Frontiers Clinical Immunological And Molecular Heterogeneity Of 173
Frontiers Clinical Immunological And Molecular Heterogeneity Of 173 Clinical, immunological, and molecular heterogeneity of 173 patients with the phenotype of immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, x linked (ipex) syndrome eleonora gambineri 1,2 * sara ciullini mannurita 1,2 david hagin 3 marina vignoli 1,2 stephanie anover sombke 3 stacey deboer 3 gesmar r. s. segundo 3 eric j. allenspach 3. Torgerson tr (2018) clinical, immunological, and molecular heterogeneity of 173 patients with the phenotype of immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, x linked (ipex) syndrome. front. immunol. 9:2411. doi: 10.3389 fimmu.2018.02411 clinical, immunological, and molecular heterogeneity of 173 patients with the phenotype of immune.
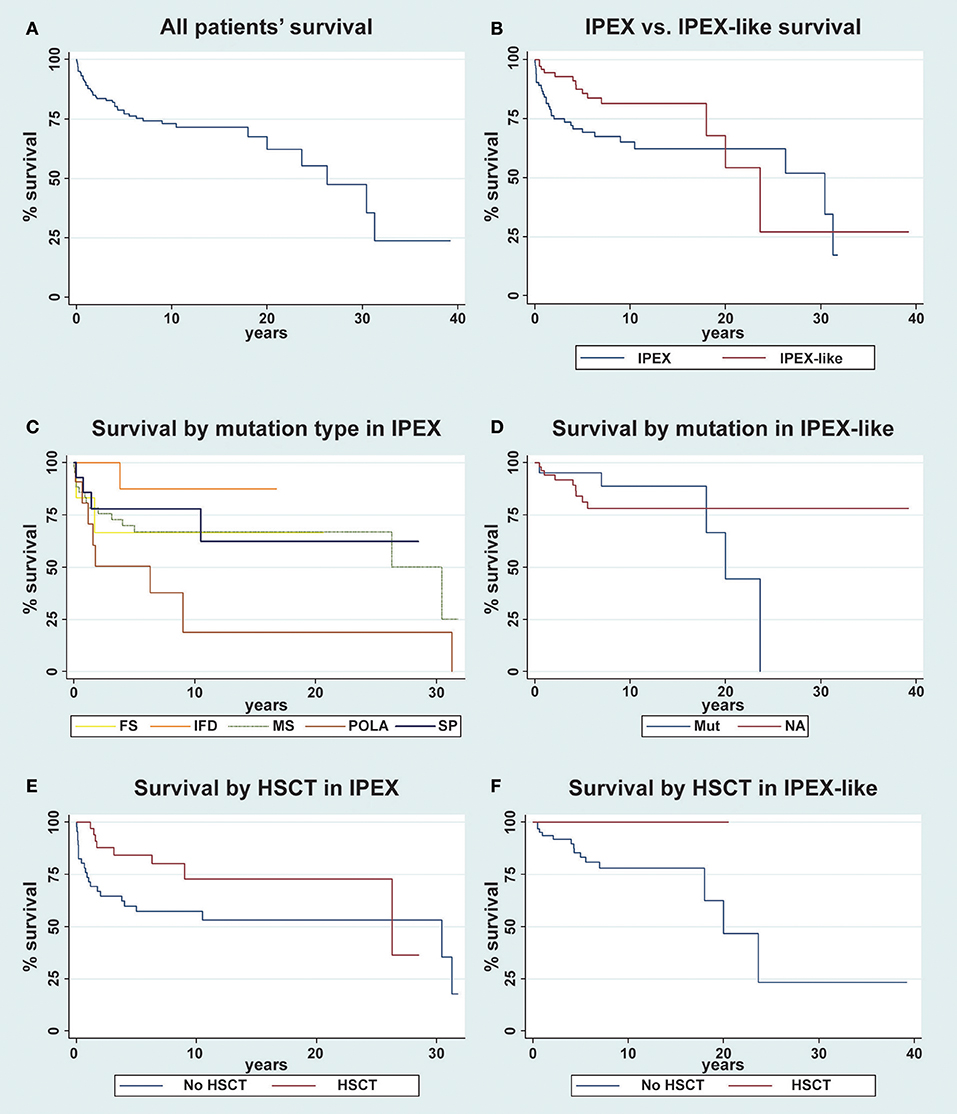
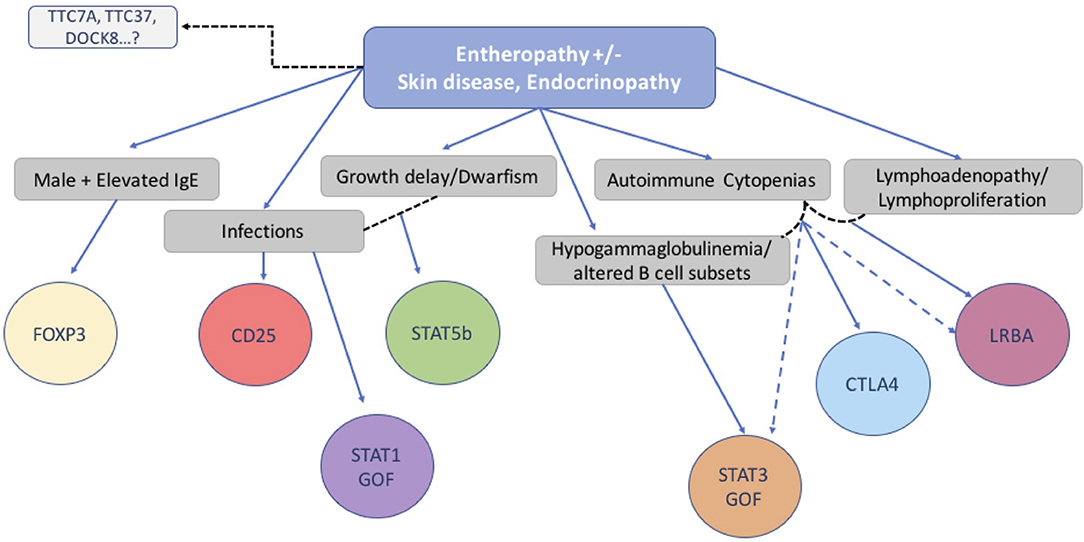
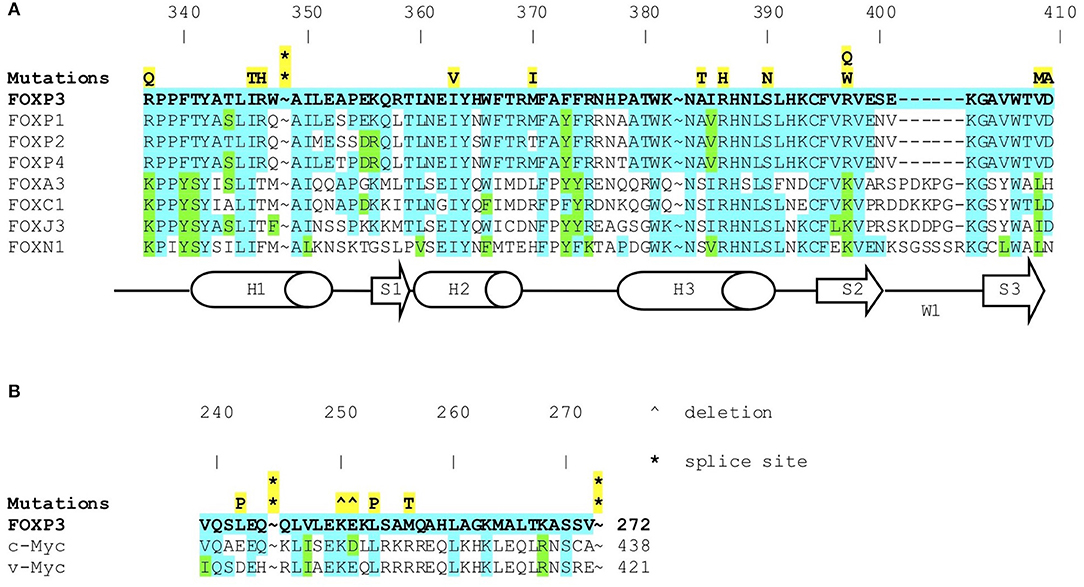
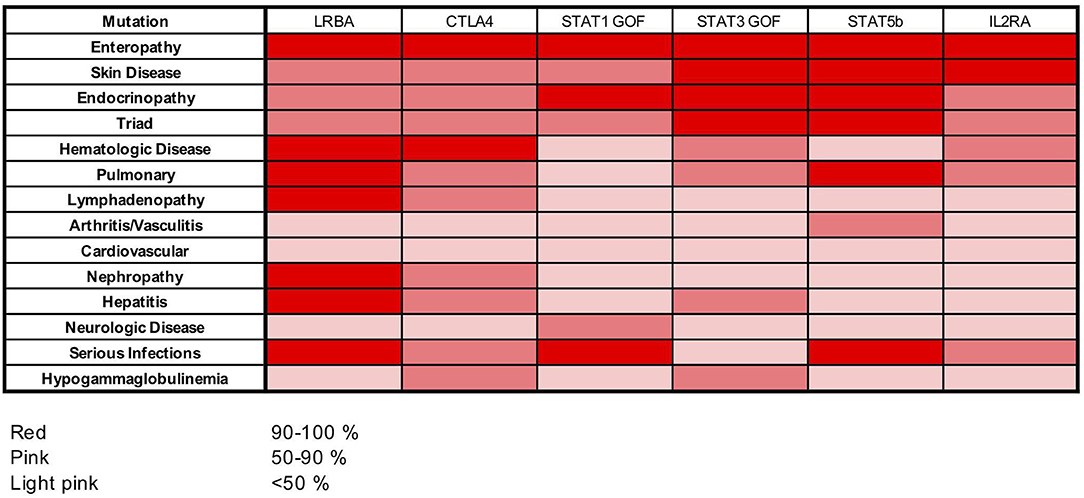
Frontiers Clinical Immunological And Molecular Heterogeneity Of 173 In addition, there has been an increasing number of patients with wild type foxp3 gene and, in some cases, mutations in other immune regulatory genes. objective: to molecularly asses a cohort of 173 patients with the ipex phenotype and to delineate the relationship between the clinical immunologic phenotypes and the genotypes. A comprehensive analysis