Frontiers Pre Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Sudden Cardiac
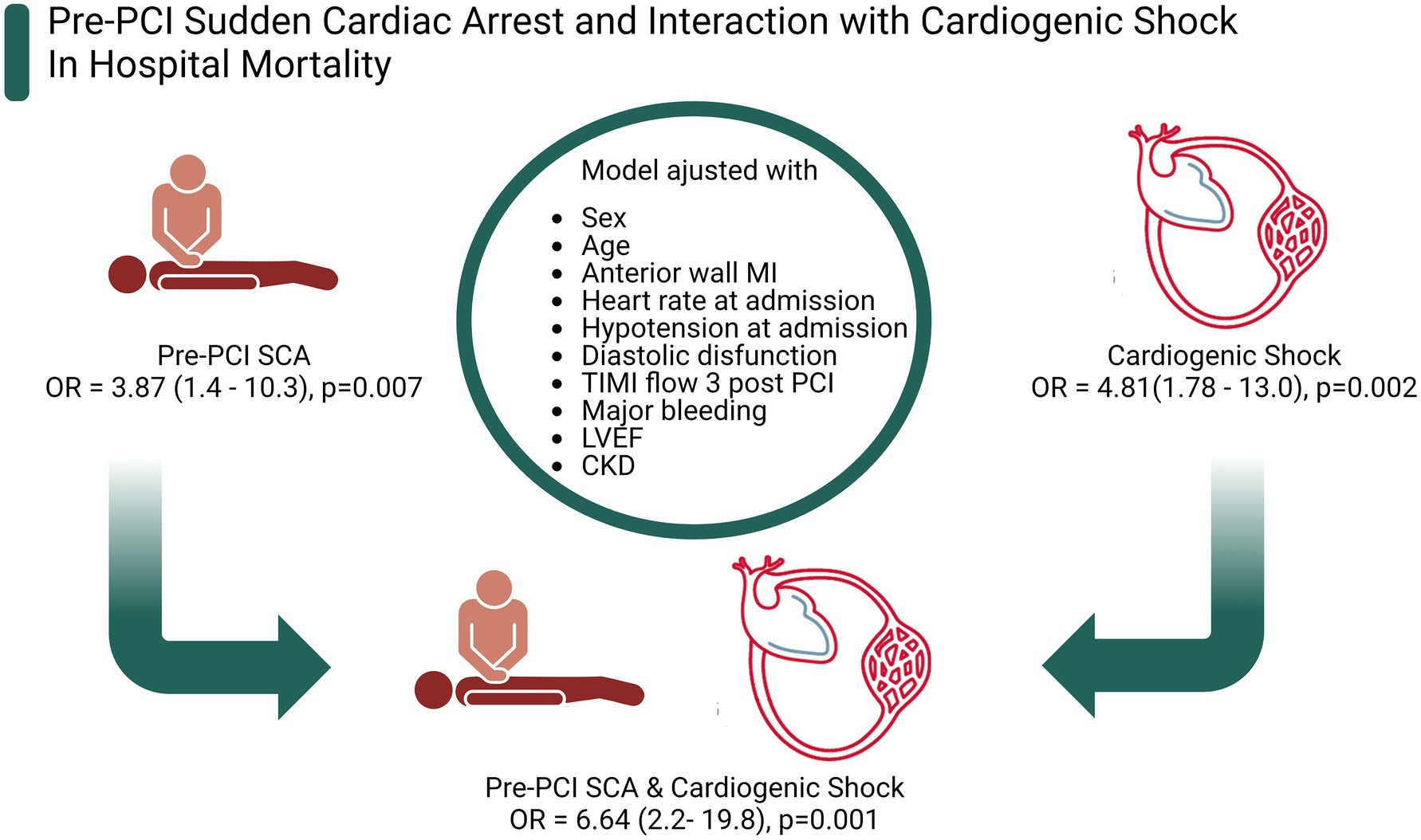
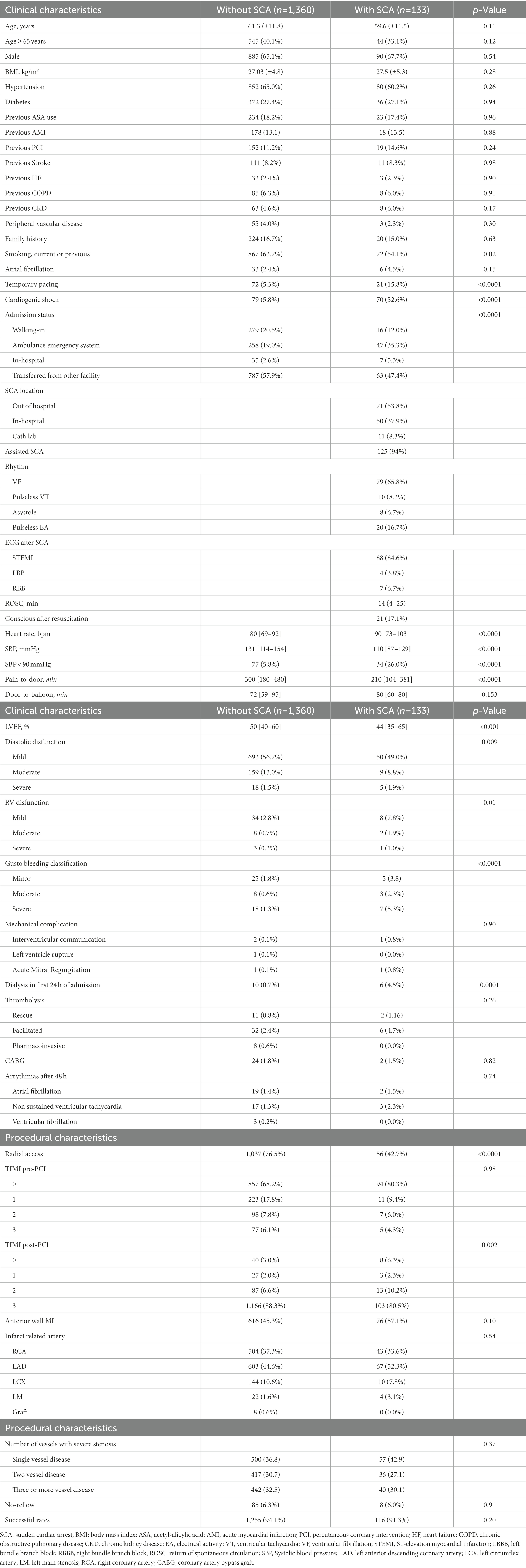
Frontiers Pre Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Sudden Cardiac Pre percutaneous coronary intervention sudden cardiac arrest in st elevation myocardial infarction: incidence, predictors, and related outcomes guilherme pinheiro machado 1,2 * andre luiz theobald 1,2 gustavo neves de araujo 3,4 anderson donelli da silveira 1,2 rodrigo vugman wainstein 1,2 julia fagundes fracasso 5 matheus niches 5 angelo chies. Background: st segment elevation myocardial infarction (stemi) is a frequent cause of sudden cardiac arrest (sca) and early percutaneous coronary intervention (pci) is associated with increased survival. despite constant improvements in sca management, survival remains poor.
