Food Chain Vs Food Web As Ecosystem Feeding Classification 51 Off
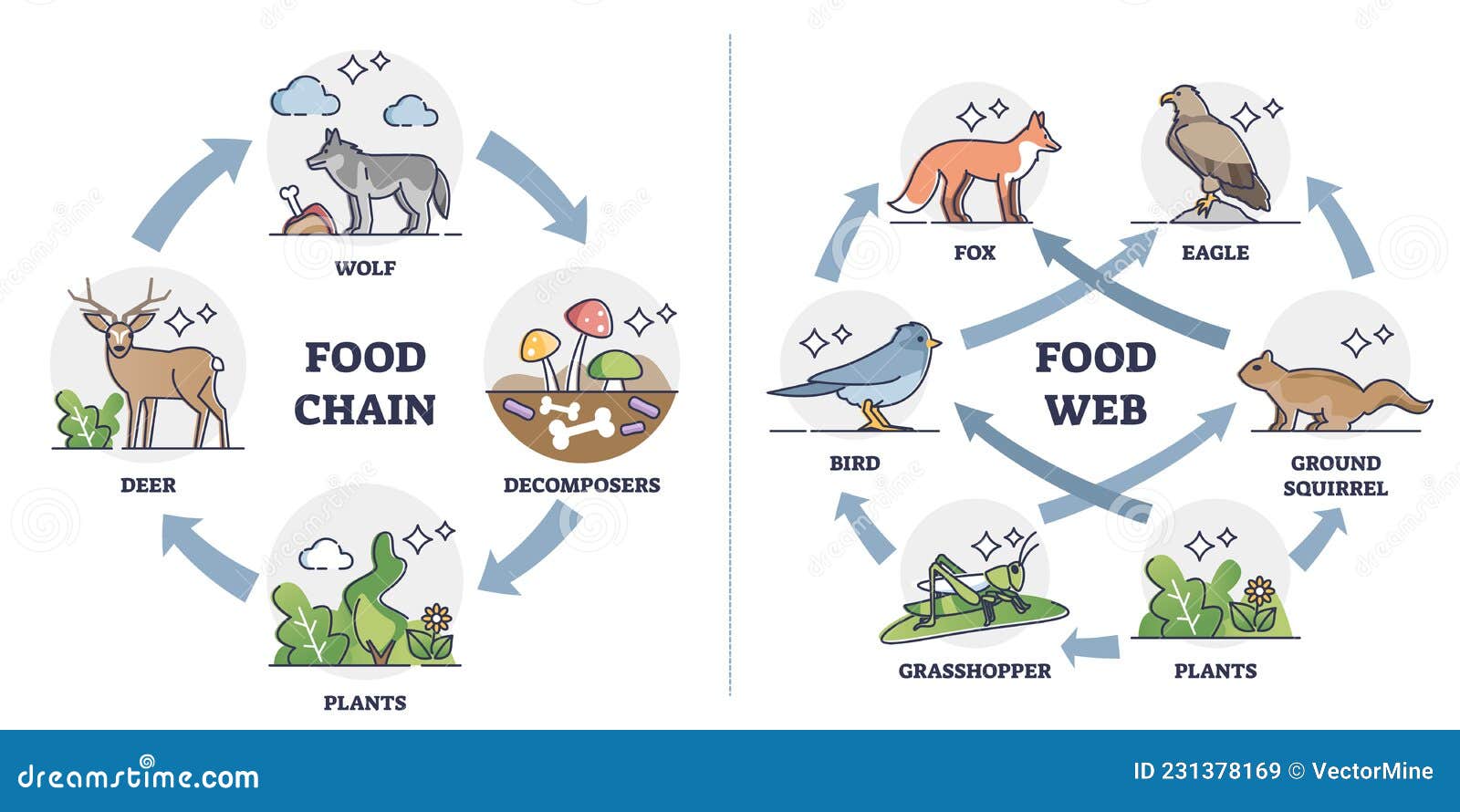
Food Chain Vs Food Web As Ecosystem Feeding Classification Outline A simple food chain with three trophic levels. food chains always start with a producer. this is usually a green plant or algae that completes. to store energy from sunlight as glucose. grass is. A food chain outlines who eats whom. a food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and.

