How An Engine Cooling System Works How A Car Works

How An Engine Cooling System Works How A Car Works The primary job of the cooling system is to keep the engine from overheating by transferring this heat to the air, but the cooling system also has several other important jobs. the engine in your car runs best at a fairly high temperature. when the engine is cold, components wear out faster, and the engine is less efficient and emits more. The job of the car’s cooling system is to allow the engine to quickly attain its maximum temperature, maintain that temperature during its use and release the excess heat into the air. the cooling system is composed of various parts: the radiator, pressure cap, fan, pump, thermostat, hoses and overflow tank. the pump sends cooling fluid to.

How An Engine Cooling System Works How A Car Works In order for the system to work, the coolant needs to move throughout the system. the water pump uses power from the crankshaft and serpentine belt to force coolant into the engine and through the rest of the cooling system. allow your engine to run for a few minutes before inspecting your water pump. visually check for leaks around the unit. When the engine warms up, the wax melts, expands and pushes the valve open, allowing coolant to flow through the radiator. when the engine stops and cools, the valve closes again. water expands when it freezes, and if the water in an engine freezes it can burst the block or radiator. so antifreeze usually ethylene glycol is added to the water. In the video, we learn about the general structure and operating principle of one of the subsystems of a car engine the engine cooling system. the video br. Coolant. at the core of the cooling system is the coolant, a specially formulated mixture of water and antifreeze. this fluid circulates through the engine and absorbs heat from the combustion process. acting as a heat exchange medium, the coolant undergoes a transformation from liquid to vapor and back, carrying away the excess heat.
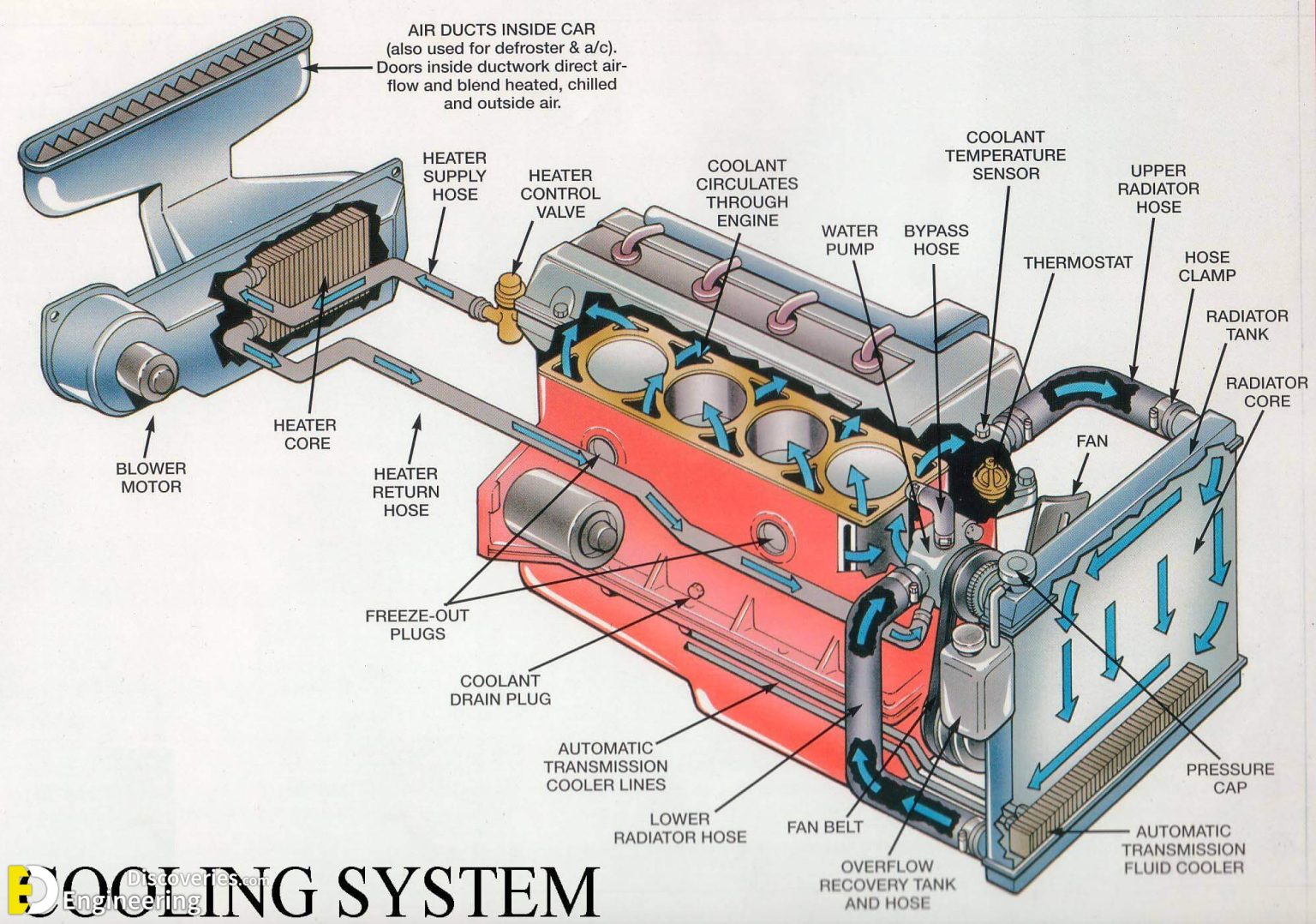
How Engine Cooling System Works Engineering Discoveries In the video, we learn about the general structure and operating principle of one of the subsystems of a car engine the engine cooling system. the video br. Coolant. at the core of the cooling system is the coolant, a specially formulated mixture of water and antifreeze. this fluid circulates through the engine and absorbs heat from the combustion process. acting as a heat exchange medium, the coolant undergoes a transformation from liquid to vapor and back, carrying away the excess heat. The basics remain the same. the cooling system is filled with a 50 50 mixture of ethylene glycol and water. this fluid is referred to as antifreeze or coolant. it is the media used by the cooling system to remove engine heat and disperse it. antifreeze is kept under pressure in the cooling system as the heat expands the fluid, up to 15 psi. A water cooling system is a complex heat exchanger comprising special coolant fluid, pipes, some clever regulating valves and a car radiator and an expansion tank. propelled by the water pump, coolant flows from the radiator to the engine, where it travels around the main engine block, in which the pistons go up and down, and the cylinder head.

Comments are closed.