Food Web Definition Trophic Levels Types And Example
Trophic Level Definition Examples And Diagram There are different types of food webs based on how it is prepared or what they emphasize. scientists often classify food webs based on the type of ecosystem being presented into the following types: 1. connectance food webs. scientists use connectance food webs to depict the predator prey relationship. A food web shows how the different trophic levels within various food chains interconnect and how energy flows through them within an ecosystem. trophic levels in a food web a lion is an example.
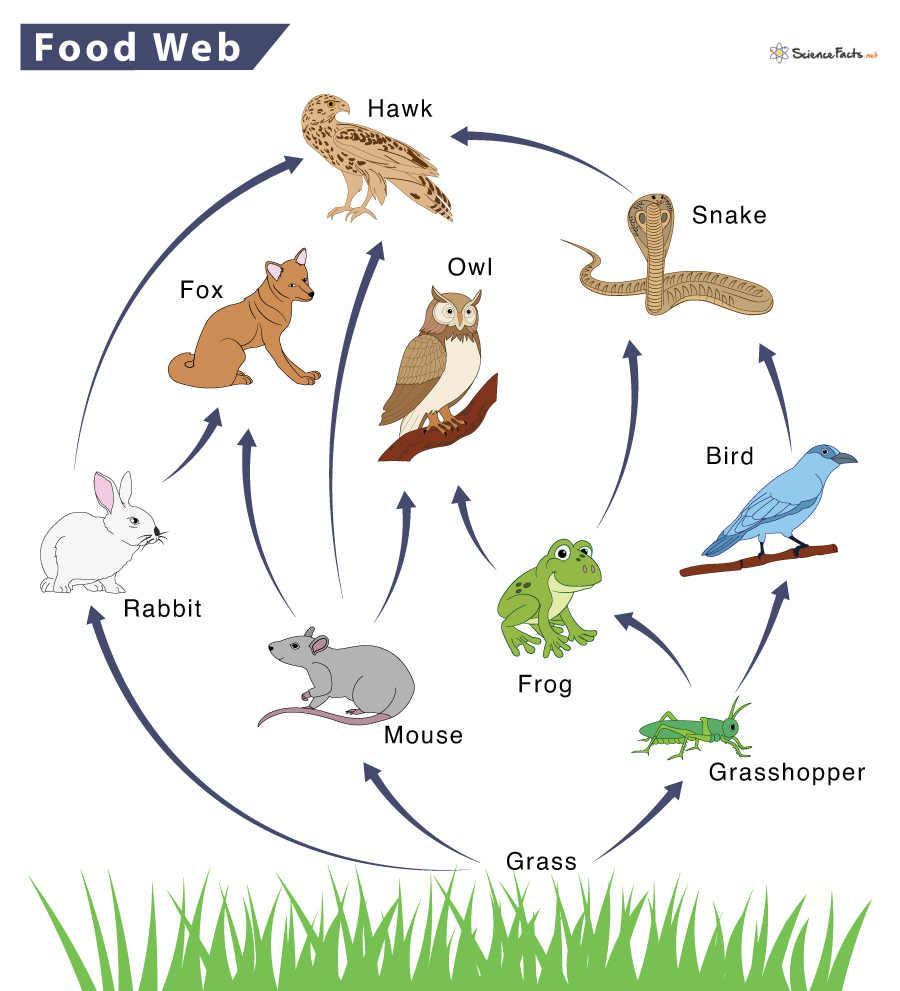
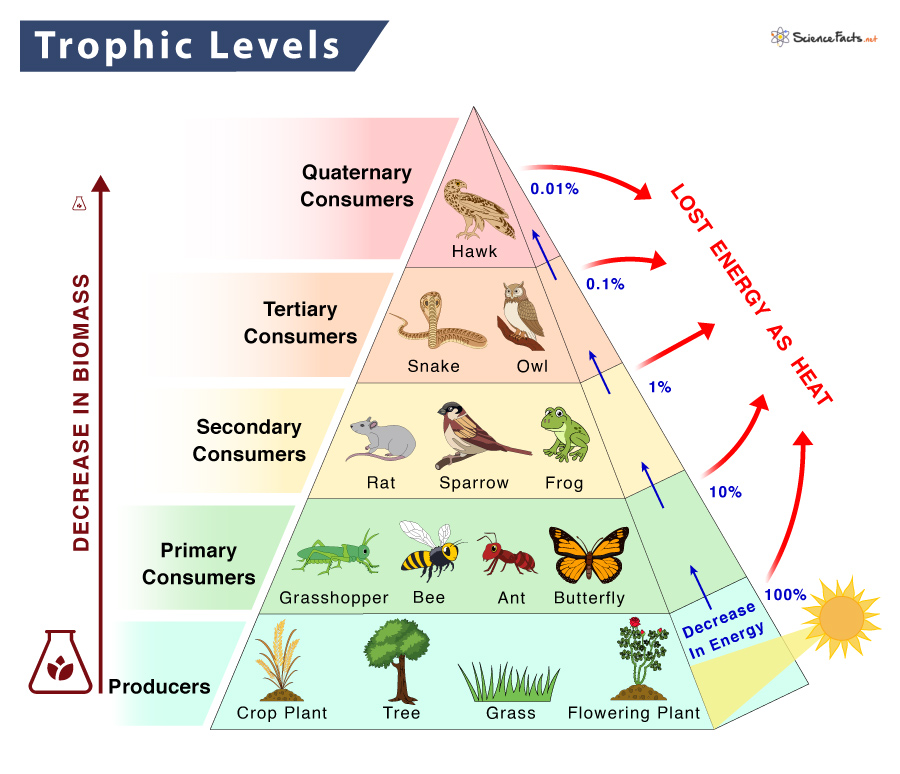
Food Web Definition Trophic Levels Types And Example Food web interactions. although depictions of food webs often show direct single line paths of consumption from producers to consumers on various trophic levels like food chains do, they can also show the ways in which some organisms diverge from these patterns. for example, larger carnivores and omnivores whose diets are not limited to a few. However, some types of materials, especially toxic chemicals, increase with each trophic level in the food web. these chemicals usually collect in the fat of animals. when an herbivore eats a plant or other autotroph that is covered in pesticides , for example, those pesticides are stored in the animal’s fat . The trophic levels refer to the position of a group of organisms in the food chain, food web, or ecological pyramid based on their feeding pattern. they are shown in a series or a succession to represent energy flow from one tropic level to another. the position of the trophic level depends upon the number of steps the organism takes from the. A trophic level is the group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain. there are five main trophic levels within a food chain, each of which differ in their nutritional relationship with the primary energy source. the primary energy source in any ecosystem is the sun (although there are exceptions in deep sea.

Ecosystem Trophic Levels Food Chains Interactions Britannica The trophic levels refer to the position of a group of organisms in the food chain, food web, or ecological pyramid based on their feeding pattern. they are shown in a series or a succession to represent energy flow from one tropic level to another. the position of the trophic level depends upon the number of steps the organism takes from the. A trophic level is the group of organisms within an ecosystem which occupy the same level in a food chain. there are five main trophic levels within a food chain, each of which differ in their nutritional relationship with the primary energy source. the primary energy source in any ecosystem is the sun (although there are exceptions in deep sea. The structure of food webs suggests that productivity and abundance of populations at any given trophic level are controlled by the productivity and abundance of populations in the trophic level. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.

Food Chain Trophic Levels And Flow Of Energy In Ecosystem Online The structure of food webs suggests that productivity and abundance of populations at any given trophic level are controlled by the productivity and abundance of populations in the trophic level. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.

Trophic Level Definition Examples Facts Britannica

Comments are closed.