Frontiers Temporal Trends In Cardiovascular Care Insights From The
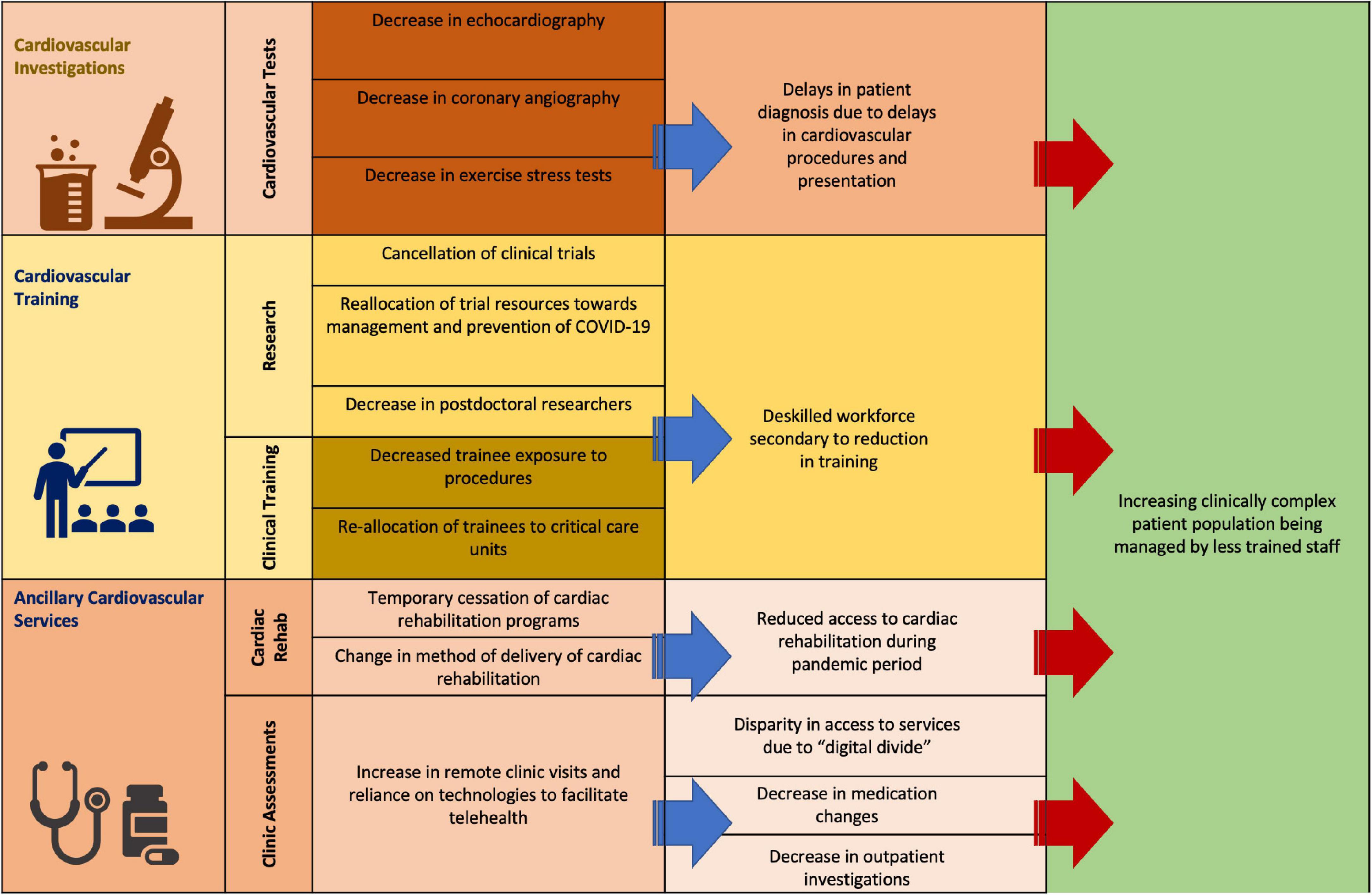
Frontiers Temporal Trends In Cardiovascular Care Insights From The Temporal trends in cardiovascular care: insights from the covid 19 pandemic. matthew kodsi 1* aditya bhat 1,2,3. 1 department of cardiology, blacktown hospital, sydney, nsw, australia. 2 school of public health and community medicine, university of new south wales, sydney, nsw, australia. 3 school of medicine, western sydney university, sydney. This review aims to identify the trends and the resultant impacts of covid . 19 on the anticipated burden and management of cardiovascular disease in the coming years. 10.3389 fcvm.2022.981023. march 2020 (17) and in austria there was a 40% reduction in acs presentations in the last week of march 2020 compared to the first week of march 2020 (18).

