Food Safety Hazards 1 Biological Hazards

Biological Hazards In Food Processing Claris Mccreary Biological hazards refer to living organisms that can contaminate food and cause negative health effects on consumers. examples of biological hazards include viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. simple food handling practices, such as proper handwashing and strict monitoring, significantly contribute to controlling biological hazards. Haccp is a management system in which food safety is addressed through the analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production, procurement and handling.

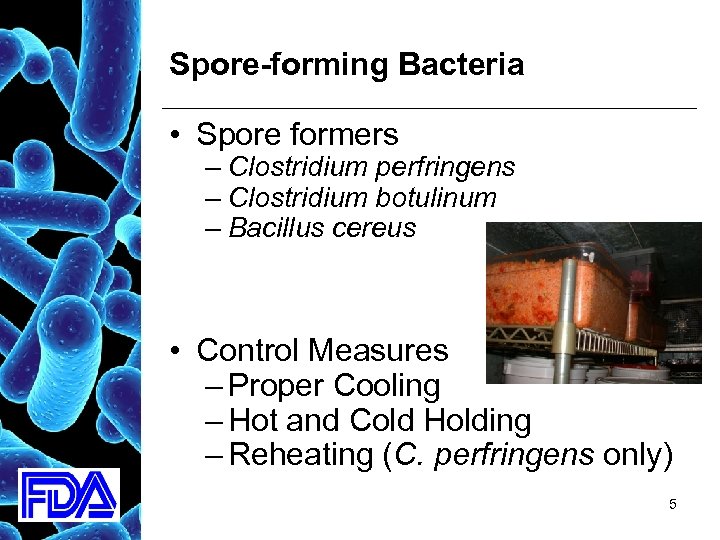
Introduction To Biological Food Hazards Biological. biological hazards are microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi that can cause foodborne illnesses. these pathogens can contaminate food at any point during production, processing, distribution, and preparation, and are often invisible to the naked eye. common biological hazards include salmonella, escherichia. Biological hazards in food, including bacteria and the toxins they produce, viruses, fungi, and parasites, can cause severe health complications. biofilms resist sanitizing, enhancing the ability of pathogens to contaminate food products. food safety management systems like haccp are essential for monitoring and controlling food safety hazards. It is useful to first understand what is a food safety hazard. a food hazard can be defined as being any biological, chemical or physical agent, found in food, that has the potential to cause harm, injury or illness. food safety hazards may occur naturally, be unintentionally introduced or intentionally introduced. Food hazard types. food that contains hazards can lead to foodborne illnesses. the three types of hazards that make food unsafe are biological, chemical, and physical. these hazards can contaminate food or food contact surfaces at any time throughout the flow of food — from the point of receiving to service — and are usually unintentional.

Food Safety Hazards 1 Biological Hazards It is useful to first understand what is a food safety hazard. a food hazard can be defined as being any biological, chemical or physical agent, found in food, that has the potential to cause harm, injury or illness. food safety hazards may occur naturally, be unintentionally introduced or intentionally introduced. Food hazard types. food that contains hazards can lead to foodborne illnesses. the three types of hazards that make food unsafe are biological, chemical, and physical. these hazards can contaminate food or food contact surfaces at any time throughout the flow of food — from the point of receiving to service — and are usually unintentional. The 5 main types of food hazards are: 1. biological hazards: these are microorganisms that can cause foodborne illnesses. examples include bacterias such as salmonella, listeria, and e coli, viruses, parasites, as well as molds and fungi. Haccp (hazard analysis critical control point) is defined as a management system in which food safety is addressed through the analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production, procurement and handling, to manufacturing, distribution and consumption of the finished product. the goal of haccp is to prevent and reduce the occurrence of food safety.

Food Hazards Definition Types Of Food Hazards Physical Chemical The 5 main types of food hazards are: 1. biological hazards: these are microorganisms that can cause foodborne illnesses. examples include bacterias such as salmonella, listeria, and e coli, viruses, parasites, as well as molds and fungi. Haccp (hazard analysis critical control point) is defined as a management system in which food safety is addressed through the analysis and control of biological, chemical, and physical hazards from raw material production, procurement and handling, to manufacturing, distribution and consumption of the finished product. the goal of haccp is to prevent and reduce the occurrence of food safety.

Ppt Module 1 Understanding Hazards Associated With Foods Powerpoint
Food Safety Hazards 1 Biological Hazards

Comments are closed.