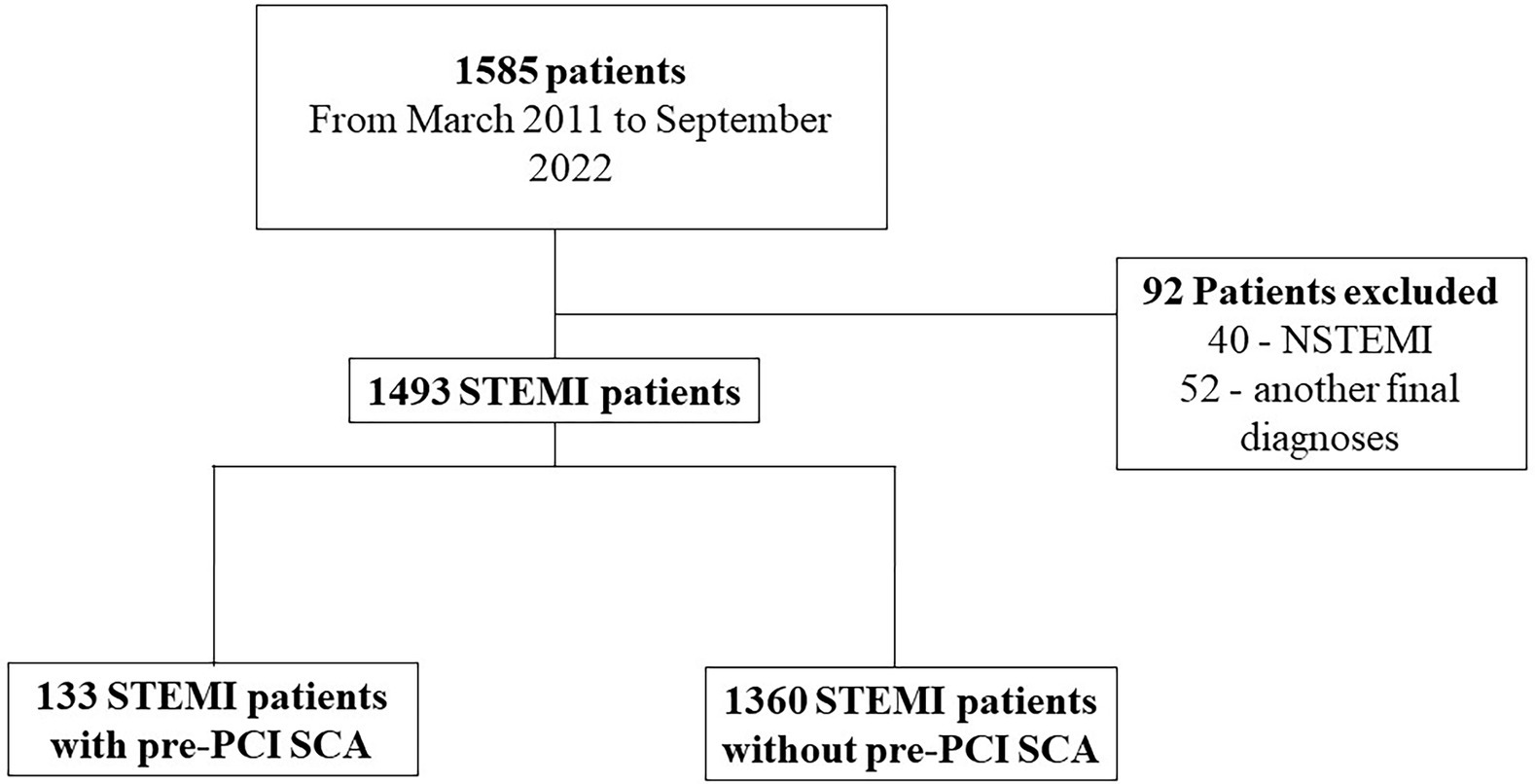
Frontiers Pre Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Sudden Cardiac The incidence of cardiac arrest (ca) during percutaneous coronary intervention (pci) is relatively low, estimated at around 1.5% (1, 2). however, despite a higher likelihood of successful resuscitation compared to other in hospital cardiac arrest (ihca) scenarios , it is still associated with the highest mortality rates (4, 5). Machado g, theobald a, de araujo g, silveira a, wainstein r, fracasso j, niches m, chies a, goncalves s, pimentel m and wainstein m (2023) pre percutaneous coronary intervention sudden cardiac arrest in st elevation myocardial infarction: incidence, predictors, and related outcomes, frontiers in cardiovascular medicine, 10.3389 fcvm.2023. Emergency percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with st elevation myocardial infarction complicated by out of hospital cardiac arrest: early and medium term outcome. am heart j . 2009;157:569.e1–575.e1. doi: 10.1016 j.ahj.2008.10.018. Percutaneous coronary intervention (pci) is widely performed in patients with coronary artery disease (cad). numerous studies have revealed that pci decreases the risk of subsequent myocardial infarction (mi) or urgent revascularization compared with medical therapy alone. 1, 2 revascularization is also an effective treatment for myocardial ischemia, 2 the major cause underlying sudden cardiac.
