How A Magnifying Glass Works Doc Physics

How A Magnifying Glass Works Doc Physics Youtube It's all about getting things closer to your eye while still keeping focused. in fact, if the image of the lens is at infinity, you won't even have eye stra. You know what this is, right? it's a big old positive lens. you hold it up to your eyeball and suddenly you can see much smaller text. but how exactly doe.

How Does A Magnifying Glass Create A Virtual Image Homework Study A magnifying glass, in effect, tricks your eyes into seeing what isn't there. light rays from the object enter the glass in parallel but are refracted by the lens so that they converge as they exit, and create a "virtual image" on the retina of your eye. this image appears to be larger than the object itself because of simple geometry: your. It is just that the ciliary muscles of the eye are most relaxed when they are set to bring to bring parallel light to a focus. it is merely the most comfortable thing to do. figure iii.2 shows a magnifying glass at work. as usual, angles are small and the lens is thin. the object is in the focal plane of the lens. A magnifying glass is usually a convex lens (a lens that bulges outwards), made of either glass or plastic. light hits the glass at an angle, and it gets refracted towards the centre of the lens. Figure \(\pageindex{1}\): example of a positive lens used as a magnifying glass (picture taken by a.j.l. adam cc by sa 4.0). 3.5.1 magnifying power the magnifying power mp or angular magnification \(m {a}\) is defined as the ratio of the size of the retinal image obtained with the instrument and the size of the retinal image as seen by the.

Magnifying Glass Spm Physics Form 4 Form 5 Revision Notes A magnifying glass is usually a convex lens (a lens that bulges outwards), made of either glass or plastic. light hits the glass at an angle, and it gets refracted towards the centre of the lens. Figure \(\pageindex{1}\): example of a positive lens used as a magnifying glass (picture taken by a.j.l. adam cc by sa 4.0). 3.5.1 magnifying power the magnifying power mp or angular magnification \(m {a}\) is defined as the ratio of the size of the retinal image obtained with the instrument and the size of the retinal image as seen by the. A convex lens used for this purpose is called a magnifying glass or a simple magnifier. figure 2.8.2: the simple magnifier is a convex lens used to produce an enlarged image of an object on the retina. (a) with no convex lens, the object subtends an angle θobject from the eye. (b) with the convex lens in place, the image produced by the convex. Magnifying glass in front of an eye has the impact of “moving” the object from op to iq. here np n p is the distance to the near point of the eye where viewing is the clearest. perceived magnification is given by the ratio of the angles subtended at the eye by the virtual image iq and the “moved object” ip q. ip q.

How A Magnifying Glass Convex Lens Works Science Education Dslr A convex lens used for this purpose is called a magnifying glass or a simple magnifier. figure 2.8.2: the simple magnifier is a convex lens used to produce an enlarged image of an object on the retina. (a) with no convex lens, the object subtends an angle θobject from the eye. (b) with the convex lens in place, the image produced by the convex. Magnifying glass in front of an eye has the impact of “moving” the object from op to iq. here np n p is the distance to the near point of the eye where viewing is the clearest. perceived magnification is given by the ratio of the angles subtended at the eye by the virtual image iq and the “moved object” ip q. ip q.
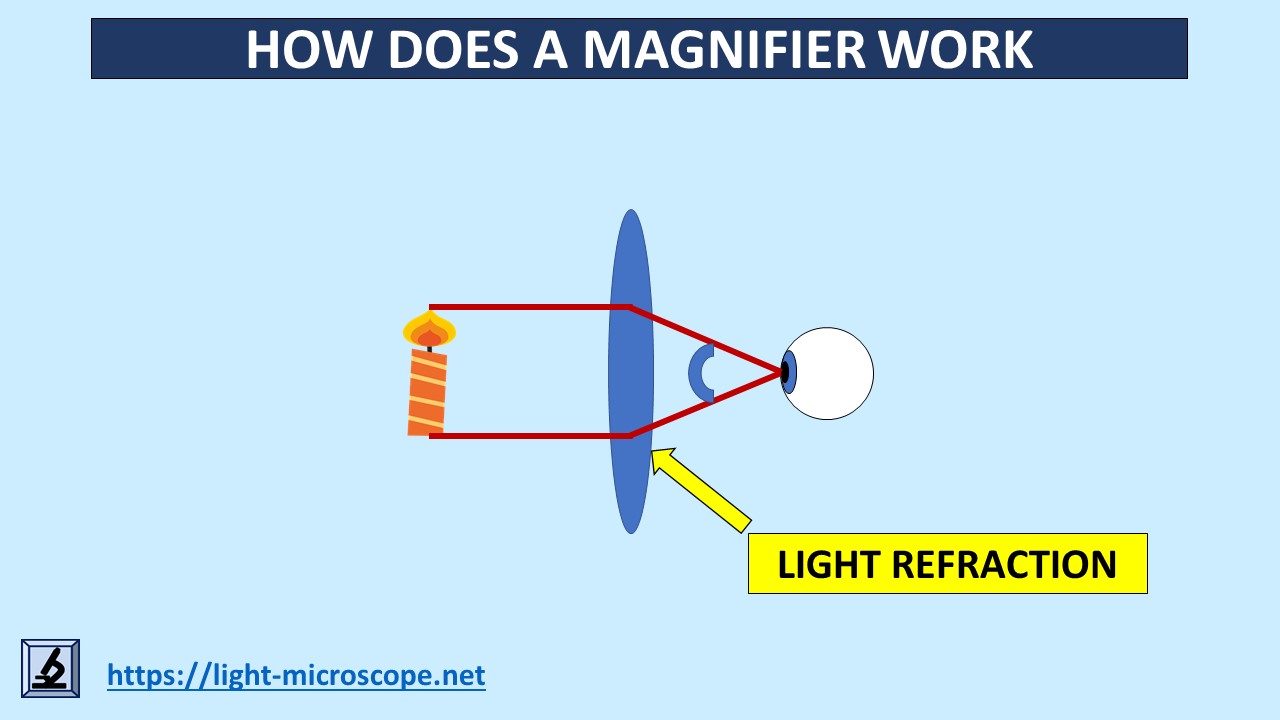
How Does A Magnifier Work Light Microscope

Bbc Gcse Bitesize Science Lenses Revision Page 5

Comments are closed.