Geometry Finding The Angle Bisectors Of A Triangle

Angle Bisector Definition Examples Cuemath The angle bisector in geometry is the ray, line, or segment which divides a given angle into two equal parts. for example, an angle bisector of a 60 degree angle will divide it into two angles of 30 degrees each. in other words, it divides an angle into two smaller congruent angles. given below is an image of an angle bisector of ∠aob. Solution. if y is on the angle bisector, then xy = yz and both segments need to be perpendicular to the sides of the angle. from the markings we know ¯ xy ⊥ → wx and ¯ zy ⊥ → wz. second, xy = yz = 6. so, yes, y is on the angle bisector of ∠xwz. example 4.21.4. → mo is the angle bisector of ∠lmn. find the measure of x.
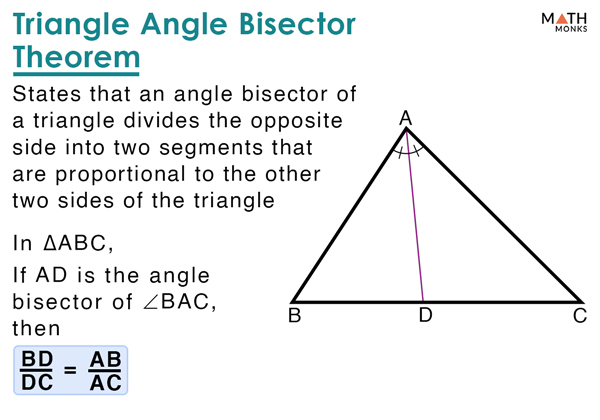
Angle Bisectors Of Triangle The converse of angle bisector theorem states that if the sides of a triangle satisfy the following condition "if a line drawn from a vertex of a triangle divides the opposite side into two parts such that they are proportional to the other two sides of the triangle", it implies that the point on the opposite side of that angle lies on its angle bisector. The angle bisector of a triangle divides the opposite side into two parts proportional to the other two sides of the triangle. converse of internal angle bisector theorem: in a triangle, if the interior point is equidistant from the two sides of a triangle, then that point lies on the angle bisector of the angle formed by the two line segments. Whether you have three sides of a triangle given, two sides and an angle or just two angles, this tool is a solution to your geometry problems. below you'll also find the explanation of fundamental laws concerning triangle angles: triangle angle sum theorem, triangle exterior angle theorem, and angle bisector theorem. An angle bisector of a triangle is a line segment that bisects a vertex angle of a triangle and meets the opposite side of the triangle when extended. they are also called the internal bisector of an angle. shown below is a Δabc, with angle bisector ad of ∠bac. angle bisector of a triangle. how many angle bisectors does a triangle have.
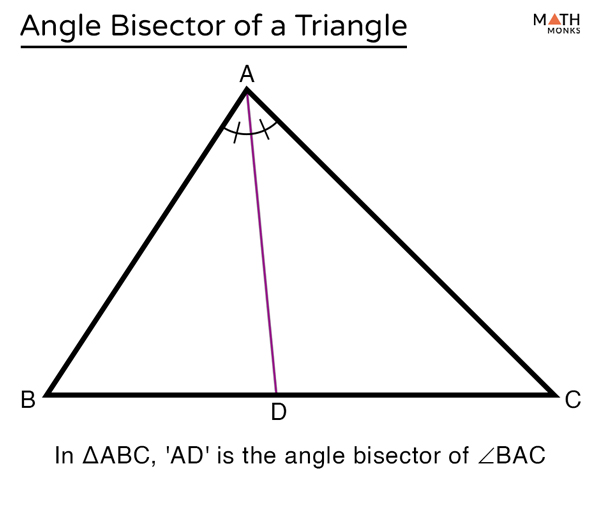
Angle Bisector Of A Triangle Definition Theorem Examples Whether you have three sides of a triangle given, two sides and an angle or just two angles, this tool is a solution to your geometry problems. below you'll also find the explanation of fundamental laws concerning triangle angles: triangle angle sum theorem, triangle exterior angle theorem, and angle bisector theorem. An angle bisector of a triangle is a line segment that bisects a vertex angle of a triangle and meets the opposite side of the triangle when extended. they are also called the internal bisector of an angle. shown below is a Δabc, with angle bisector ad of ∠bac. angle bisector of a triangle. how many angle bisectors does a triangle have. Step by step guide: angle bisectors of triangles. 1. definition of angle bisector: an angle bisector in a triangle is a ray or segment that divides an interior angle of the triangle into two congruent or equal angles. every triangle has three angle bisectors, one for each interior angle. 2. properties of angle bisectors:. The angle bisector theorem is concerned with the relative lengths of the two segments that a triangle's side is divided into by a line that bisects the opposite angle. it equates their relative lengths to the relative lengths of the other two sides of the triangle. to bisect an angle means to cut it into two equal parts or angles. say that we wanted to bisect a 50 degree angle, then we.

Comments are closed.