Frontiers Mtorc1 As A Regulator Of Mitochondrial Functions And A
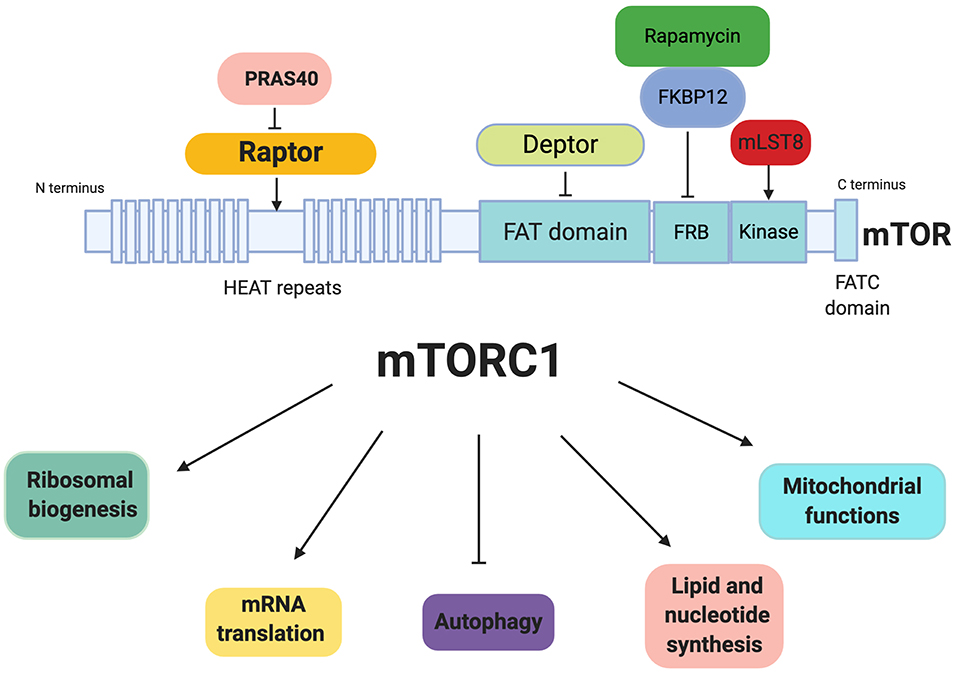
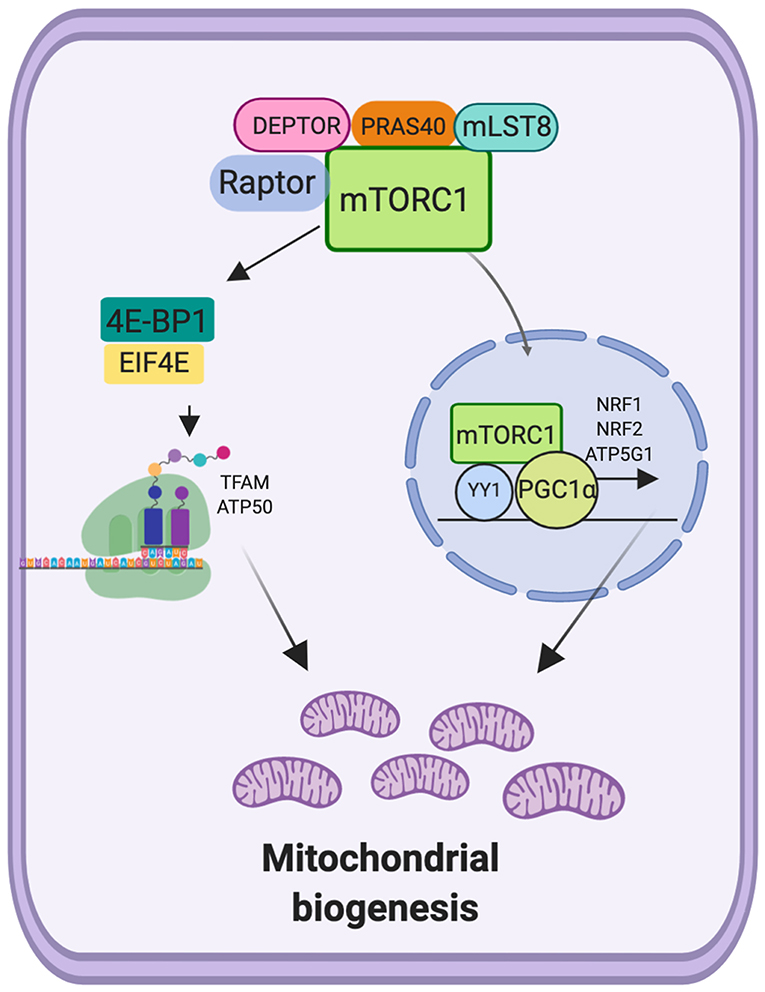
Frontiers Mtorc1 As A Regulator Of Mitochondrial Functions And A Mtorc1 is widely described as an important regulator of cell growth, acting on the regulation of anabolic processes such as the synthesis of proteins, lipids, and the inhibition of autophagy. importantly, mtorc1 is also involved in the regulation of mitochondrial metabolism and mitochondrial functions. Interestingly it has been shown that mtorc1 regulates mitochondrial metabolism, thus representing an important regulator in mitochondrial function. here we present an overview on the role of mtorc1 in the regulation of mitochondrial functions in cancer, considering new evidences showing that mtorc1 regulates the translation of nucleus encoded.
