Food Chains Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary
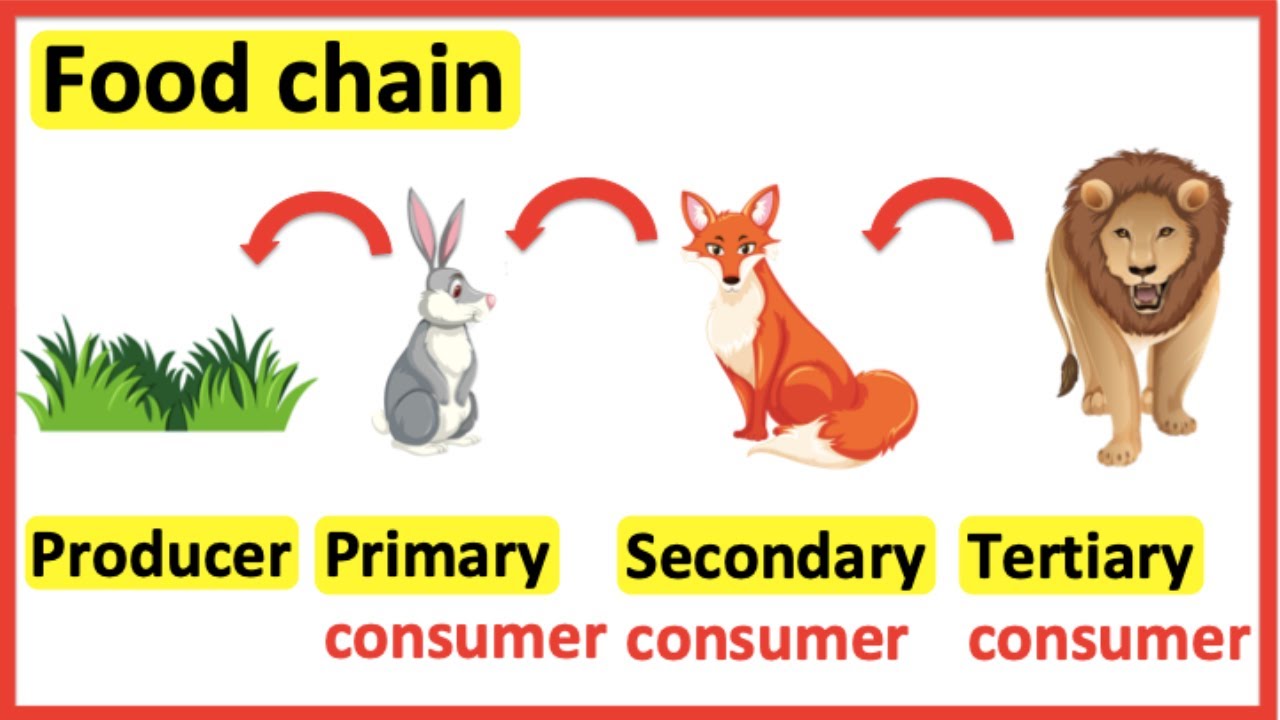
Food Chains Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. as every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web. The first consumer in the chain is also called the primary consumer. the next one is the secondary consumer. the producer in the food chain always goes at the bottom of the pyramid of numbers.
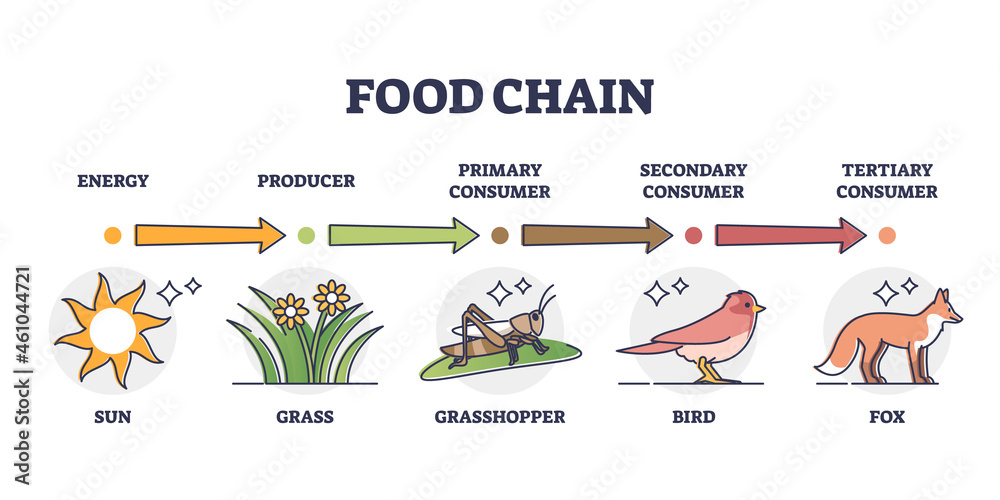
Vettoriale Stock Food Chain And Animal Classification By Eating Type Secondary consumers are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers. tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{2. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. Higher level consumers include secondary consumers (third trophic level), which are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers, and tertiary consumers (fourth trophic level), which are carnivores that eat other carnivores. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{g}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the.

This Is A Food Web Showing Primary Secondary And Tertiary Consumers A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and. Higher level consumers include secondary consumers (third trophic level), which are usually carnivores that eat the primary consumers, and tertiary consumers (fourth trophic level), which are carnivores that eat other carnivores. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{g}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the. Noun. aquatic animal that strains nutrients from water. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. A primary consumer eats a producer. the rabbit is the primary consumer in the example food chain. this is in turn eaten by a secondary consumer, which is the fox. after this might be a.

Comments are closed.