Gut Microbiota And Obesity
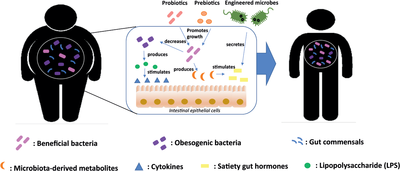
Ijms Free Full Text Microbial Medicine Prebiotic And Probiotic The gut microbiota affects appetite, energy absorption, fat storage, circadian rhythm, and chronic inflammation, leading to obesity. therefore, targeted reconstruction of the gut microbiota structure, such as through fecal bacterial transplantation, is one of the means of treating obesity. The prevalence of obesity continues to rise at alarming rates. due to its chronic and relapsing nature, management of this condition remains a challenge. while its pathogenesis is known to be multipronged — with the involvement of diet, lifestyle and genetics — recent studies have suggested that gut microbiota may play a role in causing.
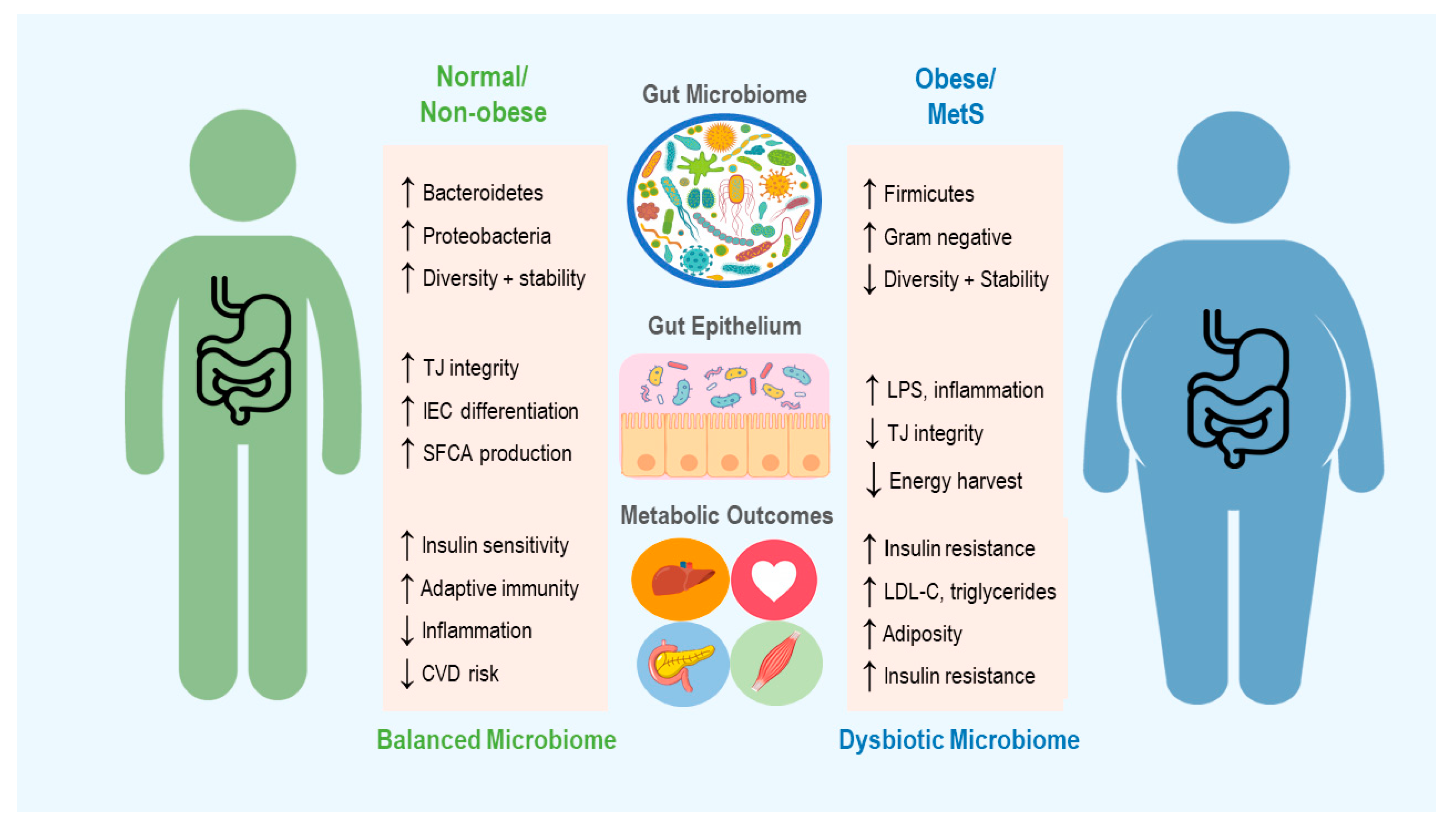
Gut Microbiota In Obesity Gutmicrobiotaforhealth Gut microbiota has a vital role in mechanisms involved in overweight and obesity, including host metabolism and energy expenditure. this review describes the physiology of white and brown adipose. Subsequently, mice lacking a gut microbiota (germ free) were shown to develop less adipose mass and were less prone to obesity compared with conventional mice (that is, mice with a gut microbiota. The pattern of bas can be modulated by dietary fibres, both through the gut microbiota 118 and independently of the gut microbiota (for example, changes in absorption by viscous soluble dietary. This review will discuss the relationship between the gut microbiota and obesity, to increase understanding of the mechanism by which the gut microbiome affects weight gain. moreover, this review will examine the effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics supplementation on body weight.

Features Of The Gut Microbiota That Promote Obesity And Insulin The pattern of bas can be modulated by dietary fibres, both through the gut microbiota 118 and independently of the gut microbiota (for example, changes in absorption by viscous soluble dietary. This review will discuss the relationship between the gut microbiota and obesity, to increase understanding of the mechanism by which the gut microbiome affects weight gain. moreover, this review will examine the effects of probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics supplementation on body weight. The gut microbiota has been recognized as an important factor in the development of metabolic diseases such as obesity and is considered an endocrine organ involved in the maintenance of energy homeostasis and host immunity. dysbiosis can change the functioning of the intestinal barrier and the gut associated lymphoid tissues (galt) by allowing. Abstract. the obesity epidemic has become a global public health crisis in recent years and is continuing to worsen at an alarming rate. however, the pathophysiological mechanisms involved in the development of obesity and obesity related diseases are still being unraveled. in the past ten years, the gut microbiota has been identified as a.

Comments are closed.