Food Web The Coral Reef
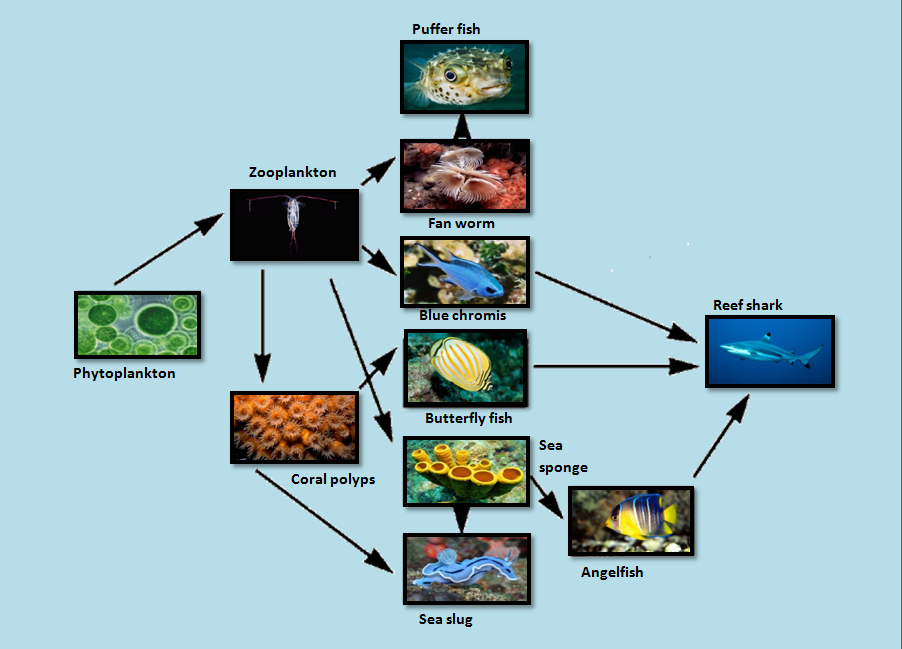
Food Web The Coral Reef Similarly, a single organism can serve more than one role in a food web. for example, a queen conch can be both a consumer and a detritivore, or decomposer. food webs consist of different organism groupings called trophic levels. in this example of a coral reef, there are producers, consumers, and decomposers. producers make up the first. Here is an example of a coral reef food web showing the interdependence of the different organisms in the arctic tundra biome: 1. producers: they form the basis for the entire food web. these are typically photosynthetic organisms that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. the primary producers of coral reefs are mainly seaweed.