of the clinical features and molecular bases of ipex and ipex like patients is provided and a simple flow chart is proposed to effectively evaluate such patients and to focus on the most likely molecular diagnosis. background: immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, x linked (ipex) syndrome is a rare recessive disorder caused by mutations in the foxp3. Gambineri e, ciullini mannurita s, hagin d, vignoli m, anover sombke s, deboer s, et al. clinical, immunological, and molecular heterogeneity of 173 patients with the phenotype of immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, x linked (ipex) syndrome. Introduction. inborn errors of immunity (iei) are a wide number of conditions featured by impaired immune response, and their classification is in a continuous update, with the discovery of new clinical entities (1). historically, the warning signs to identify children at risk of iei have been defined according to the susceptibility to multiple.
Frontiers Clinical Immunological And Molecular Heterogeneity Of 173 Gambineri e, ciullini mannurita s, hagin d, vignoli m, anover sombke s, deboer s, et al. clinical, immunological, and molecular heterogeneity of 173 patients with the phenotype of immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, x linked (ipex) syndrome. Introduction. inborn errors of immunity (iei) are a wide number of conditions featured by impaired immune response, and their classification is in a continuous update, with the discovery of new clinical entities (1). historically, the warning signs to identify children at risk of iei have been defined according to the susceptibility to multiple. Abstract. ovarian carcinoma is characterized by heterogeneity at the molecular, cellular and anatomical levels, both spatially and temporally. this heterogeneity affects response to surgery and or. Understanding the role of individual variation in cellular and molecular mechanisms related to rheumatoid arthritis will considerably improve clinical care and patient outcomes. in this review, we discuss the source of pathophysiological heterogeneity derived from genetic, molecular, and cellular heterogeneity and their possible impact on.
Frontiers Clinical Immunological And Molecular Heterogeneity Of 173 Abstract. ovarian carcinoma is characterized by heterogeneity at the molecular, cellular and anatomical levels, both spatially and temporally. this heterogeneity affects response to surgery and or. Understanding the role of individual variation in cellular and molecular mechanisms related to rheumatoid arthritis will considerably improve clinical care and patient outcomes. in this review, we discuss the source of pathophysiological heterogeneity derived from genetic, molecular, and cellular heterogeneity and their possible impact on.

Comments are closed.