Frontiers Mtorc1 As A Regulator Of Mitochondrial Functions And A Mtorc1 signaling pathway. mtor is an atypical serine threonine specific protein kinase that belongs to the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase related kinases (pikk) family (16). mtor functions as a downstream effector of the pi3k akt signaling pathway in two distinct sets of intracellular complexes, mtorc1 and mtorc2 (3). Figure 2 | mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mtorc1) as a regulator of mitochondrial functions. mtorc1 can be activated by growth factor, and can regulate the mitochondrial biogenesis. Signals and adapting the metabolic activity of the tumor cell. the mammalian mechanistic. target of rapamycin complex 1 (mtorc1) is a master regulator of numerous cellular. processes implicated in. The mammalian mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mtorc1) is a master regulator of numerous cellular processes implicated in proliferation, metabolism, and cell growth. mtorc1 controls cellular metabolism mainly by regulating the translation and transcription of metabolic genes, such as peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ.
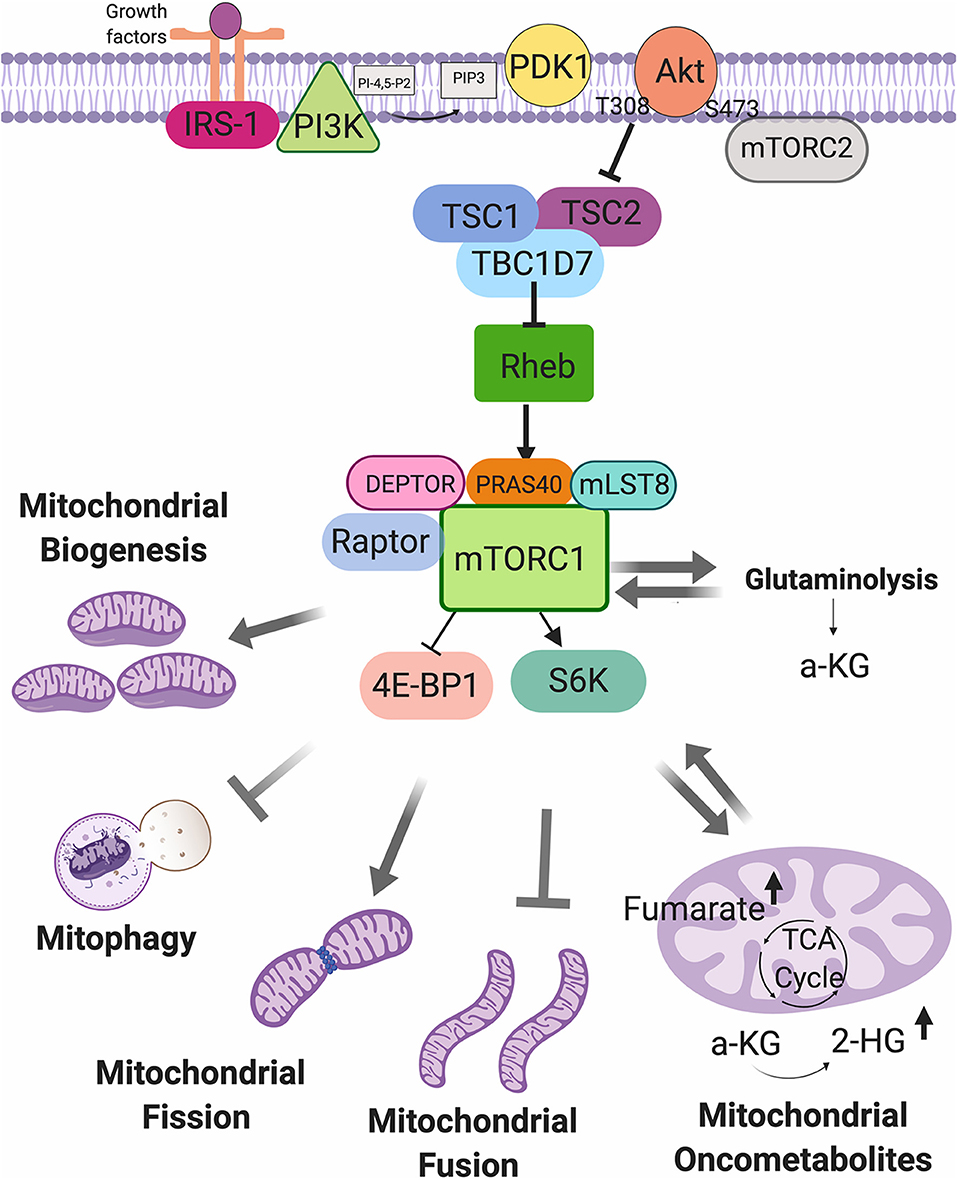
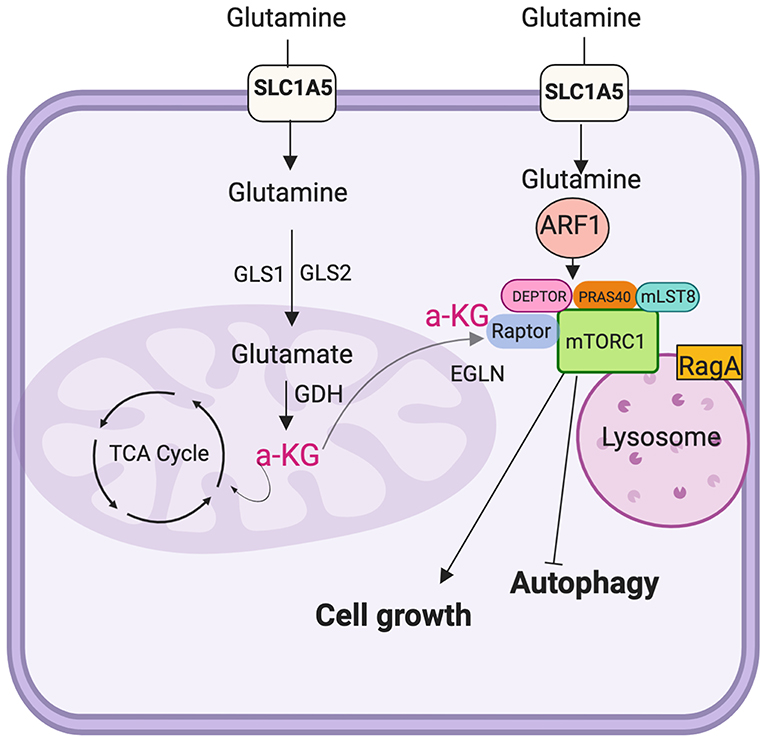
Frontiers Mtorc1 As A Regulator Of Mitochondrial Functions And A Signals and adapting the metabolic activity of the tumor cell. the mammalian mechanistic. target of rapamycin complex 1 (mtorc1) is a master regulator of numerous cellular. processes implicated in. The mammalian mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mtorc1) is a master regulator of numerous cellular processes implicated in proliferation, metabolism, and cell growth. mtorc1 