Food Supply And Demand Note S Represents Food Supply D Represents

Food Supply And Demand Note S Represents Food Supply D Represents For a good that is taxed, the area on the relevant supply and demand graph that represents government’s tax revenue is a answers:a. triangle. b. rectangle. c. trapezoid. d. none of the above is correct; government's tax revenue is the area between the supply and demand curves, above the horizontal axis, and below the effective price to. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like below are the supply and demand equations for blenders in a certain market. in these equations, p represents price, d represents demand, and s represents supply. what is p at the point of equilibrium, to the nearest tenth? a. 56.0 b. 43.3 c. 37.4 d. 36.7, using the above supply demand graph, what is the price at the point of.

A Simplifi Ed Schematic Description Of The Food Supply Demand System Download scientific diagram | food supply and demand note: s represents food supply, d represents food demand, p represents food prices and q represents quantity of food. from publication. The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied. it is determined by the intersection of the demand and supply curves. a surplus exists if the quantity of a good or service supplied exceeds the quantity demanded at the current price; it causes downward pressure on price. Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the accompanying supply and demand graph represents a hypothetical market for spaghetti pasta. demonstrate how an increase in the price of penne, a different type of pasta, and a decrease in the price of meatballs will affect the supply and demand of spaghetti pasta. assume that producers of spaghetti pasta do not also produce. Step 3. it is important to remember that in step 2, the only thing to change was the supply or demand. therefore, coming into step 3, the price is still equal to the initial equilibrium price. since either supply or demand changed, the market is in a state of disequilibrium. thus, there is either a surplus or shortage.
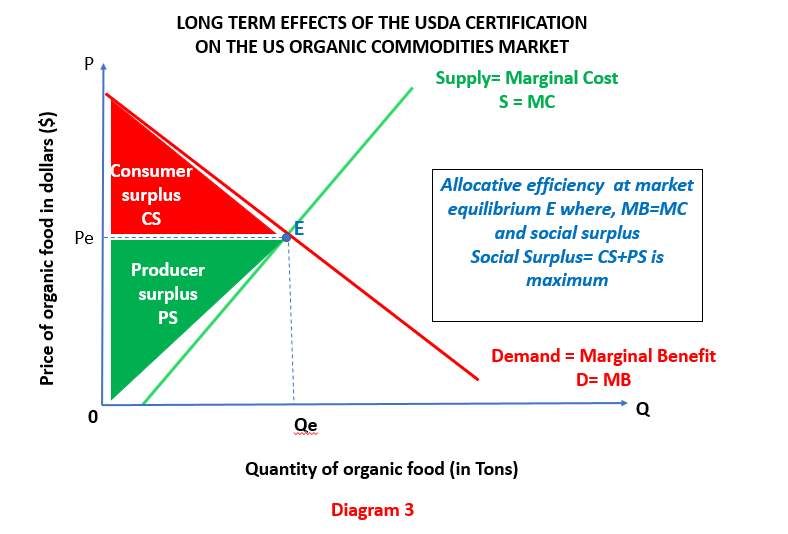
Demand And Supply Of Organic Foods Study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like the accompanying supply and demand graph represents a hypothetical market for spaghetti pasta. demonstrate how an increase in the price of penne, a different type of pasta, and a decrease in the price of meatballs will affect the supply and demand of spaghetti pasta. assume that producers of spaghetti pasta do not also produce. Step 3. it is important to remember that in step 2, the only thing to change was the supply or demand. therefore, coming into step 3, the price is still equal to the initial equilibrium price. since either supply or demand changed, the market is in a state of disequilibrium. thus, there is either a surplus or shortage. Together, demand and supply determine the price and the quantity that will be bought and sold in a market. figure 3.4 illustrates the interaction of demand and supply in the market for gasoline. the demand curve (d) is identical to figure 3.2. the supply curve (s) is identical to figure 3.3. table 3.3 contains the same information in tabular form. In this case, the decrease in income would lead to a lower quantity of cars demanded at every given price, and the original demand curve d 0 would shift left to d 2. the shift from d 0 to d 2 represents such a decrease in demand: at any given price level, the quantity demanded is now lower. in this example, a price of $20,000 means 18 million.

Index 14 Notes 44 I Food Supply And Demand Explanation Statistics Together, demand and supply determine the price and the quantity that will be bought and sold in a market. figure 3.4 illustrates the interaction of demand and supply in the market for gasoline. the demand curve (d) is identical to figure 3.2. the supply curve (s) is identical to figure 3.3. table 3.3 contains the same information in tabular form. In this case, the decrease in income would lead to a lower quantity of cars demanded at every given price, and the original demand curve d 0 would shift left to d 2. the shift from d 0 to d 2 represents such a decrease in demand: at any given price level, the quantity demanded is now lower. in this example, a price of $20,000 means 18 million.

Comments are closed.