First Let S Look At The Different Ways To Position The Second Pair Of

First Let S Look At The Different Ways To Position The Second Pair Of A lever is a simple machine made of a rigid beam and a fulcrum. the effort (input force) and load (output force) are applied to either end of the beam. the fulcrum is the point on which the beam pivots. when an effort is applied to one end of the lever, a load is applied at the other end of the lever. Tools made from metal, wood, and plastic work like extensions of your body, making you feel stronger and helping you work faster and more efficiently. in science, tools like this are called simple machines. and although you might think there's a big difference between a tiny little wrench and a huge great earthmover, exactly the same physics is.

Which Of The Following Completes The Second Pair In The Same Way As The First, let’s look at the different ways to position the second pair of arms (there are many other ways, but these are very common): any advice for what to do when posing a character with four arms? i don't know how to pose the other two without them just doing the same thing as the top two. This raises an interesting point — we’ve got some redundancies here. alice bob charlie = charlie bob alice. for a moment, let’s just figure out how many ways we can rearrange 3 people. well, we have 3 choices for the first person, 2 for the second, and only 1 for the last. so we have $3 * 2 * 1$ ways to re arrange 3 people. With 5 science book on the bookshelf, we have 4 1 1 = 6 possible positions for the math books (4 positions between the science books, one position on the left and one position on the right). so, the number of all different placements of 4 different math books is = = 3*5 = 15. The first and second pair of data points comprise the horizontal line from the y axis to (x value, y value) and the second and third points make up the vertical line extending upward from the x axis. so if we start with the data from our table of air density and temperature, then add a second series with those pairs of data (using a scatter.

Pinterest With 5 science book on the bookshelf, we have 4 1 1 = 6 possible positions for the math books (4 positions between the science books, one position on the left and one position on the right). so, the number of all different placements of 4 different math books is = = 3*5 = 15. The first and second pair of data points comprise the horizontal line from the y axis to (x value, y value) and the second and third points make up the vertical line extending upward from the x axis. so if we start with the data from our table of air density and temperature, then add a second series with those pairs of data (using a scatter. An ordered pair tells you the location of a point by relating the point’s location along the x axis (the first value of the ordered pair) and along the [latex]y axis[ latex] (the second value of the ordered pair). in an ordered pair, such as [latex](x, y)[ latex], the first value is called the x coordinate and the second value is the y. The x coordinate is − 4 because it comes first in the ordered pair. start at the origin and move 4 units in a negative direction (left) along the x axis. the y coordinate is − 2 because it comes second in the ordered pair. now move 2 units in a negative direction (down). if you look over to the y axis, you should be lined up with − 2 on.

Terms Positions Gaynor Minden An ordered pair tells you the location of a point by relating the point’s location along the x axis (the first value of the ordered pair) and along the [latex]y axis[ latex] (the second value of the ordered pair). in an ordered pair, such as [latex](x, y)[ latex], the first value is called the x coordinate and the second value is the y. The x coordinate is − 4 because it comes first in the ordered pair. start at the origin and move 4 units in a negative direction (left) along the x axis. the y coordinate is − 2 because it comes second in the ordered pair. now move 2 units in a negative direction (down). if you look over to the y axis, you should be lined up with − 2 on.
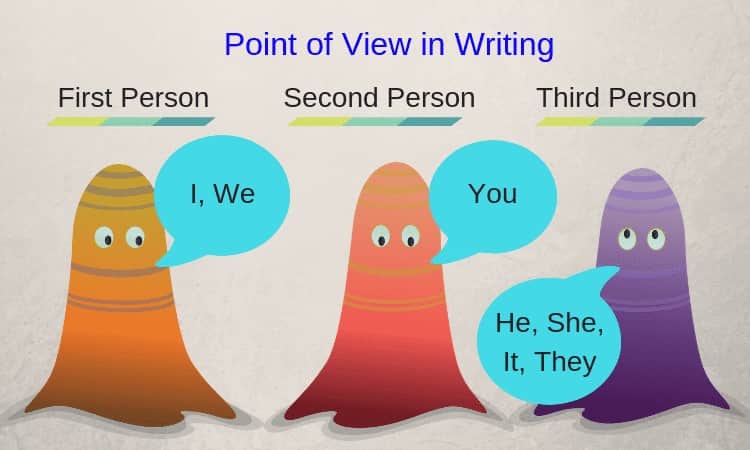
How To Use The Second Person Point Of View In Writing

Point Of View Part I First Second And Third Person Video

Comments are closed.