on the secondary side of the.

How To Calculate Fault Current 3 Phase Role of percentage impedance in short circuit calculations. the impedance of the transformer limits the fault current. the higher the percentage impedance lower will be the fault current magnitude. the fault current of the system can be expressed with the following mathematical expression. a 132 6.6 kv, 30 mva transformer has an impedance of 9 %. A transformer’s nameplate details are 25 kva, 440v secondary voltage, 5% of percentage impedance, calculate the short circuit fault current. i (fault) = 25 x 100 (1.732 x 440 x 5) i (fault) = 0.66 ka. notes: we have assumed the transformer is connected with the infinity bus to get the worse case fault level on the secondary side of the. Short circuit current (i sc) is sometimes supplied by the power company rather than sc mva. this current is the current in one phase of a three phase bolted fault. the sc mva can be calculated from the short circuit current using the following equation: sc mva = 1.732 i v , where i is expressed in ka and. sc ll sc. Ea = normal phase voltage at the fault location. z1 = positive phase sequence network impedance to the fault. z2 = negative phase sequence network impedance to the fault. z0 = zero phase sequence network impedance to the fault. single phase to earth – fault from phase ‘a’ to earth: va = 0ib = ic = 0.
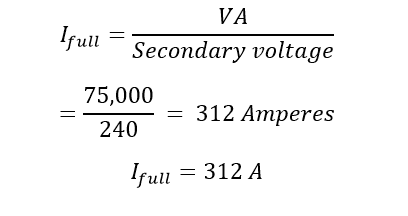
What Is Percentage Impedance Calculate Percentage Impedance Short circuit current (i sc) is sometimes supplied by the power company rather than sc mva. this current is the current in one phase of a three phase bolted fault. the sc mva can be calculated from the short circuit current using the following equation: sc mva = 1.732 i v , where i is expressed in ka and. sc ll sc. Ea = normal phase voltage at the fault location. z1 = positive phase sequence network impedance to the fault. z2 = negative phase sequence network impedance to the fault. z0 = zero phase sequence network impedance to the fault. single phase to earth – fault from phase ‘a’ to earth: va = 0ib = ic = 0.
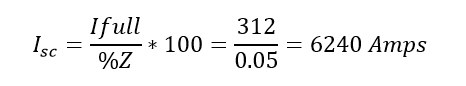
What Is Percentage Impedance Calculate Percentage Impedance
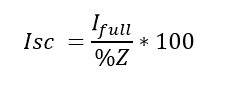
What Is Percentage Impedance Calculate Percentage Impedance

Comments are closed.