Pdf Temporal Trends In Cardiovascular Care Insights From The Covid Abstract. in response to the ongoing covid 19 pandemic, public health care measures have been implemented to limit spread of the contagion and ensure adequate healthcare resource allocation. correlating with these measures are observed changes in the incidence and outcomes of cardiovascular conditions in the absence of covid 19 infection. This raises concerns regarding the current and longer term effects of covid 19 on cardiovascular disease presentations and management, which is an evolving area of study given changing dynamics of the disease and the public health response measures. this review aims to identify the trends and the resultant impacts of covid 19 on the anticipated. The range of initiatives undertaken by local authorities, such as tobacco control interventions, the observed decline in female smoking prevalence , and the significant enhancement of healthcare expenditure—including the upgrading of public hospital facilities and expansion of long term care services —offers valuable insights for. The temporal trends in patient characteristics are presented in table 1. the mean age increased significantly over time (from 75.2 [sd, 12.5] years in 2011–2012 to 76.4 [sd, 13.5] years in 2020–2021, p for trend<0.001; table 1 ).
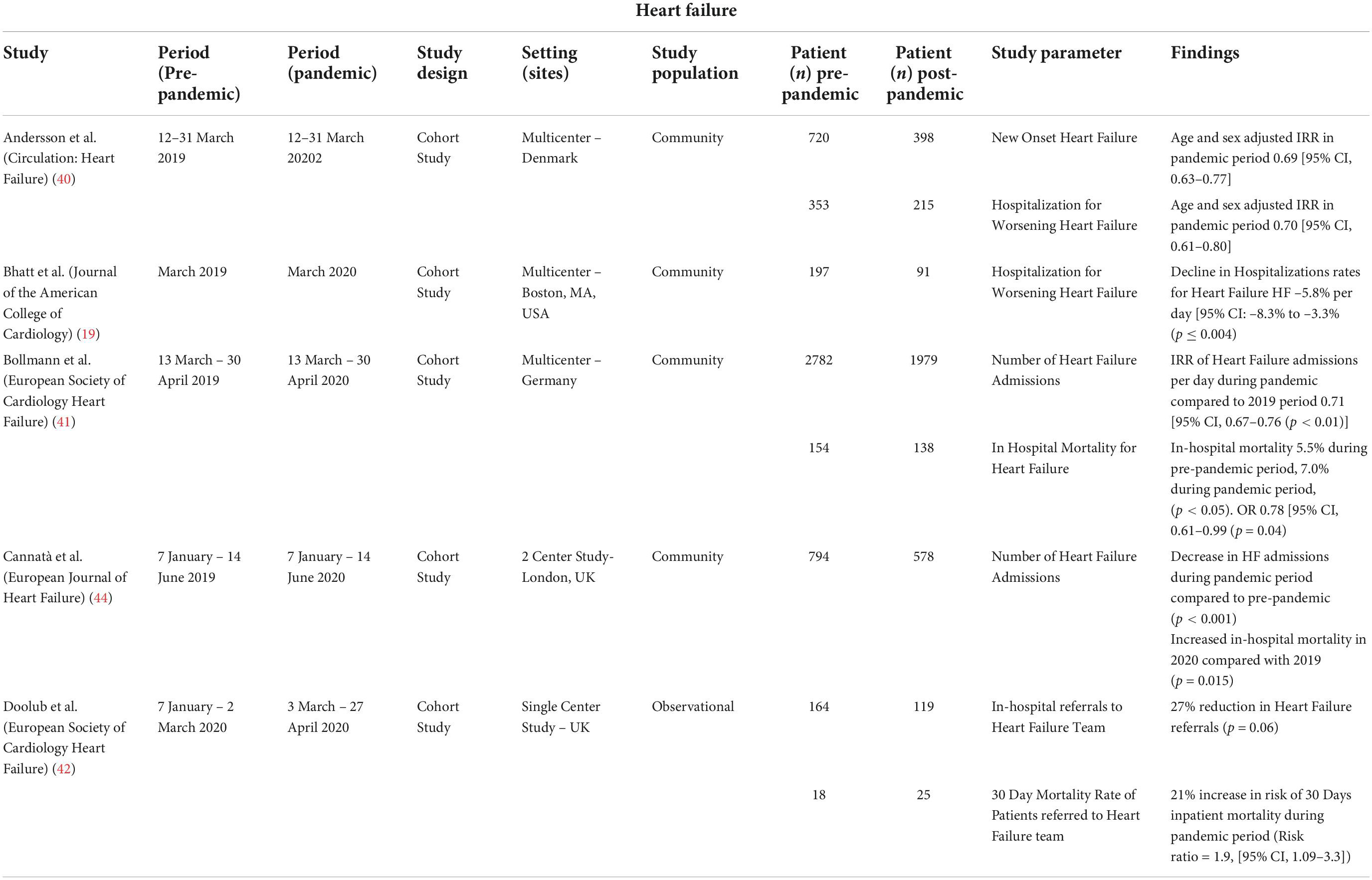
Frontiers Temporal Trends In Cardiovascular Care Insights From The The range of initiatives undertaken by local authorities, such as tobacco control interventions, the observed decline in female smoking prevalence , and the significant enhancement of healthcare expenditure—including the upgrading of public hospital facilities and expansion of long term care services —offers valuable insights for. The temporal trends in patient characteristics are presented in table 1. the mean age increased significantly over time (from 75.2 [sd, 12.5] years in 2011–2012 to 76.4 [sd, 13.5] years in 2020–2021, p for trend<0.001; table 1 ). We also examined disease specific temporal trends by cancer site. ischaemic heart disease (ihd) was the most common cardiovascular cause of death across all cancer types (55.6%), being more common in men (59.8%), older ages, and in those with lung (67.8%) and prostate (58.3%) cancers. Abstract. artificial intelligence (ai) has the potential to transform every facet of cardiovascular practice and research. the exponential rise in technology powered by ai is defining new frontiers in cardiovascular care, with innovations that span novel diagnostic modalities, new digital native biomarkers of disease, and high performing tools evaluating care quality and prognosticating.
