How Does Trauma Affect The Brain And What It Means For You

How Trauma Affects The Brain Key points. trauma can affect your brain's emotion networks to make you overreact or under react to stressful situations. trauma creates fixed neural networks that are isolated from other parts of. Trauma can cause your brain to remain in a state of hypervigilance, suppressing your memory and impulse control and trapping you in a constant state of strong emotional reactivity. it might seem like trauma does irreversible damage to your brain that’s not true. our brains are extremely adaptable. neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to.
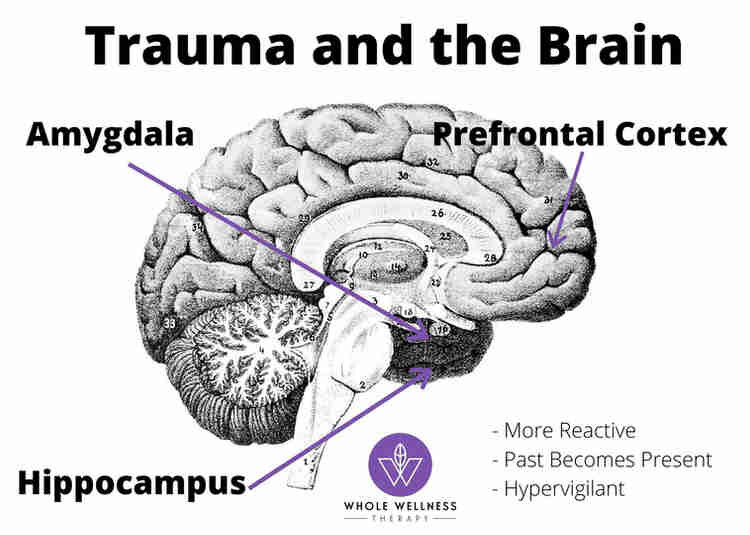
How Does Trauma Affect The Brain And What It Means For You With so many changes taking place in the brain, along with stress hormones circulating through your system on a regular basis, you may experience several symptoms of ptsd. according to the. Yes, emotional trauma can affect the brain. a traumatic event can impact the brain’s memory center as well as how we process fear. here’s what science and experts say about it. chronic stress. It can also cause phobias, sleep disturbance, negative mood, anxiety, and attention concentration difficulties that interfere with academic or career success. research in neuroscience suggests. Trauma is a response to an intensely stressful event (s) or situations. the effects can be long lasting, but healing is possible. traumatic events can happen at any age and have lasting effects on.

How Does Trauma Impact The Brain Domestic Violence Network Domestic It can also cause phobias, sleep disturbance, negative mood, anxiety, and attention concentration difficulties that interfere with academic or career success. research in neuroscience suggests. Trauma is a response to an intensely stressful event (s) or situations. the effects can be long lasting, but healing is possible. traumatic events can happen at any age and have lasting effects on. Publications. neuroscience. researchers reveal how trauma changes the brain. exposure to trauma can be life changing – and researchers are learning more about how traumatic events may physically change our brains. but these changes are not happening because of physical injury, rather our brain appears to rewire itself after these experiences. Ptsd is associated with changes in different regions of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, the mid anterior cingulate cortex, and the right inferior frontal gyrus. these areas are associated with functions such as fear conditioning, emotional regulation, and autonomic functions. following trauma, areas of the brain linked to the fear.

How Does Trauma Affect The Brain Publications. neuroscience. researchers reveal how trauma changes the brain. exposure to trauma can be life changing – and researchers are learning more about how traumatic events may physically change our brains. but these changes are not happening because of physical injury, rather our brain appears to rewire itself after these experiences. Ptsd is associated with changes in different regions of the brain, including the prefrontal cortex, the mid anterior cingulate cortex, and the right inferior frontal gyrus. these areas are associated with functions such as fear conditioning, emotional regulation, and autonomic functions. following trauma, areas of the brain linked to the fear.

Comments are closed.