controls cellular metabolism mainly by regulating the translation and transcription of metabolic genes, such as peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ. Figure 4 | glutaminolysis and mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mtorc1) the α ketoglutarate (α kg) produced by glutaminolysis is used for tricarboxilic acid (tca) cycle intermediates replenish, a process known as anaplerosis. once α kg is exported from the mitochondria to the cytosol activates eglns, which in turn triggers mtorc1 activity promoting cell growth and inhibits. We previously demonstrated that placental mtor functions as a positive regulator of amino acid transporter systems a and l (rosario et al., 2013), folate transporters (rosario et al., 2016), and mitochondrial respiration (rosario et al., 2019). however, mtorc1 regulation of other trophoblast functions remains largely unexplored.
Frontiers Mtorc1 As A Regulator Of Mitochondrial Functions And A Figure 4 | glutaminolysis and mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 1 (mtorc1) the α ketoglutarate (α kg) produced by glutaminolysis is used for tricarboxilic acid (tca) cycle intermediates replenish, a process known as anaplerosis. once α kg is exported from the mitochondria to the cytosol activates eglns, which in turn triggers mtorc1 activity promoting cell growth and inhibits. We previously demonstrated that placental mtor functions as a positive regulator of amino acid transporter systems a and l (rosario et al., 2013), folate transporters (rosario et al., 2016), and mitochondrial respiration (rosario et al., 2019). however, mtorc1 regulation of other trophoblast functions remains largely unexplored.

Comments are closed.