Framework To Investigate Lateral Exchange Dynamics Of Water Flows And

Framework To Investigate Lateral Exchange Dynamics Of Water Flows And The aim of this study is to present a framework that provides new ways to characterize the spatio temporal variability of lateral exchanges for water flow and solute transport in a karst conduit. Framework to investigate lateral exchange dynamics of water flows and solute fluxes along a channel reach. the fourbanne karst system: (a) geographical localization, (b) hydrogeological map, (c.
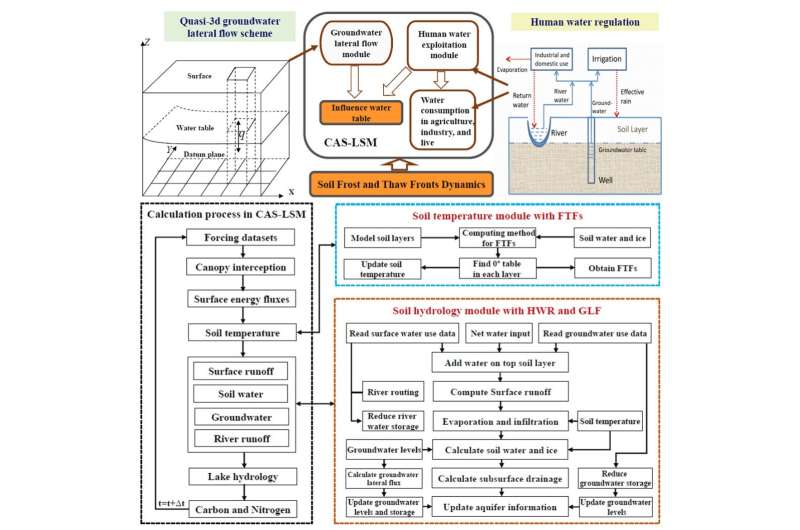
A Land Model With Groundwater Lateral Flow Water Use And Soil Freeze The dashed green curve qa,f lood corresponds to the lateral flow exchanges which are positive for lateral inflows or negative for lateral outflows. 25 figure 2. framework to investigate lateral exchange dynamics of water flows and solute fluxes along a channel reach. 26 figure 3. Framework to investigate lateral exchange dynamics of water flows and solute fluxes along a channel reach. tion (for example for rectangular sections, cq = 5 3cm ). figure 2 gives a graphical representation of this framework whose 7 stages are listed below. Water resources research is an agu hydrology journal publishing original research articles and commentaries on hydrology, water resources, and the social sciences of water. abstract quantifying dynamic hydrologic exchange flows (hefs) within river corridors that experience high frequency flow variations caused by dam regulations is important. A numerical modeling study of the influence of the lateral flow on the estuarine exchange flow was conducted in the north passage of the changjiang estuary. the lateral flows show substantial variabilities within a flood ebb tidal cycle. the strong lateral flow occurring during flood tide is caused primarily by the unique cross shoal flow that induces a strong northward (looking upstream.
Schematic Diagram Of Groundwater Lateral Runoff Exchange Between Hrus Water resources research is an agu hydrology journal publishing original research articles and commentaries on hydrology, water resources, and the social sciences of water. abstract quantifying dynamic hydrologic exchange flows (hefs) within river corridors that experience high frequency flow variations caused by dam regulations is important. A numerical modeling study of the influence of the lateral flow on the estuarine exchange flow was conducted in the north passage of the changjiang estuary. the lateral flows show substantial variabilities within a flood ebb tidal cycle. the strong lateral flow occurring during flood tide is caused primarily by the unique cross shoal flow that induces a strong northward (looking upstream. Comparing the slopes between water flood flow (fig 7b) and mass flood flux (fig 7d), it appears that lateral losses were systematically less mineralized than input water from station s2. 4.3 15 4.3.1 transport dynamics towards the conduit network distribution of model parameters in this section we present the distribution of the model. Hydrologic exchange flows (hefs) play a critical role in river corridor biogeochemical and ecological functions. they are broadly defined as all lateral and vertical water exchanges between the river channel and the adjacent subsurface, including hyporheic exchange, bank storage, and overbank flows (harvey & gooseff, 2015). exchange flows.

Water Flow Velocities In The Active Layer Lateral Advective Transport Comparing the slopes between water flood flow (fig 7b) and mass flood flux (fig 7d), it appears that lateral losses were systematically less mineralized than input water from station s2. 4.3 15 4.3.1 transport dynamics towards the conduit network distribution of model parameters in this section we present the distribution of the model. Hydrologic exchange flows (hefs) play a critical role in river corridor biogeochemical and ecological functions. they are broadly defined as all lateral and vertical water exchanges between the river channel and the adjacent subsurface, including hyporheic exchange, bank storage, and overbank flows (harvey & gooseff, 2015). exchange flows.

Comments are closed.