Food Chain Vs Food Web As Ecosystem Feeding Classification 51 Off In ecology, food chains are linear sequences of species where each organism consumes and is consumed by another organism. they typically involve a few trophic levels and show a single path of energy transfer from producers to consumers. food chains are simplistic and do not consider organisms that feed from multiple trophic levels like. Figure 46.1b. 1 46.1 b. 1: food chain: these are the trophic levels of a food chain in lake ontario. energy and nutrients flow from photosynthetic green algae at the bottom to the salmon at the top of the food chain. there are only four links in this chain because significant energy is lost between each successive trophic level. Food chains. a food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

Food Chain Vs Food Web As Ecosystem Feeding Classification Outline Food chains. a food chain represents a single pathway by which energy and matter flow through an ecosystem. an example is shown in figure below. food chains are generally simpler than what really happens in nature. most organisms consume—and are consumed by—more than one species. this food chain includes producers and consumers. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. Food chain. the food chain is an ideal representation of flow of energy in the ecosystem. in food chain, the plants or producers are consumed by only the primary consumers, primary consumers are fed by only the secondary consumers and so on. the producers that are capable to produce their own food are called autotrophs. Food webs. a food chain is just one of the many paths that allow energy to flow through an ecosystem. but ecosystems are more complicated than a single food chain: every ecosystem includes many food chains that overlap and connect. for example, several different herbivores might all feed on one large field of grass.
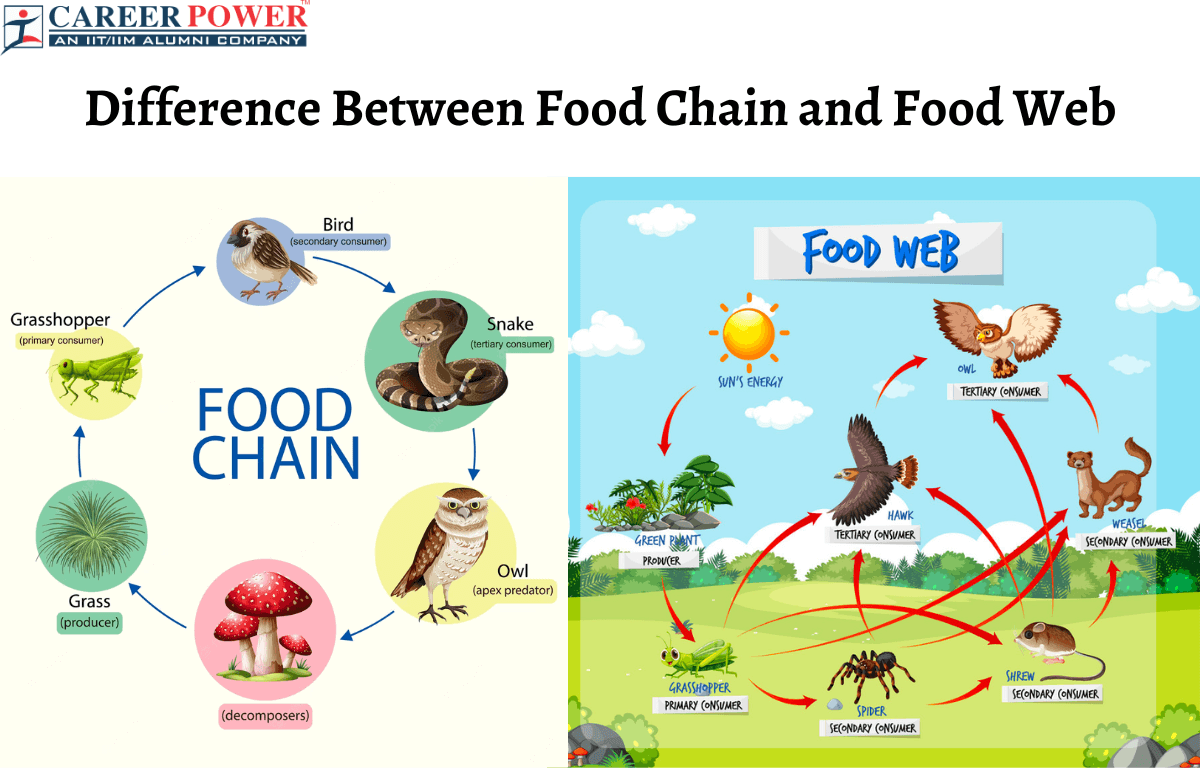
Food Chain Vs Food Web As Ecosystem Feeding Classification 51 Off Food chain. the food chain is an ideal representation of flow of energy in the ecosystem. in food chain, the plants or producers are consumed by only the primary consumers, primary consumers are fed by only the secondary consumers and so on. the producers that are capable to produce their own food are called autotrophs. Food webs. a food chain is just one of the many paths that allow energy to flow through an ecosystem. but ecosystems are more complicated than a single food chain: every ecosystem includes many food chains that overlap and connect. for example, several different herbivores might all feed on one large field of grass.

Comments are closed.