Histology Of The Vagina 4k

Histology Of The Vagina 4k Youtube The elastic lp and smooth muscle enable the vagina to distend, particularly during birth. show labels. the vagina is lubricated by cervical mucus, which is derived from the rich vascular network, and mucus from glands in the labia minora. the smooth muscle contracts during after coitus to keep the pool of semen close to the cervix. The vagina is part of the internal genitalia of the female reproductive system. the internal female sex organs form a pathway, the internal female genital tract, composed of the vagina, uterus, the paired uterine tubes and ovaries. the vagina serves a multitude of functions. it facilitates menstruation, childbirth and sexual intercourse, as it.

Vagina Tutorial Histology Atlas For Anatomy And Physiology The vagina is a flexible muscular tube that extends approximately 3 3.5 inches (7 9 cm) from the cervical region of the uterus to the outside of a woman’s body at the vestibule (urogenital sinus). the vagina runs parallel to both the urethra and the rectum, with the urethra lying anterior and the rectum directly posterior to the vagina. the. Slide 250 1 vagina, h&e view virtual slide. slide 250 2 vagina, trichrome stain view virtual slide. the vagina connects the female reproductive system to the exterior of the body. at low magnification, note its three layered structure: the mucosal lining, smooth muscle layer, and outer adventitial layer. The vagina is closely related to many of the organs in the pelvic region: anterior – bladder and urethra. posterior – rectouterine pouch, rectum and anal canal. lateral – ureters and levator ani muscle. fig 2. sagittal section of the female pelvis, showing the anatomical relations of the vagina. Vagina. the vagina is a fibromuscular tube extending from the uterine cervix to the outside of the body. the vagina is composed of a mucosa, muscularis externa and adventitia. the vagina serves as the depository for sperm and serves as part of the birth canal at parturition. 10x. the vaginal mucosa possesses stratified squamous moist epithelium.
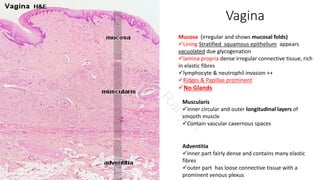
Histology Of Cervix And Vagina Ppt The vagina is closely related to many of the organs in the pelvic region: anterior – bladder and urethra. posterior – rectouterine pouch, rectum and anal canal. lateral – ureters and levator ani muscle. fig 2. sagittal section of the female pelvis, showing the anatomical relations of the vagina. Vagina. the vagina is a fibromuscular tube extending from the uterine cervix to the outside of the body. the vagina is composed of a mucosa, muscularis externa and adventitia. the vagina serves as the depository for sperm and serves as part of the birth canal at parturition. 10x. the vaginal mucosa possesses stratified squamous moist epithelium. These are the mons pubis, labia majora and minora, clitoris, vestibule, vestibular bulb and glands. the vagina, uterus, ovaries and uterine tubes compose the internal genital organs. female reproductive organs undergo substantial structural and functional changes every month. these changes are not only there to make women’s lives miserable. The ill defined muscle layers contain bundles of smooth muscle. the muscle layers grade into an adventitia. the vagina connects the female reproductive system to the exterior of the body. at low magnification, note its three layered structure: the mucosal lining, smooth muscle layer, and outer adventitial layer.

Histology Of Female Reproductive System Petek Korkusuz Md These are the mons pubis, labia majora and minora, clitoris, vestibule, vestibular bulb and glands. the vagina, uterus, ovaries and uterine tubes compose the internal genital organs. female reproductive organs undergo substantial structural and functional changes every month. these changes are not only there to make women’s lives miserable. The ill defined muscle layers contain bundles of smooth muscle. the muscle layers grade into an adventitia. the vagina connects the female reproductive system to the exterior of the body. at low magnification, note its three layered structure: the mucosal lining, smooth muscle layer, and outer adventitial layer.

Comments are closed.