Food Web Definition Examples Expii
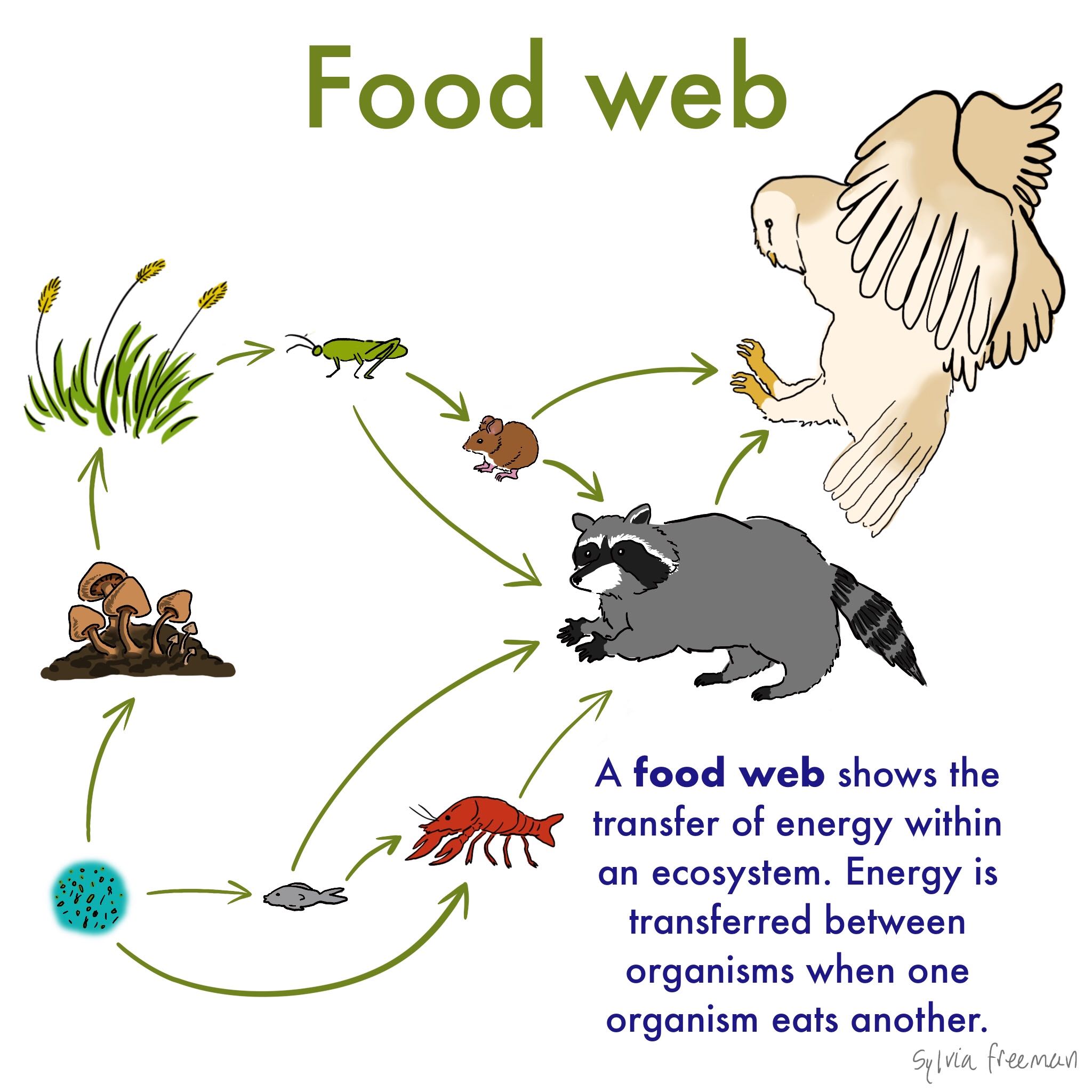
Food Web Definition Examples Expii Food web : the interaction of all the food chains in an ecosystem. producer : organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. consumer : organisms that consume other organisms for energy. decomposer : organisms, like bacteria and fungi, that break down waste and dead organic matter. report. Food chain : how energy passes through an ecosystem through organisms eating and being eaten. producer : organisms that produce their own food through photosynthesis or chemosynthesis. consumer : organisms that consume other organisms for energy. decomposer : organisms that break down waste and dead matter. report.

