Graph Of Price Elasticity Of Demand

Elasticity Of Demand Explained This is because price and demand are inversely related which can yield a negative value of demand (or price). price elasticity of demand for bread is: e p = Δq Δp × p q. e p = 30 0 × 23 100. e p = ∞. the price elasticity of demand for bread is ∞. therefore, in such a case, the demand for bread is perfectly elastic. The demand curve in panel (c) has price elasticity of demand equal to −1.00 throughout its range; in panel (d) the price elasticity of demand is equal to −0.50 throughout its range. empirical estimates of demand often show curves like those in panels (c) and (d) that have the same elasticity at every point on the curve.
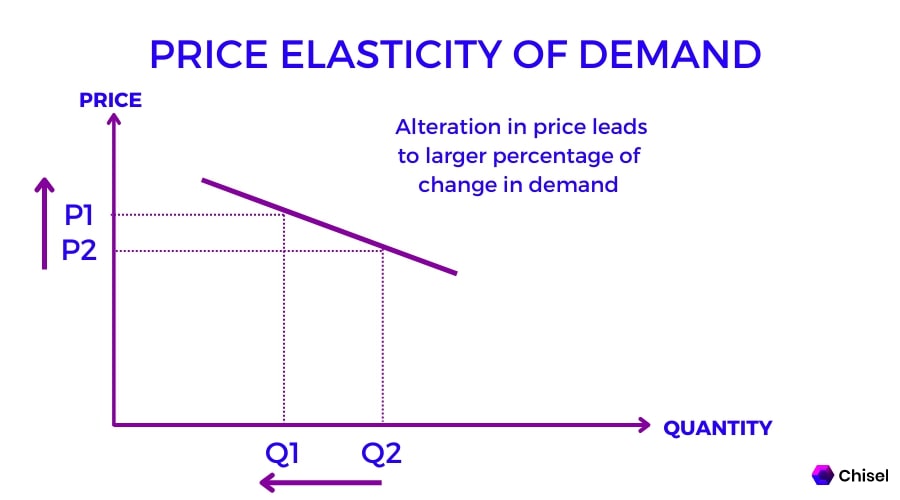
What Is Price Elasticity Of Demand Definition Formula Glossary Learn how to calculate and interpret ped, which measures the responsiveness of demand after a change in price. see examples, graphs and factors that affect elasticity of demand. Example. in fig 6.1, at each point between a and b, shown on the demand curve, price drops by $1.50 and the number of units demanded increases by 2. the slope is –1.5 2 = – 0.75 along the entire demand curve and does not change. the price elasticity, however, changes along the curve. the elasticity between points a and b was – 1 and. The demand curve in panel (c) has price elasticity of demand equal to −1.00 throughout its range; in panel (d) the price elasticity of demand is equal to −0.50 throughout its range. empirical estimates of demand often show curves like those in panels (c) and (d) that have the same elasticity at every point on the curve. A good's price elasticity of demand ( , ped) is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. when the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good (law of demand), but it falls more for some than for others. the price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent.

Graph Of Price Elasticity Of Demand The demand curve in panel (c) has price elasticity of demand equal to −1.00 throughout its range; in panel (d) the price elasticity of demand is equal to −0.50 throughout its range. empirical estimates of demand often show curves like those in panels (c) and (d) that have the same elasticity at every point on the curve. A good's price elasticity of demand ( , ped) is a measure of how sensitive the quantity demanded is to its price. when the price rises, quantity demanded falls for almost any good (law of demand), but it falls more for some than for others. the price elasticity gives the percentage change in quantity demanded when there is a one percent. Therefore, the elasticity of demand between these two points is 6.9% –15.4% 6.9% –15.4% which is 0.45, an amount smaller than one, showing that the demand is inelastic in this interval. Example. calculate the price elasticity of demand when the price changes from $9 to $7 and the quantity demanded changes from 10 units per consumer per month to 14 units per consumer per month. use the mid point formula. solution. price elasticity of demand ≈ 33.33% ÷ −25% ≈ −1.33 or simply 1.33.

Comments are closed.