Guide To Prenatal Genetic Testing And Screening

Guide To Prenatal Genetic Testing And Screening Detects whether you, your partner, or both carry a mutation in a gene for a certain genetic disorder. first trimester screening. timing: 10–13 weeks. blood test plus nt ultrasound exam. screens for down syndrome and trisomy 18. integrated screening and sequential screening. timing: 10–22 weeks. Carrier screening can be done before or during pregnancy. prenatal genetic screening tests of the pregnant woman’s blood and findings from ultrasound exams can screen the fetus for aneuploidy; defects of the brain and spine called neural tube defects (ntds); and some defects of the abdomen, heart, and facial features.

Prenatal Genetic Testing Chart Infographic Infographics Medicpresents After review and discussion, every patient has the right to pursue or decline prenatal genetic screening and diagnostic testing. if screening is accepted, patients should have one prenatal screening approach, and should not have multiple screening tests performed simultaneously. cell free dna is the most sensitive and specific screening test. Prenatal cell free dna screening. this blood test can be done in any trimester. it checks the baby's dna in the pregnant person's bloodstream. it looks for a higher risk of specific genetic conditions such as down syndrome and trisomy 18. this screening test also can provide information about a baby's sex. Cell free fetal dna testing. doctors use this test to find your baby’s dna in your blood and check it for down syndrome and two other genetic conditions, trisomy 18 and trisomy 13. this test has. Prenatal genetic testing gives parents information about genetic disorders or birth abnormalities the fetus may have. unlike some of the routine prenatal tests like blood type, blood count or glucose screening, these tests are optional. talk with your healthcare provider and decide which tests are right for you.
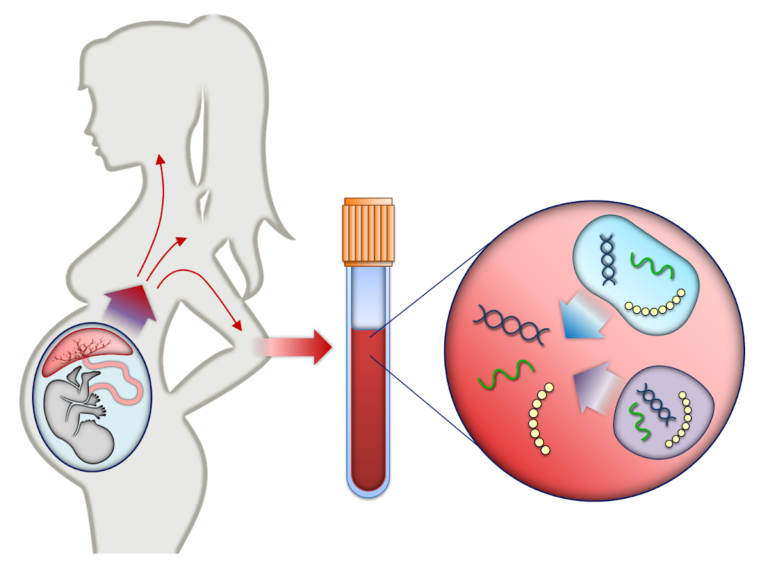
Nipt Test Non Invasive Prenatal Screening Geneton Cell free fetal dna testing. doctors use this test to find your baby’s dna in your blood and check it for down syndrome and two other genetic conditions, trisomy 18 and trisomy 13. this test has. Prenatal genetic testing gives parents information about genetic disorders or birth abnormalities the fetus may have. unlike some of the routine prenatal tests like blood type, blood count or glucose screening, these tests are optional. talk with your healthcare provider and decide which tests are right for you. Serum marker screening can consist of different combinations of tests. markers are usually measured at 10 to 13 weeks of pregnancy (first trimester screening). other markers are measured at 16 to 18 weeks of pregnancy (second trimester screening). sometimes serum testing is done along with a test that measures fetal nuchal translucency. Before pregnancy: genetic carrier screening tests. first trimester screening tests. second trimester screening tests. diagnostic tests: amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (cvs) 5 min read.

Comments are closed.