Frontiers Supervised Learning Computer Vision Benchmark For Snake
Frontiers Supervised Learning Computer Vision Benchmark For Snake Citation: durso am, moorthy gk, mohanty sp, bolon i, salathé m and ruiz de castañeda r (2021) supervised learning computer vision benchmark for snake species identification from photographs: implications for herpetology and global health. front. artif. intell. 4:582110. doi: 10.3389 frai.2021.582110. received: 10 july 2020; accepted: 09. Performance of computer vision algorithms depends on the quality of the training data as well as on the learning mechanism. generating realistic and unbiased training and testing data is a major challenge for most computer vision applications, especially for species of animals, which have greater intraclass (inter.
Frontiers Supervised Learning Computer Vision Benchmark For Snake Supervised learning computer vision benchmark for snake species identification from photographs: implications for herpetology and global health andrew m. durso , 1 , 2 , * gokula krishnan moorthy , 3 , * sharada p. mohanty , 4 isabelle bolon , 2 marcel salathé , 4 , 5 and rafael ruiz de castañeda 2. Author=durso andrew m. , moorthy gokula krishnan , mohanty sharada p. , bolon isabelle , salathé marcel , ruiz de castañeda rafael title=supervised learning computer vision benchmark for snake species identification from photographs: implications for herpetology and global health journal=frontiers in artificial intelligence volume=4 year=2021. We trained a computer vision algorithm to identify 45 species of snakes from photos and compared its performance to that of