How Humans Evolved Bigger Brains Elife Science Digests Elife
How Humans Evolved Bigger Brains Elife Science Digests Elife How humans evolved bigger brains. brain size increased rapidly during human evolution due to the expansion of many brain regions, resulting in human brains being exceptionally larger than those of our closest relatives. humans have much larger brains than other primates, but it is not clear exactly when and how this difference emerged during. Humans have much larger brains than other primates, but it is not clear exactly when and how this difference emerged during evolution. some scientists believe that the expansion of a part of the brain called the neocortex – which handles sight, hearing, conscious decision making and language – drove the increase in the size of the human brain.

Brain Expansion How And Why Humans Evolved Bigger Brains ёяза By Ehsan The human brain owes its characteristic wrinkled appearance to its outer layer, the cerebral cortex. all mammals have a cerebral cortex, but its size varies greatly between species. as the brain evolved, the neocortex, the evolutionarily youngest part of the cerebral cortex, expanded dramatically and so had to fold into wrinkles to fit inside. The human brain is about three times as large as that of our closest living relatives, the great apes. overall brain size is a good predictor of cognitive performance in a variety of tests in primates. 1, 2 therefore, hypotheses explaining the evolution of this remarkable difference have attracted much interest. in this review, we give an. Figure 1. open in a new tab. superior pattern processing (spp) capabilities of the human brain evolved in association with expansion of the cerebral cortex. a comparison of the gross anatomy of the brains of humans and chimpanzees (pan troglodytes) reveals considerable expansion of three regions in humans, the prefrontal cortex, the visual. From 800,000–200,000 years ago. human brain size evolved most rapidly during a time of dramatic climate change. larger, more complex brains enabled early humans of this time period to interact with each other and with their surroundings in new and different ways. as the environment became more unpredictable, bigger brains helped our ancestors.

Human Brain Size Evolved Gradually Over 3 Million Years Gw Today Figure 1. open in a new tab. superior pattern processing (spp) capabilities of the human brain evolved in association with expansion of the cerebral cortex. a comparison of the gross anatomy of the brains of humans and chimpanzees (pan troglodytes) reveals considerable expansion of three regions in humans, the prefrontal cortex, the visual. From 800,000–200,000 years ago. human brain size evolved most rapidly during a time of dramatic climate change. larger, more complex brains enabled early humans of this time period to interact with each other and with their surroundings in new and different ways. as the environment became more unpredictable, bigger brains helped our ancestors. Scientists were somewhat surprised to find human brains had shrunk as recently as 3,000 years ago (credit: mohamed el shahed getty images) when people age, their myelin breaks down, reducing the. Abstract. the human brain is about three times as large as that of our closest living relatives, the great apes. overall brain size is a good predictor of cognitive performance in a variety of.
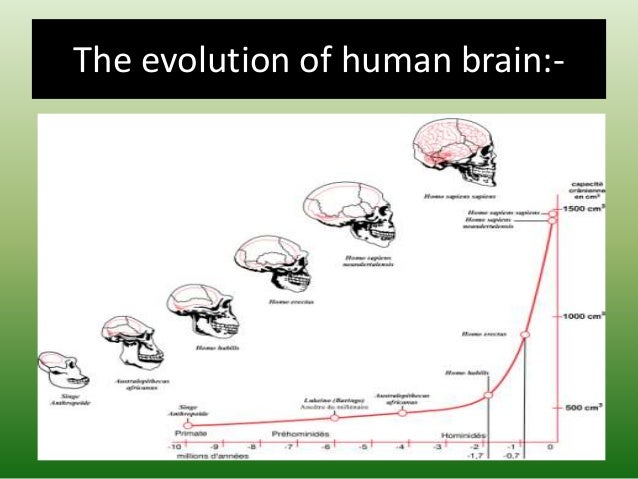
The Evolution Of Human Brain Scientists were somewhat surprised to find human brains had shrunk as recently as 3,000 years ago (credit: mohamed el shahed getty images) when people age, their myelin breaks down, reducing the. Abstract. the human brain is about three times as large as that of our closest living relatives, the great apes. overall brain size is a good predictor of cognitive performance in a variety of.

Comments are closed.