Heat Transfer Physics By Manoj Pandey Sir Modes Of Heat Transfer

Heat Transfer Physics By Manoj Pandey Sir Modes Of Heat Transfer #rankerslearning #heattransfer #physicsin this video heat transfer (modes of heat transfer) related to physics is explained by manoj pandey sir which are bes. #rankerslearning #heattransfer #physicsin this video heat transfer (thermal resistor in series) related to physics is explained by manoj pandey sir which are.

Heat Transfer Physics By Manoj Pandey Sir Thermal Radiation Prevost Explore the fascinating world of heat transfer with manoj pandey in this detailed session on thermal radiation and newton's law of cooling. this video is tai. By manoj pandey 16 04 2024. contents hide. 1 (i) caloric theory of heat. 2 (ii) dynamic theory of heat. 2.1 (a) translatory motion. 2.2 (b) vibrational motion. 2.3 (c) rotational motion. 3 related. heat is the form of energy which flows from hotter body to colder body by virtue of temperature difference. Definition: radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation. it is the fastest mode of heat transfer. it doesn’t require a medium and can even occur in a vacuum. mechanism: all objects with a temperature above absolute zero (0 k) emit electromagnetic radiation. hotter objects emit more intense. Figure 5.4.2 – differential heat conduction. the more chains of spring connected particles we can use, the faster the energy can be transferred. the number of chains is proportional to the cross sectional area of the cylinder, so the rate of heat transfer is also proportional to the cross sectional area: dq dt ∝ a (5.4.1) (5.4.1) d q d t ∝ a.

Heat Transfer Physics By Manoj Pandey Sir Thermal Resistor In Series Definition: radiation is the transfer of heat through electromagnetic waves, such as infrared radiation. it is the fastest mode of heat transfer. it doesn’t require a medium and can even occur in a vacuum. mechanism: all objects with a temperature above absolute zero (0 k) emit electromagnetic radiation. hotter objects emit more intense. Figure 5.4.2 – differential heat conduction. the more chains of spring connected particles we can use, the faster the energy can be transferred. the number of chains is proportional to the cross sectional area of the cylinder, so the rate of heat transfer is also proportional to the cross sectional area: dq dt ∝ a (5.4.1) (5.4.1) d q d t ∝ a. The three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: conduction requires contact. convection requires fluid flow. radiation does not require any medium. conduction is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. usually, it is heat transfer through a solid. The rate of heat transfer q t q t (energy per unit time) is proportional to the temperature difference t2 −t1 t 2 − t 1 and the contact area a a and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects: q t = ka(t2 −t1) d. (14.1) (14.1) q t = k a (t 2 − t 1) d. 14.6: convection. convection is heat transfer by the macroscopic.

Heat Transfer Heat Conduction Through Various Types Of Conductors The three types of heat transfer differ according to the nature of the medium that transmits heat: conduction requires contact. convection requires fluid flow. radiation does not require any medium. conduction is heat transfer directly between neighboring atoms or molecules. usually, it is heat transfer through a solid. The rate of heat transfer q t q t (energy per unit time) is proportional to the temperature difference t2 −t1 t 2 − t 1 and the contact area a a and inversely proportional to the distance between the objects: q t = ka(t2 −t1) d. (14.1) (14.1) q t = k a (t 2 − t 1) d. 14.6: convection. convection is heat transfer by the macroscopic.

Heat Transfer Conduction Through Spherical Surface Physics Manoj
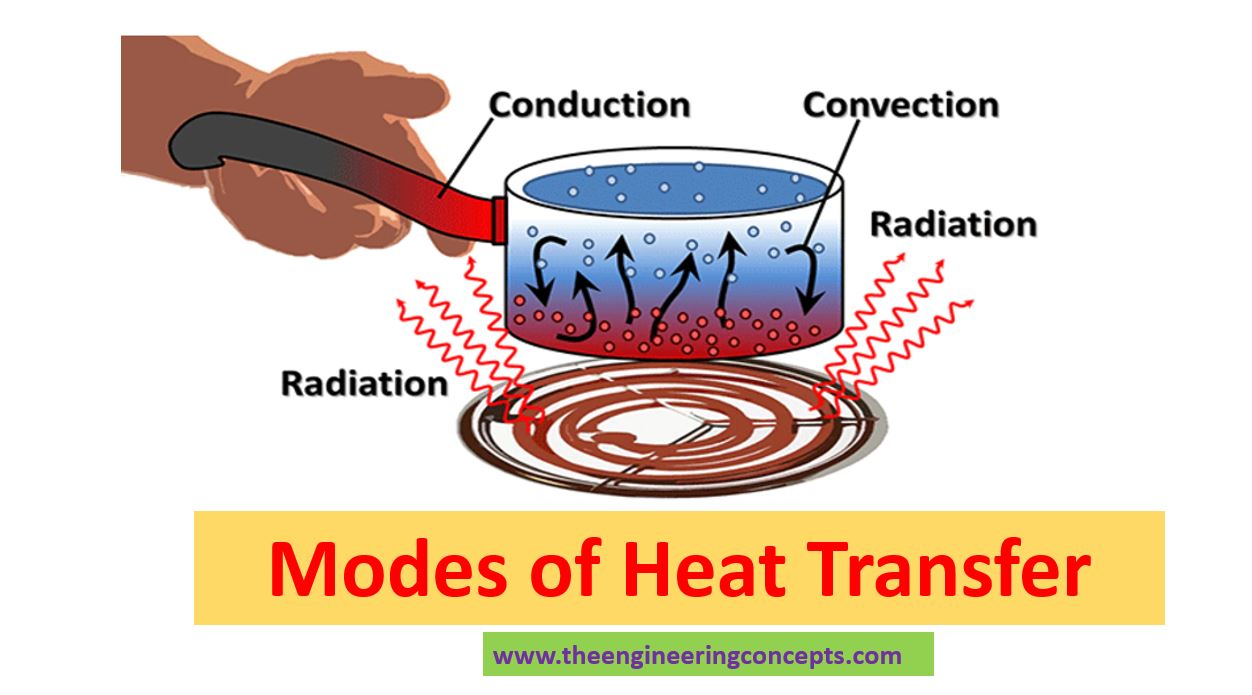
Modes Of Heat Transfer The Engineering Concepts

Comments are closed.