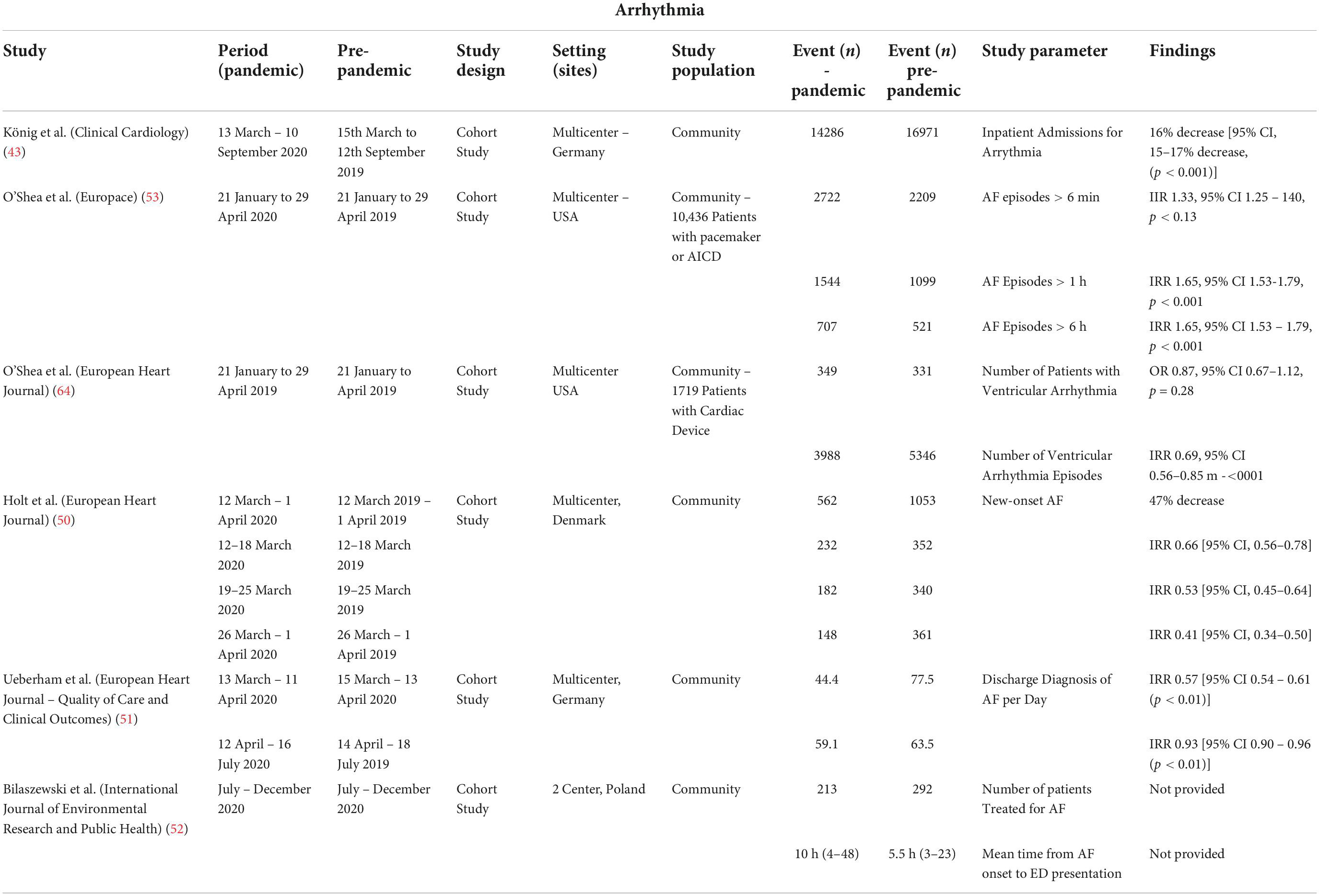
Frontiers Temporal Trends In Cardiovascular Care Insights From The We also examined disease specific temporal trends by cancer site. ischaemic heart disease (ihd) was the most common cardiovascular cause of death across all cancer types (55.6%), being more common in men (59.8%), older ages, and in those with lung (67.8%) and prostate (58.3%) cancers. Abstract. artificial intelligence (ai) has the potential to transform every facet of cardiovascular practice and research. the exponential rise in technology powered by ai is defining new frontiers in cardiovascular care, with innovations that span novel diagnostic modalities, new digital native biomarkers of disease, and high performing tools evaluating care quality and prognosticating.

Comments are closed.