How A Heat Pump Works Intro To Heat Pumps

How A Heat Pump Works Intro To Heat Pumps Youtube Learn how heat pumps work as dual purpose devices for heating and cooling and why they are more efficient than heaters and air conditioners. in this lesson,. How a heat pump works. a heat pump uses technology similar to that found in a refrigerator or an air conditioner. it extracts heat 1 from a source, such as the surrounding air, geothermal energy stored in the ground, or nearby sources of water or waste heat from a factory. it then amplifies and transfers the heat to where it is needed.
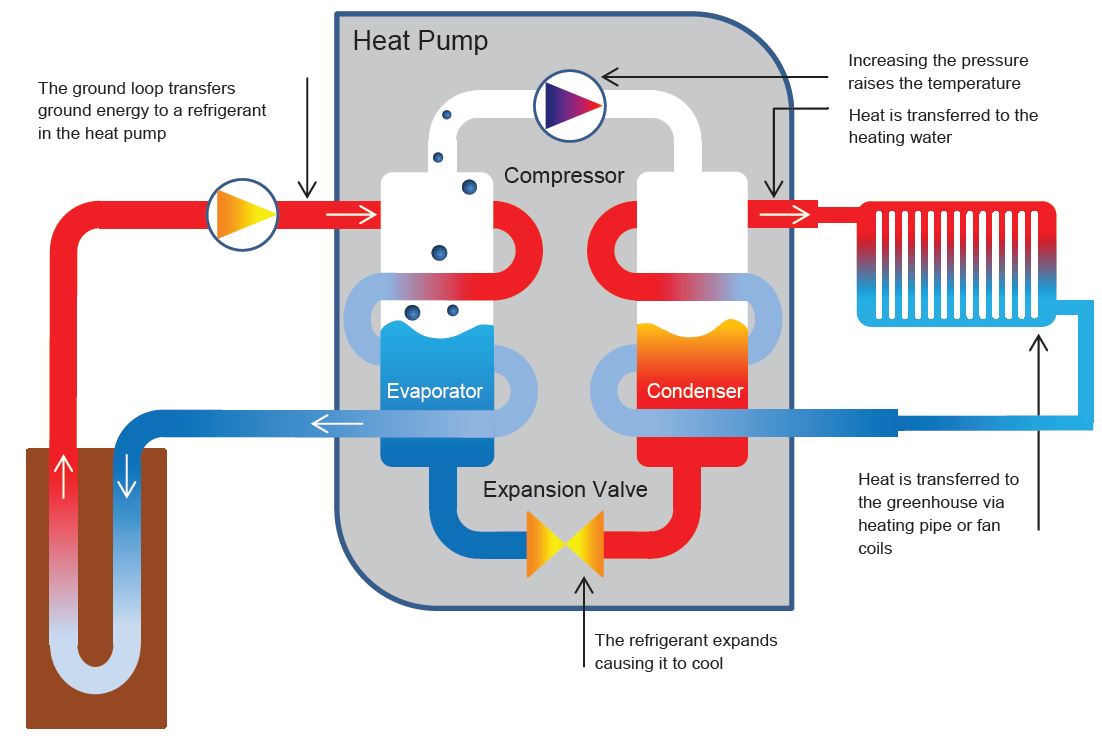
A Detailed Look At Heat Pumps And How They Work Growsave Smarter heating by david mackay, includes a simple introduction to heat pumps, and comes from his book sustainable energy without the hot air. articles. why mainers are falling hard for heat pumps by cara buckley, the new york times, march 2, 2024. heat pumps are now outselling gas furnaces in the united states—and maine is most enthusiastic. Hvac introduction to heat pumps. in this module, we take an introductive look at air source heat pumps in hvac systems and how they move heat. their benefits and energy efficiency advantages are discussed, as well as best practices for determining ideal sizing and design for installation. lastly, calculations are detailed in order to know how. Section 1. systems. heat pumps offer an energy efficient alternative to furnaces and air conditioners for all climates. like your refrigerator, heat pumps use electricity to transfer heat from a cool space to a warm space, making the cool space cooler and the warm space warmer. during the heating season, heat pumps move heat from the cool. How heat pumps work. heat pumps work by finding and moving heat in and out of a building. a heat pump will take heat from within the home during the summer and let it dissipate outside, allowing the air conditioning system to work more efficiently. in the winter, a heat pump can scavenge heat from the outdoors (even in temperatures as low as.
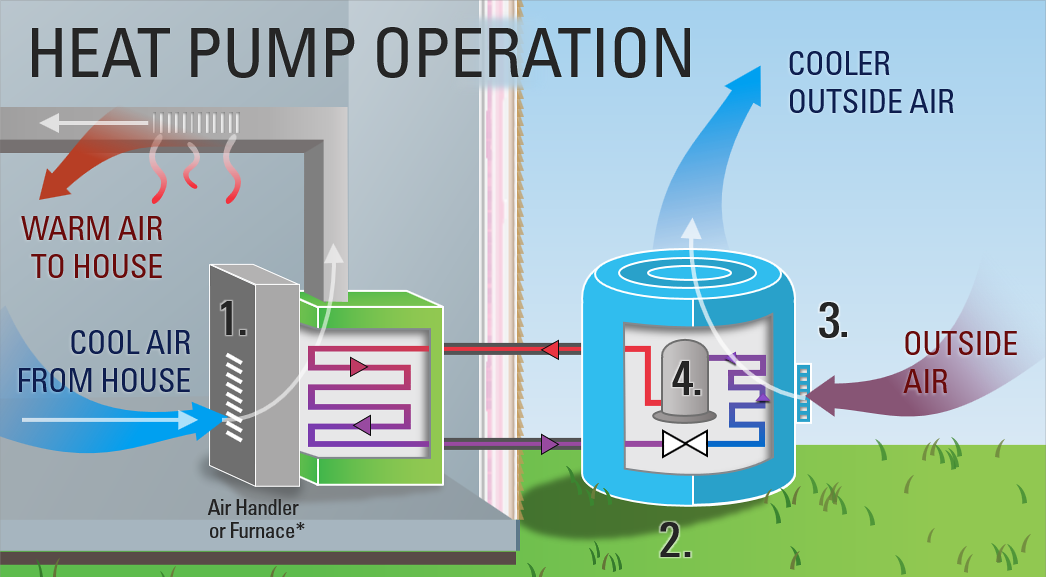
How A Heat Pump Actually Works With Physics And Charts 2040 Energy Section 1. systems. heat pumps offer an energy efficient alternative to furnaces and air conditioners for all climates. like your refrigerator, heat pumps use electricity to transfer heat from a cool space to a warm space, making the cool space cooler and the warm space warmer. during the heating season, heat pumps move heat from the cool. How heat pumps work. heat pumps work by finding and moving heat in and out of a building. a heat pump will take heat from within the home during the summer and let it dissipate outside, allowing the air conditioning system to work more efficiently. in the winter, a heat pump can scavenge heat from the outdoors (even in temperatures as low as. The main difference between a standard air source heat pump and an absorption pump is that instead of compressing a refrigerant, an absorption pump absorbs ammonia into water, and then a low power pump pressurizes it. the heat source then boils the ammonia out of the water — and the process starts all over again. Heat pumps rely on this physical property, putting heat in contact with cooler, lower pressure environments so that the heat can naturally transfer. this is how a heat pump works. step 1. liquid refrigerant is pumped through an expansion device at the indoor coil, which is functioning as the evaporator.

Comments are closed.