How Axial Expansion Joints Absorb Movements

How Axial Expansion Joints Absorb Movements Youtube This animation shows how movements are absorbed in an axial expansion joint. axial expansion joints are designed to absorb axial movements (extension and com. 2.3 unrestrained expansion joints 2.4 restrained expansion joints 2.5 the inner sleeve (protection tube) 2.6 types of connection 2.6.1 expansion joint for welding in 2.6.2 expansion joint with welded flange connection 2.6.3 expansion joint with loose (movable) flange connection 2.7 determination of movement parameters.
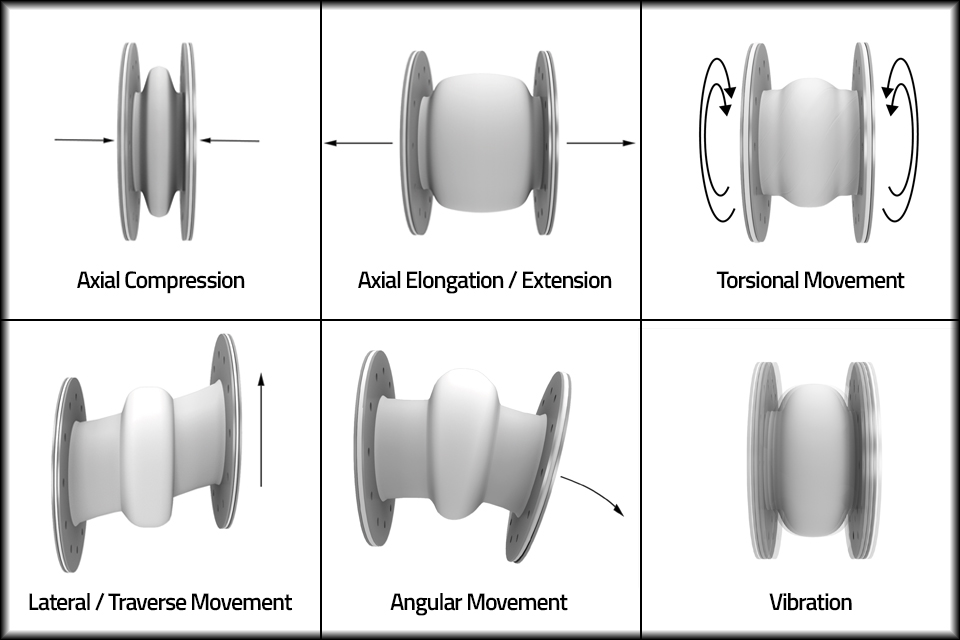
What Is Axial Movement Of A Shaft At Walter Adams Blog Bellows expansion joints: feature corrugated metal sections that flex to absorb movement; slip joints: use sliding components to accommodate axial expansion and contraction; universal expansion joints: capable of handling multiple types of movement simultaneously; hinged expansion joints: designed for angular rotation in specific planes. These deflections can include axial, lateral, angular, torsional, combined, or cyclic, and all occur simultaneously. axial deflection refers to the movement parallel to the center line of the expansion joint. lateral deflection refers to movement perpendicular to the center line. angular deflection is when the expansion joint bends around its. An expansion joint is designed to allow deflection in the axial (compressive), lateral (shear), or angular (bending) deflections. expansion joints can be non metallic or metallic (often called bellows type). non metallic can be a single ply of rubberized material or a composite made of multiple layers of heat and erosion resistant flexible. Axial expansion joints, also known as single bellows expansion joints, are designed to absorb axial, or linear, movement in piping and duct systems. these flexible components prevent pressure, vibration, and damage by accommodating expansion and contraction caused by temperature fluctuations. they are essential in maintaining the stability and.

Axial Expansion Joints Flexpert Bellows An expansion joint is designed to allow deflection in the axial (compressive), lateral (shear), or angular (bending) deflections. expansion joints can be non metallic or metallic (often called bellows type). non metallic can be a single ply of rubberized material or a composite made of multiple layers of heat and erosion resistant flexible. Axial expansion joints, also known as single bellows expansion joints, are designed to absorb axial, or linear, movement in piping and duct systems. these flexible components prevent pressure, vibration, and damage by accommodating expansion and contraction caused by temperature fluctuations. they are essential in maintaining the stability and. Expansion joints are available in slip, ball, metal bellows, and rubber bellows configurations. slip type expansion joints (fig. 1) have a sleeve that telescopes into the body. leakage is controlled by packing located between the sleeve and the body. leakage is minimal and can be near zero in many applications. 5 pressure balanced expansion joints: designed to absorb axial movement without transferring thrust to the pipe anchors. used in systems with high pressure conditions where thrust forces need to be minimized. materials. depending on the application, expansion joints are usually made from materials like stainless steel, rubber, or ptfe.

Comments are closed.