Hits That Dont Cause Symptoms Can Cause Cte

Traumatic Brain Injuries Scor Global Life Americas August Ppt Download Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (cte) is a brain disorder likely caused by repeated head injuries. it causes the death of nerve cells in the brain, known as degeneration. cte gets worse over time. the only way to definitively diagnosis cte is after death during an autopsy of the brain. cte is a rare disorder that is not yet well understood. Over time they may have mood or personality changes or become forgetful and struggle with daily tasks. 1,4,5 mental health problems can increase for those with cte. 4 the link between cte and suicide is unclear. 6. symptoms of cte are similar to those of other health problems.

Study Repeated Hits Not Concussions Cause Cte Cbs Baltimore These may include symptomatic concussions as well as non concussive hits that do not cause symptoms. non concussive hits are routine in many sports, including checking in ice hockey and heading the ball in soccer. cte has been known to affect boxers since the 1920’s (when it was initially termed punch drunk syndrome or dementia pugilistica). "evidence suggests that hits to the head that don't cause symptoms or can't be diagnosed with standard tests can still cause brain damage." cumulative damage. the potential dangers of cumulative subconcussive hits—blows that don't cause diagnosable symptoms—are now a major research focus. Cte is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by abnormal accumulation of tau protein around small blood vessels in the brain. cte causes brain cell death, cognitive deficits, and dementia. the brain pathology of cte has been observed in brains of teenagers and adults with exposure to repeated head injury, both concussive and subconcussive. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (cte) is a progressive degenerative disease of the brain found in people with a history of repetitive brain trauma, including symptomatic concussions as well as subconcussive hits to the head that do not cause symptoms. cte has been known to affect boxers since the 1920’s (when it was termed punch drunk.
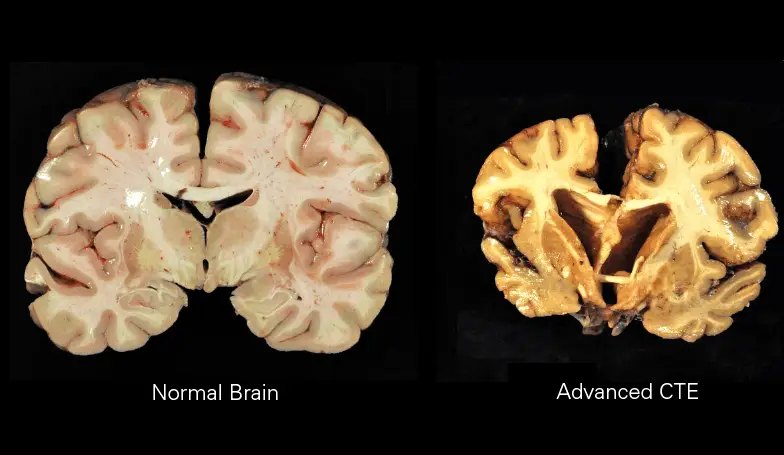
Know Your Brain Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy Cte Cte is a neurodegenerative disease characterized by abnormal accumulation of tau protein around small blood vessels in the brain. cte causes brain cell death, cognitive deficits, and dementia. the brain pathology of cte has been observed in brains of teenagers and adults with exposure to repeated head injury, both concussive and subconcussive. Chronic traumatic encephalopathy (cte) is a progressive degenerative disease of the brain found in people with a history of repetitive brain trauma, including symptomatic concussions as well as subconcussive hits to the head that do not cause symptoms. cte has been known to affect boxers since the 1920’s (when it was termed punch drunk. Scientists have been referring to head impacts that don’t cause concussion symptoms as “subconcussive impacts,” which implies they are less than concussions. this has even led to cte experts saying cte is caused by “small, repetitive impacts.”. but when it comes to size of the hit, 10% of head impacts are more than concussions. This can be. getting ones “bell rung” or repeated blows to the head. hits can be symptomatic concussions as well as sub concussive hits to the head that do not cause symptoms (repetitive head impacts). many routine american football tackles involve sub concussive hits. just the action of stopping a moving brain quickly can create a sub.

A New Study Shows That Hits To The Head Not Concussions Cause Cte Scientists have been referring to head impacts that don’t cause concussion symptoms as “subconcussive impacts,” which implies they are less than concussions. this has even led to cte experts saying cte is caused by “small, repetitive impacts.”. but when it comes to size of the hit, 10% of head impacts are more than concussions. This can be. getting ones “bell rung” or repeated blows to the head. hits can be symptomatic concussions as well as sub concussive hits to the head that do not cause symptoms (repetitive head impacts). many routine american football tackles involve sub concussive hits. just the action of stopping a moving brain quickly can create a sub.

Comments are closed.