First Law Of Thermodynamics Work Heat Internal Energy Work Done
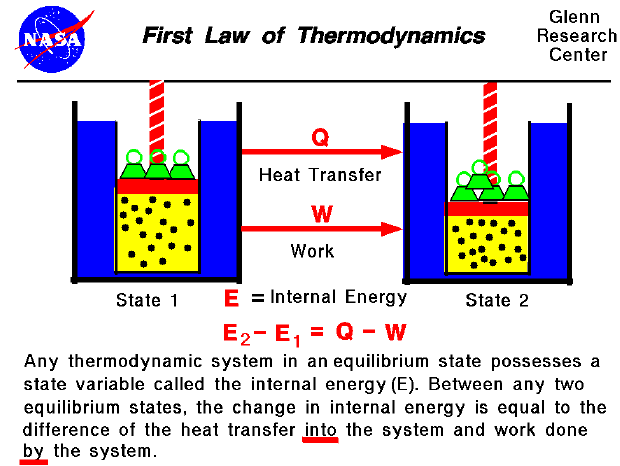
First Law Of Thermodynamics Energy is transferred along with the genetic material and so obeys the first law of thermodynamics. energy is transferred—not created or destroyed—in the process. when work is done on a cell or heat transfers energy to a cell, the cell’s internal energy increases. when a cell does work or loses heat, its internal energy decreases. The first law of thermodynamics is given as Δu = q − w Δ u = q − w, where Δu Δ u is the change in internal energy of a system, q q is the net heat transfer (the sum of all heat transfer into and out of the system), and w w is the net work done (the sum of all work done on or by the system). both q q and w w are energy in transit; only.

First Law Of Thermodynamics Work Heat Internal Energy Work Done The change in the internal energy of the system, Δu, is related to heat and work by the first law of thermodynamics, Δu = q − w. Δu = q − w. (14.2.1) here Δu is the change in internal energy u of the system, q is the net heat transferred into the system, and w is the net work done by the system. we use the following sign conventions: if. The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system equals the net heat transfer into the system minus the net work done by the system. in equation form, the first law of thermodynamics is. Δu = q − w. (15.1.1) (15.1.1) Δ u = q − w. here Δu Δ u is the change in internal energy u u of the system. The first law of thermodynamics is a formulation of the law of conservation of energy in the context of thermodynamic processes. the law distinguishes two principal forms of energy transfer, heat and thermodynamic work, that modify a thermodynamic system containing a constant amount of matter. the law also defines the internal energy of a. The first law of thermodynamics relates the internal energy change, work done by the system, and the heat transferred to the system in a simple equation. the internal energy is a function of state and is therefore fixed at any given point regardless of how the system reaches the state.

First Law Of Thermodynamics Basic Introduction Internal Energy Heat The first law of thermodynamics is a formulation of the law of conservation of energy in the context of thermodynamic processes. the law distinguishes two principal forms of energy transfer, heat and thermodynamic work, that modify a thermodynamic system containing a constant amount of matter. the law also defines the internal energy of a. The first law of thermodynamics relates the internal energy change, work done by the system, and the heat transferred to the system in a simple equation. the internal energy is a function of state and is therefore fixed at any given point regardless of how the system reaches the state. A from equation 12.2.3 12.2.3, we know that Δu = q w Δ u = q w (first law of thermodynamics). we are given the magnitude of q q (140 j) and need only determine its sign. because energy is transferred from the system (the gas) to the surroundings, q q is negative by convention. b because the gas is being compressed, we know that work is. Define the first law of thermodynamics. describe how conservation of energy relates to the first law of thermodynamics. identify instances of the first law of thermodynamics working in everyday situations, including biological metabolism. calculate changes in the internal energy of a system, after accounting for heat transfer and work done.
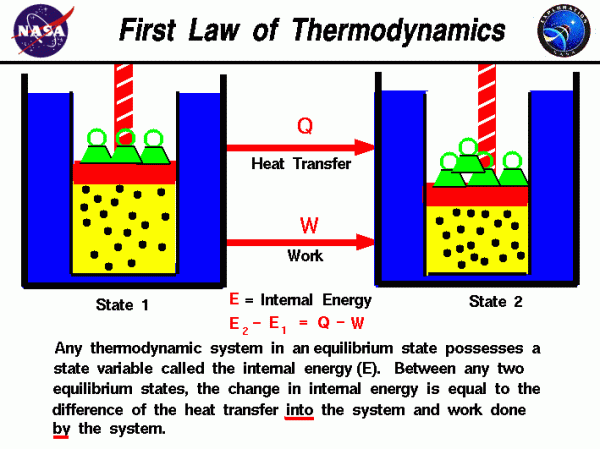
First Law Internal Energy Glenn Research Center Nasa A from equation 12.2.3 12.2.3, we know that Δu = q w Δ u = q w (first law of thermodynamics). we are given the magnitude of q q (140 j) and need only determine its sign. because energy is transferred from the system (the gas) to the surroundings, q q is negative by convention. b because the gas is being compressed, we know that work is. Define the first law of thermodynamics. describe how conservation of energy relates to the first law of thermodynamics. identify instances of the first law of thermodynamics working in everyday situations, including biological metabolism. calculate changes in the internal energy of a system, after accounting for heat transfer and work done.

First Law Of Thermodynamics Thermal Energy And Work Done Youtube

Comments are closed.