humans. both human and algorithm performance is substantially better. Frontiers in artificial intelligence (apr 2021) . supervised learning computer vision benchmark for snake species identification from photographs: implications for herpetology and global health.
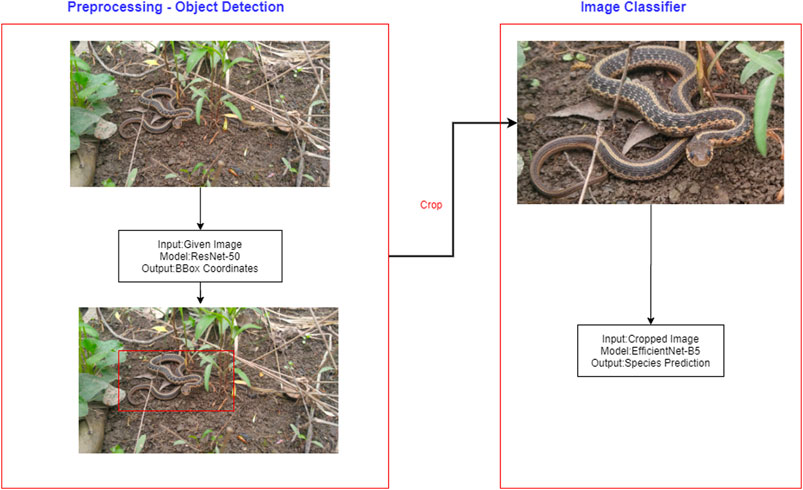
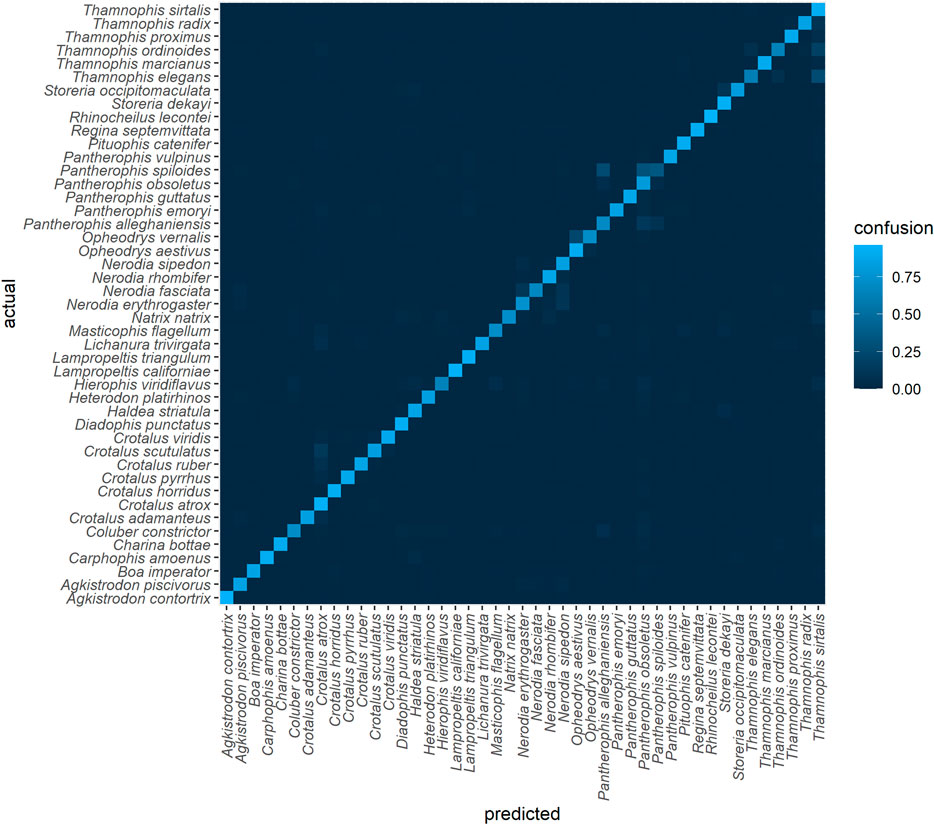
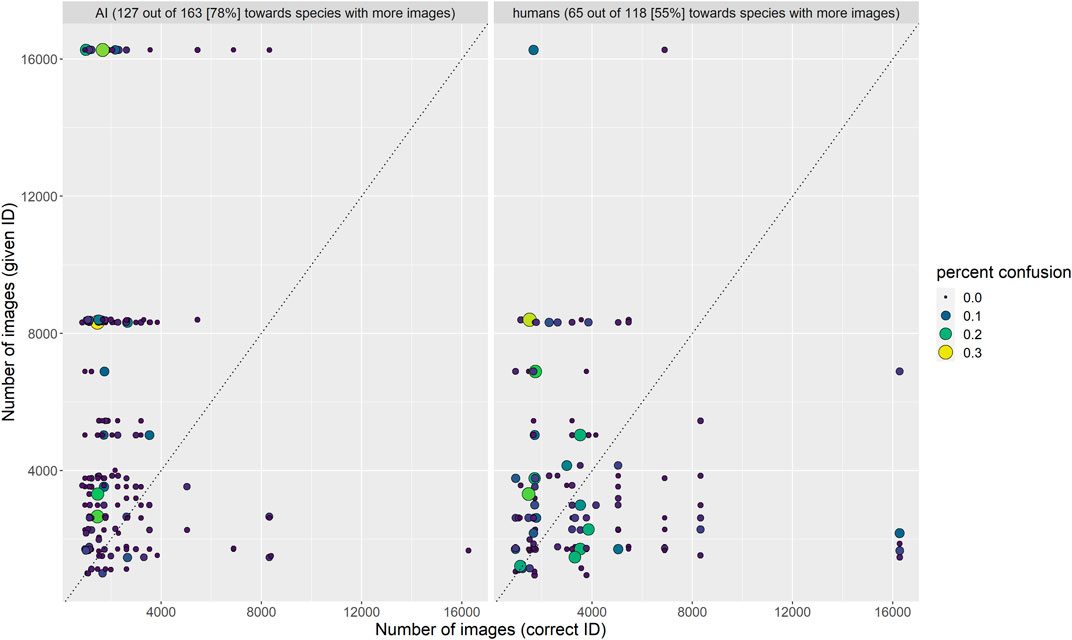
Frontiers Supervised Learning Computer Vision Benchmark For Snake We trained a computer vision algorithm to identify 45 species of snakes from photos and compared its performance to that of humans. both human and algorithm performance is substantially better. Frontiers in artificial intelligence (apr 2021) . supervised learning computer vision benchmark for snake species identification from photographs: implications for herpetology and global health. With future improvement, computer vision could play a larger role in snakebite epidemiology, particularly when combined with information about geographic location and input from human experts. we trained a computer vision algorithm to identify 45 species of snakes from photos and compared its performance to that of humans. both human and algorithm performance is substantially better than. We trained a computer vision algorithm to identify 45 species of snakes from photos and compared its performance to that of humans. both human and algorithm performance is substantially better than randomly guessing (null probability of guessing correctly given 45 classes = 2.2%). some species (e.g., boa constrictor) are routinely identified with ease by both algorithm and humans, whereas.
