How Scientists Measure The Distance To Stars And Galaxies

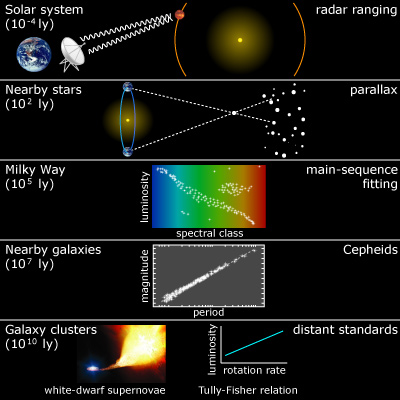
How Scientists Measure The Distance To Stars And Galaxies Youtube But all of the methods are wonderful combinations of science and mathematics! the links below will take you to descriptions of various common methods. radar measuring distances in our solar system. parallax measuring distances to nearby stars. cepheids measuring distances in our galaxy and to nearby galaxies. As a general rule, if we incorrectly place the galaxy very far away, scientists measure less dark matter. using the sbf technique, to measure the distance to kks2000 04 resulted in a distance of 64 million light years. a galaxy at that distance would represent the first example of a galaxy without dark matter.

Method Of Measuring Distances To Stars And Galaxies Updated: feb 27, 2024. it turns out that measuring the distance to a star is an interesting problem! astronomers have come up with two different techniques to estimate how far away any given star is. the first technique uses triangulation (a.k.a. parallax). the earth's orbit around the sun has a diameter of about 186 million miles (300 million. By measuring this small change and knowing the distance between your eyes, you can calculate the distance to your thumb. that's trigonometry. when it comes to measuring distances to other stars. Measuring the intrinsic brightness of a cepheid variable, or other kinds of standard candles such as supernovae, allows astronomers to calculate the distance to the standard candle’s home galaxy. for the most distant galaxies, standard candles are too faint to be useful, so astronomers often use the ‘hubble lemaître’ law, which shows. A common method for measuring distance in space is to measure how far light travels in one year: known as a lightyear, which is around 9.5 trillion km. if you want to be precise, the iau regards a year as 365.25 days, making a lightyear 9,460,730,472,580,800m.

Remarkable Methods To Measure Distances In The Vastness Of Space By Measuring the intrinsic brightness of a cepheid variable, or other kinds of standard candles such as supernovae, allows astronomers to calculate the distance to the standard candle’s home galaxy. for the most distant galaxies, standard candles are too faint to be useful, so astronomers often use the ‘hubble lemaître’ law, which shows. A common method for measuring distance in space is to measure how far light travels in one year: known as a lightyear, which is around 9.5 trillion km. if you want to be precise, the iau regards a year as 365.25 days, making a lightyear 9,460,730,472,580,800m. When light from a distant galaxy (or any object in space) reaches us, we are seeing that galaxy as it appeared in the past. to determine the ‘when’ in the past, we use the galaxy’s redshift. “redshift tells us how long the light has spent being stretched to longer wavelengths by the expansion of the universe as it travels to reach us. Nasa's james webb space telescope has helped astronomers determine the distance to nearly 200 galaxies and galaxy clusters formed in the universe's early days. one of the first publicly released.

Scientists Use Special Stars To Measure Galaxy Distances When light from a distant galaxy (or any object in space) reaches us, we are seeing that galaxy as it appeared in the past. to determine the ‘when’ in the past, we use the galaxy’s redshift. “redshift tells us how long the light has spent being stretched to longer wavelengths by the expansion of the universe as it travels to reach us. Nasa's james webb space telescope has helped astronomers determine the distance to nearly 200 galaxies and galaxy clusters formed in the universe's early days. one of the first publicly released.
Esa Science Technology Galaxies And The Expanding Universe

Comments are closed.