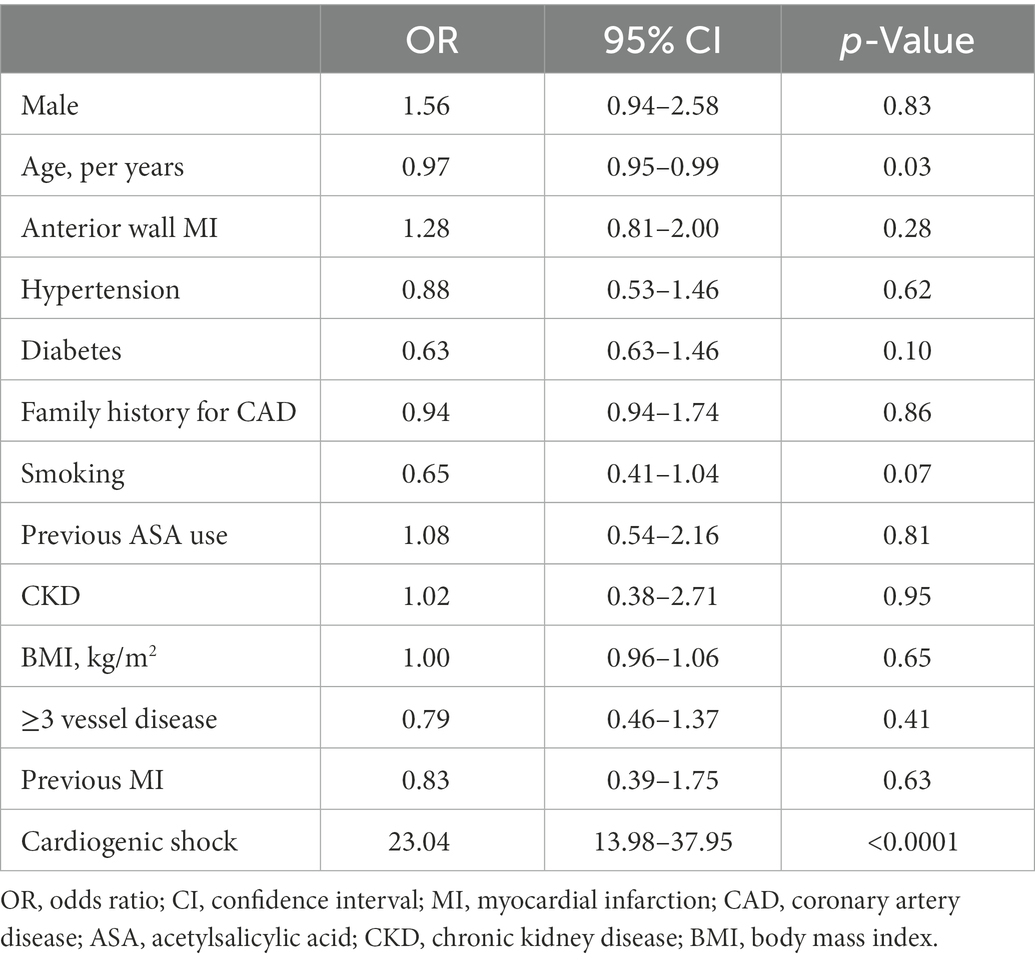
Frontiers Pre Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Sudden Cardiac Emergency percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with st elevation myocardial infarction complicated by out of hospital cardiac arrest: early and medium term outcome. am heart j . 2009;157:569.e1–575.e1. doi: 10.1016 j.ahj.2008.10.018. Percutaneous coronary intervention (pci) is widely performed in patients with coronary artery disease (cad). numerous studies have revealed that pci decreases the risk of subsequent myocardial infarction (mi) or urgent revascularization compared with medical therapy alone. 1, 2 revascularization is also an effective treatment for myocardial ischemia, 2 the major cause underlying sudden cardiac. Ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation (vt vf) are fatal arrhythmias causing cardiac collapse in acute myocardial infarction (ami). vt is a marked sudden cardiac death predictors after adjustment for age, diabetes, and left ventricular ejection fraction (lvef) in ami patients [1, 2]. Out of hospital cardiac arrest (ohca) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. clinical decision making is extremely difficult in this understudied patient population with high prevalence of neurological injury and inexorable shock states. as such, there are uncertain benefits from therapies available in the cardiac catheterization laboratory. fear of futility and public.
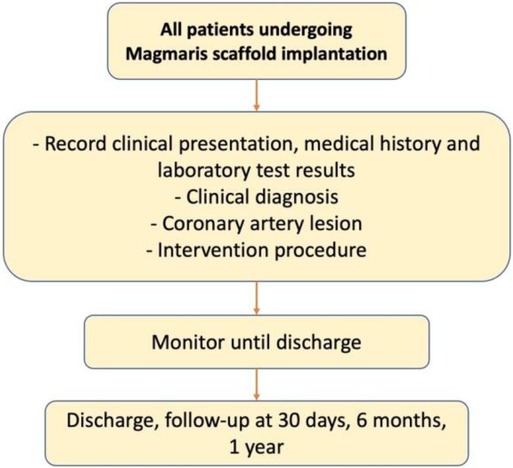
Frontiers Mid Term Safe And Effective Profile Of The Magmaris Ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation (vt vf) are fatal arrhythmias causing cardiac collapse in acute myocardial infarction (ami). vt is a marked sudden cardiac death predictors after adjustment for age, diabetes, and left ventricular ejection fraction (lvef) in ami patients [1, 2]. Out of hospital cardiac arrest (ohca) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. clinical decision making is extremely difficult in this understudied patient population with high prevalence of neurological injury and inexorable shock states. as such, there are uncertain benefits from therapies available in the cardiac catheterization laboratory. fear of futility and public.

Frontiers Pre Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Sudden Cardiac
Frontiers Pre Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Sudden Cardiac

Comments are closed.