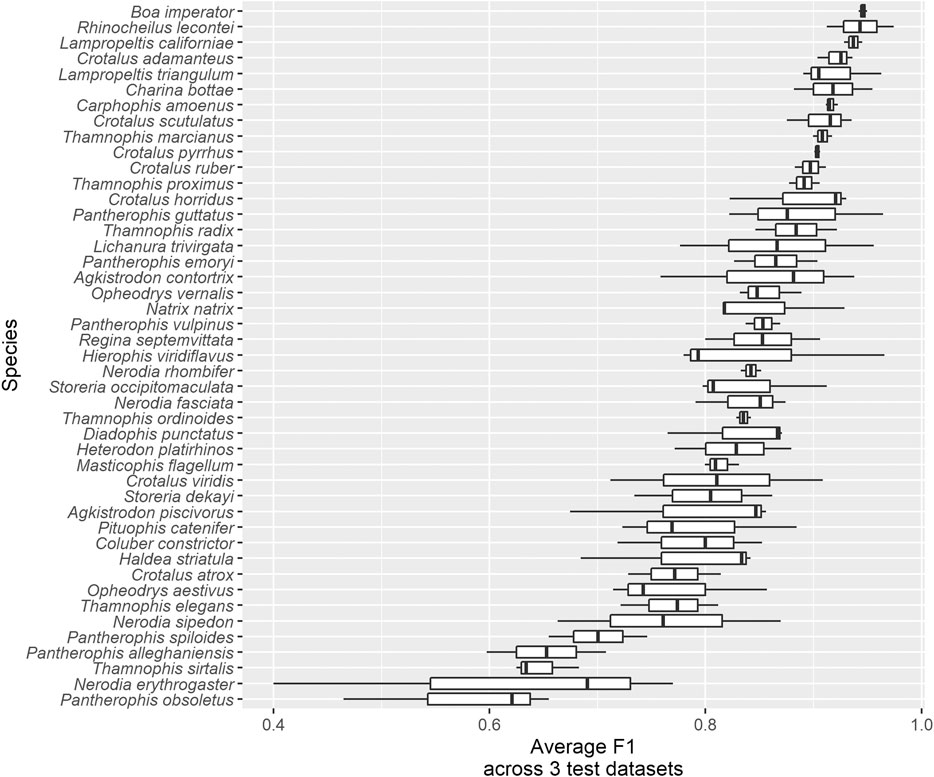
Frontiers Supervised Learning Computer Vision Benchmark For Snake With future improvement, computer vision could play a larger role in snakebite epidemiology, particularly when combined with information about geographic location and input from human experts. we trained a computer vision algorithm to identify 45 species of snakes from photos and compared its performance to that of humans. both human and algorithm performance is substantially better than. We trained a computer vision algorithm to identify 45 species of snakes from photos and compared its performance to that of humans. both human and algorithm performance is substantially better than randomly guessing (null probability of guessing correctly given 45 classes = 2.2%). some species (e.g., boa constrictor) are routinely identified with ease by both algorithm and humans, whereas.

Comments are closed.