How Is Serum Extracted From The Blood Sample
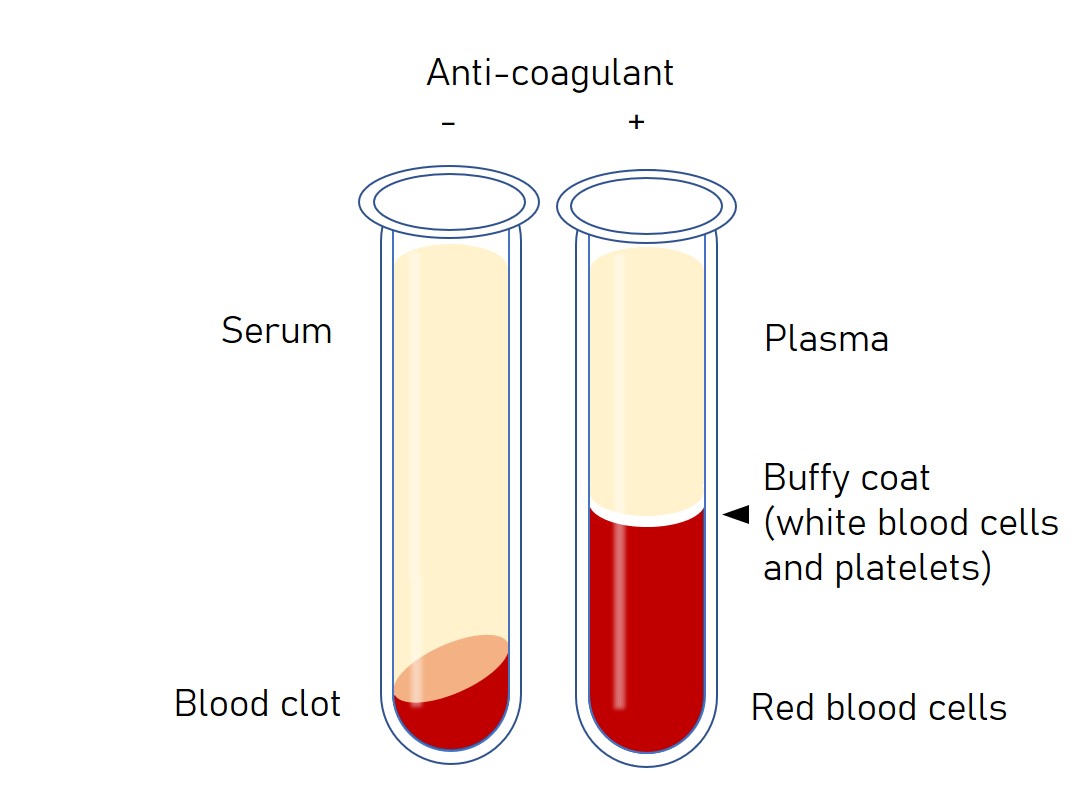
Serum Vs Plasma After collection of the whole blood, allow the blood to clot by leaving it undisturbed at room temperature. this usually takes 15–30 minutes. remove the clot by centrifuging at 1,000–2,000 x g for 10 minutes in a refrigerated centrifuge. the resulting supernatant is designated serum. following centrifugation, it is important to immediately. 2.1. serum samples. blood was collected from a healthy rabbit housed at the small animal facility of the csiro australian animal health laboratory. serum was obtained by allowing the blood to clot at room temperature for 2 h. the clotted blood was then centrifuged for 10 min at 12,000g. serum was then collected and stored at −20 °c. 2.2.

Laboratory Part 1 Serum Plasma Preparation Specimen Storage And After centrifugation, the blood sample shows the separation of its components the separation leads to the formation of serum and the settled red blood cells . Such attractiveness of blood for metabolomic studies is due to the low invasiveness of its extraction. blood is usually analyzed either as serum or plasma. the serum is a biological liquid obtained when whole blood coagulates. coagulation is a vital process that prevents excessive blood loss from a minor wound. Serum and plasma can be extracted from the blood through a process called centrifugation. the sample of the blood is collected in a tube and then spun in a centrifuge to separate the components by density. this separates the blood into three layers: plasma or serum at the top, a thin layer of platelets and white blood cells in the middle, and. Maintain tubes at 4°c during processing. place the blood collection tubes in a centrifuge and spin at 1,300g for 10 min at 4°c. record the time processing initiated in the study specific documentation or data management system. avoid mixing agitation of tubes between centrifugation and aliquoting as this may lead to mixing and or re.
Blood Drawn From A Patient With Serum Separate In The Chemistry Serum and plasma can be extracted from the blood through a process called centrifugation. the sample of the blood is collected in a tube and then spun in a centrifuge to separate the components by density. this separates the blood into three layers: plasma or serum at the top, a thin layer of platelets and white blood cells in the middle, and. Maintain tubes at 4°c during processing. place the blood collection tubes in a centrifuge and spin at 1,300g for 10 min at 4°c. record the time processing initiated in the study specific documentation or data management system. avoid mixing agitation of tubes between centrifugation and aliquoting as this may lead to mixing and or re. Serum ( ˈsɪərəm ) is the fluid and solvent component of blood which does not play a role in clotting. [1] it may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. serum contains all proteins except clotting factors (involved in blood clotting), including all electrolytes. Introduction. blood, under the form of plasma and serum, is the biofluid of choice for clinical studies in general, particularly as regards metabolomics and lipidomics. 1 blood can be collected with low invasiveness and is rich in biological information. blood derivatives contain metabolites as well as lipoproteins secreted by different tissues.

Lipemic Blood Sample Frees Serum Whole Blood Hemolyzed Serum Lipemia In Serum ( ˈsɪərəm ) is the fluid and solvent component of blood which does not play a role in clotting. [1] it may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. serum contains all proteins except clotting factors (involved in blood clotting), including all electrolytes. Introduction. blood, under the form of plasma and serum, is the biofluid of choice for clinical studies in general, particularly as regards metabolomics and lipidomics. 1 blood can be collected with low invasiveness and is rich in biological information. blood derivatives contain metabolites as well as lipoproteins secreted by different tissues.

Comments are closed.