Hot Dip Galvanizing Process Animation

A Complete Guide To Galvanizing Process Of Steel Materials The steps involved in the galvanizing process. galvanizeit.org hot dip galvanizing. Ani metal, as one of the leading plant suppliers in the hot dip galvanizing industry, in addition to the assembly of turnkey galvanizing plants, provides a n.
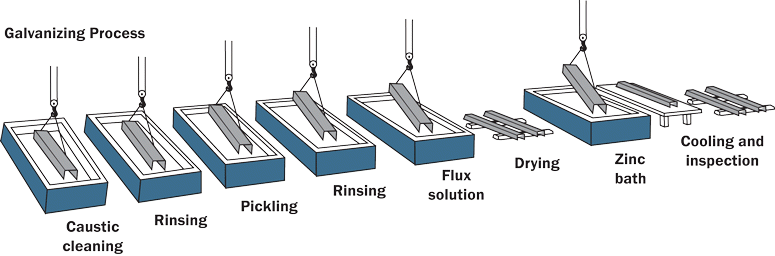
Hot Dip Galvanizing The Ultimate Guide This page galvanizeit.org galvanize it online seminar hot dip galvanizing hdg process details more information relating to the hdg process. Testing methods and interpretation of results can be found in the inspection section of this site, as well as in the inspection course, and inspection of hot dip galvanized steel products. the hot dip galvanizing (hdg) process consists of three basic steps: surface preparation galvanizing inspection surface preparation surface preparation is…. Step 2: galvanizing. when steel is entirely immersed in a bath (kettle) of molten zinc, the galvanizing step of the process happens. the bath chemistry must be at least 98% pure zinc and kept at a temperature of around 850 °f (450 °c), according to the specifications. the crane hoist lowers the steel at an angle. The drying process is crucial to prevent splattering when the metal is introduced to the hot zinc. any moisture left on the metal can react violently with the molten zinc, compromising the quality of the galvanized coating. 3. step#3 galvanizing bath. following the crucial fluxing process, the metal is ready for the centerpiece of the hot dip.

Hot Dipping Industrial Process Britannica Step 2: galvanizing. when steel is entirely immersed in a bath (kettle) of molten zinc, the galvanizing step of the process happens. the bath chemistry must be at least 98% pure zinc and kept at a temperature of around 850 °f (450 °c), according to the specifications. the crane hoist lowers the steel at an angle. The drying process is crucial to prevent splattering when the metal is introduced to the hot zinc. any moisture left on the metal can react violently with the molten zinc, compromising the quality of the galvanized coating. 3. step#3 galvanizing bath. following the crucial fluxing process, the metal is ready for the centerpiece of the hot dip. The hot dip galvanizing kettle. the freshly cleaned steel is submerged into a kettle of molten zinc at 830° 850° f. the zinc then bonds with the steel in a diffusion reaction, creating a brand new layer of metallurgically bonded zinc alloy. before the newly coated steel can be removed from the tank, the surface of the molten zinc must be. I. protective performance of the hot dip galvanized layer. typically, the thickness of an electroplated zinc layer ranges from 5 to 15μm, while the thickness of a hot dip galvanized layer is generally above 65μm, and can even reach up to 100μm. hot dip galvanizing provides good coverage, the coating is compact, and free from organic impurities.

Comments are closed.