Food Web Definition Examples Expii Definition, types, and examples. a food web is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular environment. the simplest explanation. Energy flow food webs. energy flow food webs depict the relationship between organisms by measuring and showing the energy flux between organisms. 4. fossil food webs. in fossil food webs, the relationship between organisms is established based on fossil records. 5. functional food webs. Food chain. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. food webs also demonstrate that most. The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that link an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. there are different kinds of consumer–resource interactions that can be roughly divided into herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism.
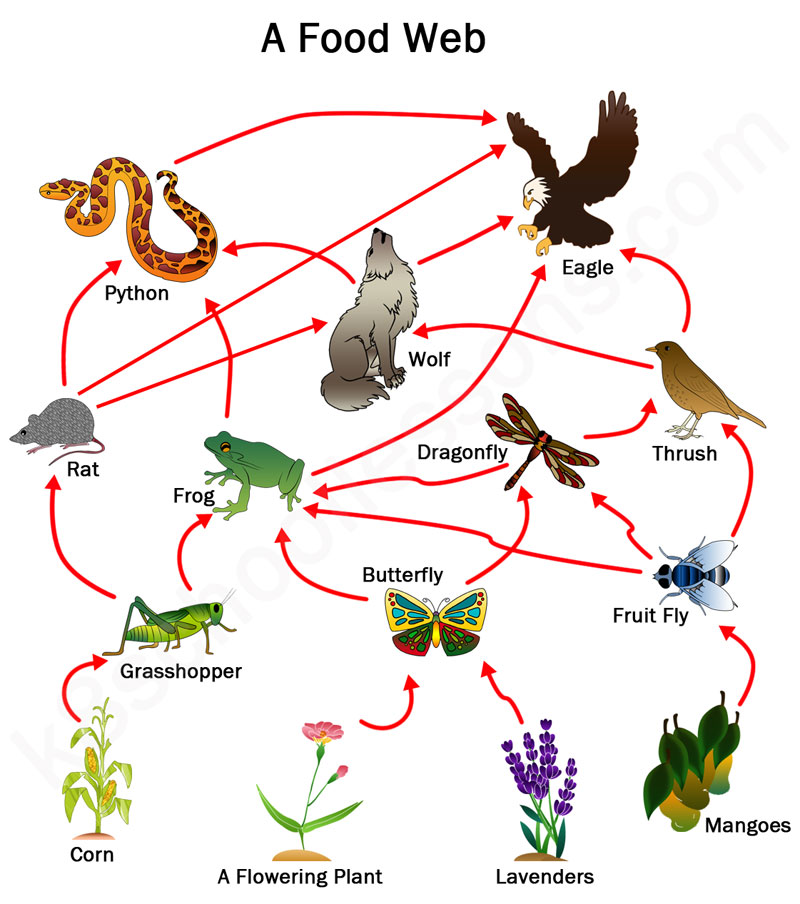
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs Food chain. food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. food webs also demonstrate that most. The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that link an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. there are different kinds of consumer–resource interactions that can be roughly divided into herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism. Definition of food web. the idea of a food web, which used to be called a food cycle, is usually given to charles elton, who first wrote about it in his 1927 book animal ecology. people think of him as one of the people who started modern ecology, and his book is an important one. in this book, he also talked about important ecological ideas. A food web is a visual way to show what the organisms in a habitat eat. it is a diagram that illustrates how food chains are connected and form an ecosystem because most species eat more than just one kind of food. a food web is usually divided into three levels, also called trophic levels: producers, consumers, and decomposers.

Food Web Explained With Examples Definition of food web. the idea of a food web, which used to be called a food cycle, is usually given to charles elton, who first wrote about it in his 1927 book animal ecology. people think of him as one of the people who started modern ecology, and his book is an important one. in this book, he also talked about important ecological ideas. A food web is a visual way to show what the organisms in a habitat eat. it is a diagram that illustrates how food chains are connected and form an ecosystem because most species eat more than just one kind of food. a food web is usually divided into three levels, also called trophic levels: producers, consumers, and decomposers.

Comments are closed.