Coral Reef Food Web By Stephanie Zarco On Prezi Summary: the coral reef food web. coral reef communities are extremely efficient at acquiring, retaining and recycling nutrients received from multiple sources. the key elements in the coral reef recycling process are (1) the symbiotic relationship between hard corals and their zooxanthellae, and (2) the rapid and effective exchange of. The intricate balance of coral reef food webs, essential for the survival of countless marine species, faces many devastating threats. from the far reaching effects of climate change to localized pollution, human activities are disrupting this delicate ecosystem at an alarming rate. The top predator in the coral reef food web is a blacktip reef shark. what are the decomposers in the coral reef food web illustration? the decomposers are the polychaete worm and the queen conch. how is energy transfered through a food web? energy is transfered through the consumption of organisms. vocabulary carnivore noun organism that eats. Coral reef food webs consist of various trophic levels, including primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers. in these ecosystems, organisms such as phytoplankton serve as primary producers, while zooplankton, corals, sponges, atlantic blue tang, and queen conch act as primary consumers.
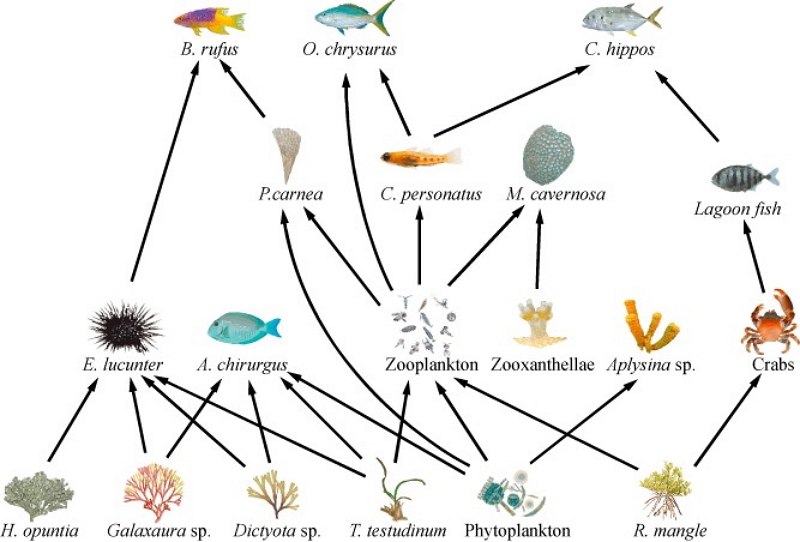
A Guide To Understand Food Web With Diagram Edrawmax Online The top predator in the coral reef food web is a blacktip reef shark. what are the decomposers in the coral reef food web illustration? the decomposers are the polychaete worm and the queen conch. how is energy transfered through a food web? energy is transfered through the consumption of organisms. vocabulary carnivore noun organism that eats. Coral reef food webs consist of various trophic levels, including primary producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers. in these ecosystems, organisms such as phytoplankton serve as primary producers, while zooplankton, corals, sponges, atlantic blue tang, and queen conch act as primary consumers. Coral reefs are the world’s most diverse marine ecosystem, harboring interaction networks of extraordinary complexity. we show that, despite this complexity, global coral reef food webs are governed by a suite of highly consistent energetic pathways, regardless of regional differences in biodiversity. all networks are characterized by species. This is a coral reef food web. see if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. look for: the producers the phytoplankton on the ocean's surface. the primary consumers – the coral, sea turtle, and fish. the secondary consumers – the sharks, anemones, starfish, baracuda, jellyfish, sea.
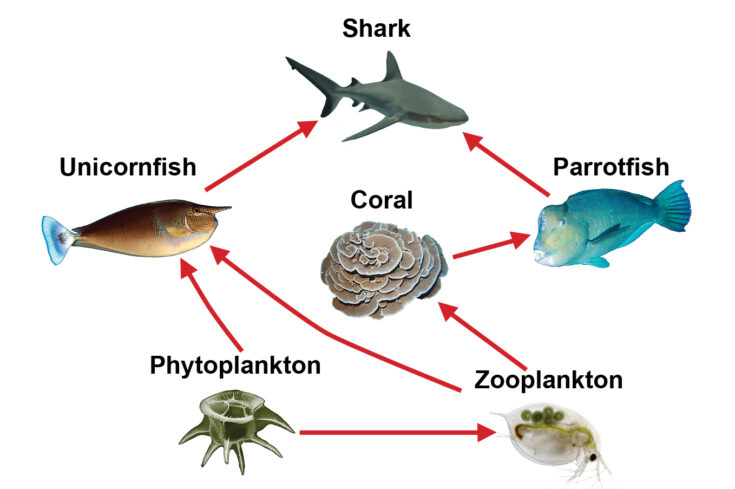
Coral Reef Food Chain Example Jae Everett Coral reefs are the world’s most diverse marine ecosystem, harboring interaction networks of extraordinary complexity. we show that, despite this complexity, global coral reef food webs are governed by a suite of highly consistent energetic pathways, regardless of regional differences in biodiversity. all networks are characterized by species. This is a coral reef food web. see if you can identify all the parts of the food web that make this a functioning, healthy ecosystem. look for: the producers the phytoplankton on the ocean's surface. the primary consumers – the coral, sea turtle, and fish. the secondary consumers – the sharks, anemones, starfish, baracuda, jellyfish, sea.

Coral Reef Food Web
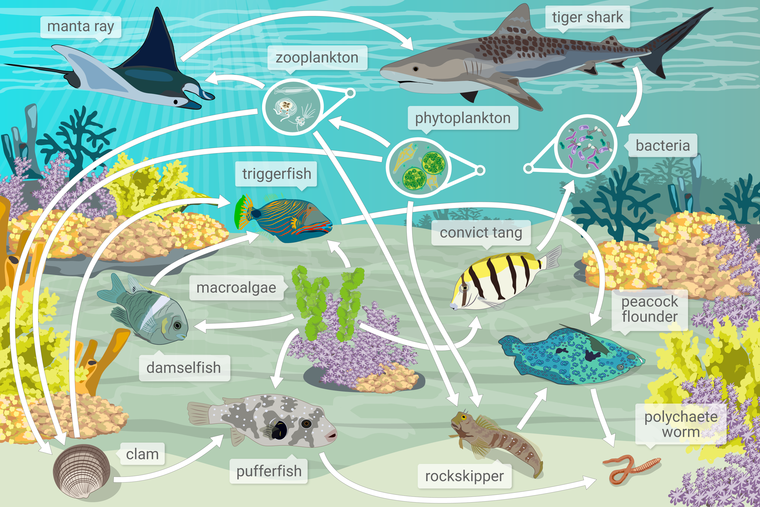
Below Is A Food Web From A Coral Reef Ecosystem Off The Coast Of The

Comments are closed.