How Did Alexander The Greats Empire End The Hellenistic Period

This Map Shows The Kingdoms And States That Formed After The Breakup Of The hellenistic world (from the greek word hellas for greece) is the known world after the conquests of alexander the great and corresponds roughly with the hellenistic period of ancient greece, from 323 bce (alexander 's death) to the annexation of greece by rome in 146 bce. although rome's rule ended greek independence and autonomy it did. The hellenistic period lasted from 323 b.c. until 31 b.c. alexander the great built an empire that stretched from greece all the way to india, and his campaign changed the world: it spread greek.

Alexander The Great And The Spread Of Hellenistic Culture By 323 b.c., alexander was head of an enormous empire and had recovered from the devastating loss of his friend hephaestion—who was also reputed to be one of alexander’s homosexual male lovers. Alexander the great (born 356 bce, pella, macedonia [northwest of thessaloníki, greece]—died june 13, 323 bce, babylon [near al Ḥillah, iraq]) was the king of macedonia (336–323 bce), who overthrew the persian empire, carried macedonian arms to india, and laid the foundations for the hellenistic world of territorial kingdoms. Accessed 2 november 2024. hellenistic age, in the eastern mediterranean and middle east, the period between the death of alexander the great in 323 bce and the conquest of egypt by rome in 30 bce. for some purposes the period is extended for a further three and a half centuries, to the move by constantine the great of his. The hellenistic period was the era of ancient greek civilisation that followed the death of alexander the great in 323 bc. it saw greek culture transform and spread across the mediterranean and into western and central asia. the end of the hellenistic period is variously attributed to the roman conquest of the greek peninsula in 146 bc and.
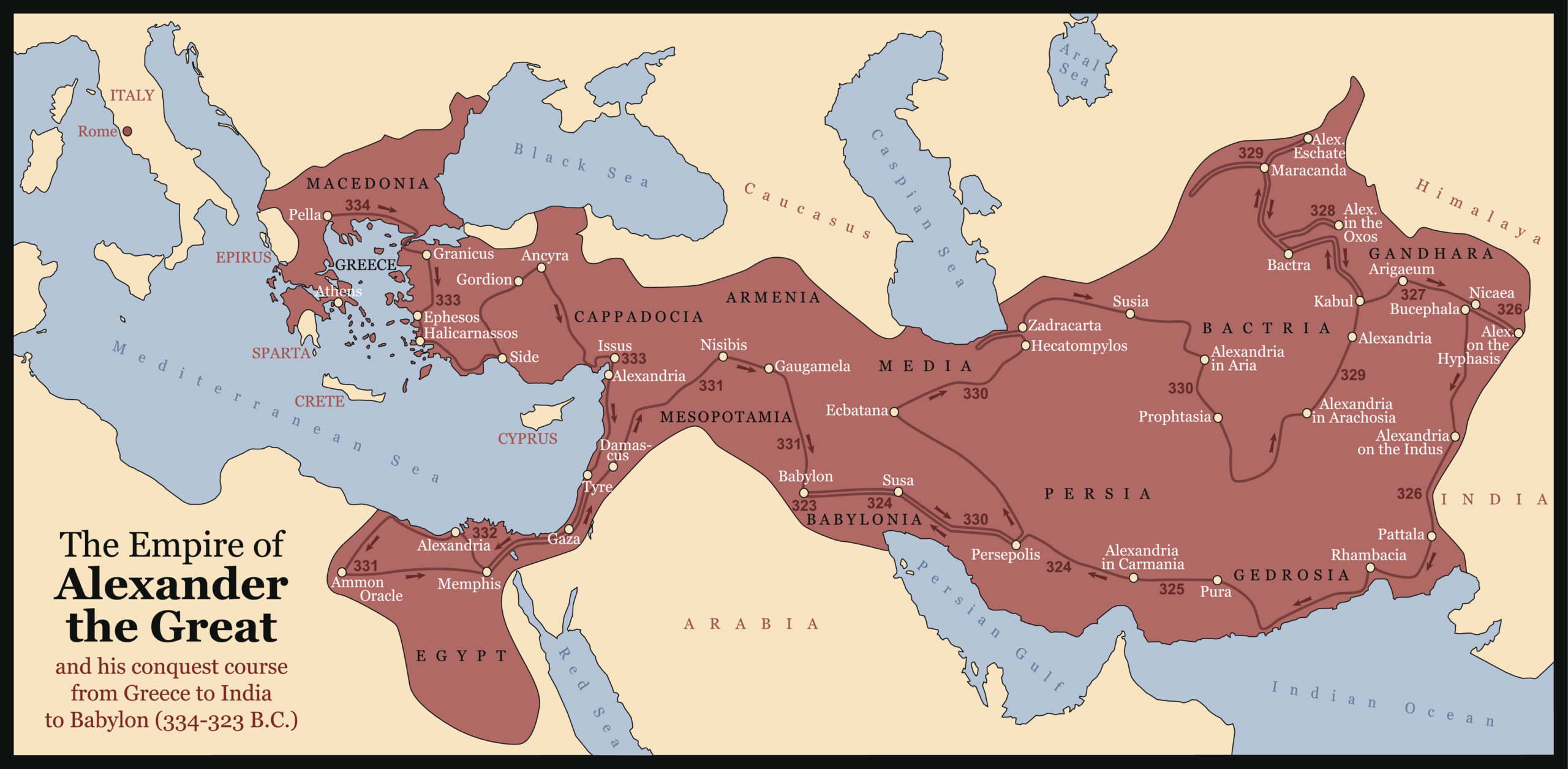
Conquests Of Alexander The Great Accessed 2 november 2024. hellenistic age, in the eastern mediterranean and middle east, the period between the death of alexander the great in 323 bce and the conquest of egypt by rome in 30 bce. for some purposes the period is extended for a further three and a half centuries, to the move by constantine the great of his. The hellenistic period was the era of ancient greek civilisation that followed the death of alexander the great in 323 bc. it saw greek culture transform and spread across the mediterranean and into western and central asia. the end of the hellenistic period is variously attributed to the roman conquest of the greek peninsula in 146 bc and. The hellenistic period refers to the time between the death of alexander the great (323 bce) and the rise of the roman empire (32 bce) in which greek culture spread throughout the mediterranean and near east. beginning with a series of conflicts between alexander 's top generals known as the wars of the diadochi, the time period would see major. T. e. in classical antiquity, the hellenistic period covers the time in greek history after classical greece, between the death of alexander the great in 323 bc and the death of cleopatra vii in 30 bc, [1] which was followed by the ascendancy of the roman empire, as signified by the battle of actium in 31 bc and the roman conquest of ptolemaic.

Comments are closed.