Find Equation Of Polynomial Given Degree Roots Complex And A Point

Find Equation Of Polynomial Given Degree Roots Complex And A Point Thanks to all of you who support me on patreon. you da real mvps! $1 per month helps!! 🙂 patreon patrickjmt !! find equation of polynomia. Free equation given roots calculator find equations given their roots step by step. high school math solutions – quadratic equations calculator, part 1. a quadratic equation is a second degree polynomial having the general form ax^2 bx c = 0, where a, b, and c.
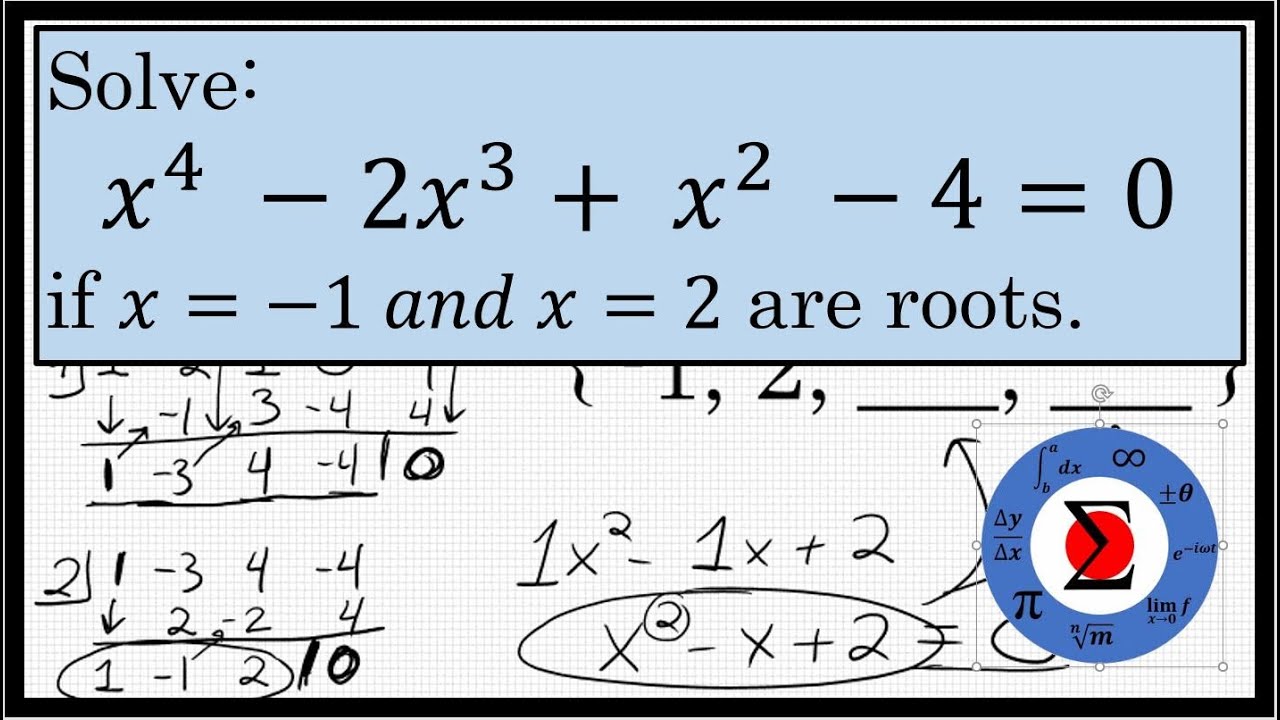
Solving A Polynomial Equation Given Roots Youtube 5. since complex number field c is algebraically closed, every polynomials with complex coefficients have linear polynomial decomposition. in this case, it's z3 − 3z2 6z − 4 = (z − 1)(z − 1 √3i)(z − 1 − √3i). so you can see the solution of the equation easily from this representation. one way to find out such decomposition. Ving complex numbers: here w 2 c is given while2 c is to be determined. we shall see. hereafter that the polynomial equation (2) has exactly n solutions in c. to compute suc. = jwjeit. and. z = jzjei#: (3) taking the n th power of z as in (1) and substituting it into (2) yields. jzjnein = jwjeit. We solve an equation with complex roots in the same way we solve any other quadratic equations. if in the form we can rearrange to solve. if in the form we can complete the square or use the quadratic formula. we use the property along with a manipulation of surds. when the coefficients of the quadratic equation are real, complex roots occur in. Fundamental theorem of algebra. a polynomial p (x) p(x) of degree n with complex coefficients has, counted with multiplicity, exactly n roots. the part “counted with multiplicity” means that we have to count the roots by their multiplicity, that is, by the times they are repeated. for example, in the equation { { (x 2)}^3} (x 2)=0 (x− 2)3.

Find The Polynomial Given The Roots We solve an equation with complex roots in the same way we solve any other quadratic equations. if in the form we can rearrange to solve. if in the form we can complete the square or use the quadratic formula. we use the property along with a manipulation of surds. when the coefficients of the quadratic equation are real, complex roots occur in. Fundamental theorem of algebra. a polynomial p (x) p(x) of degree n with complex coefficients has, counted with multiplicity, exactly n roots. the part “counted with multiplicity” means that we have to count the roots by their multiplicity, that is, by the times they are repeated. for example, in the equation { { (x 2)}^3} (x 2)=0 (x− 2)3. The quadratic factor can produce two real roots or two complex conjugates. consider f(x) = x4 2x3 26x2 38x 145 = 0. starting with the factor x2 x 1, the next estimate is x2 1.960x 5.191, then the factor x2 2.000x 4.998, and then x2 2x 5. this gives the roots 1 ± 2i and the reduced polynomial is a quadratic with roots 2. About solving equations. a value c is said to be a root of a polynomial p x if p c =0. the largest exponent of x appearing in p x is called the degree of p. if p x has degree n, then it is well known that there are n roots, once one takes into account multiplicity. to understand what is meant by multiplicity, take, for example, x2 6x 9= x 3.

Find The Polynomial Given The Roots The quadratic factor can produce two real roots or two complex conjugates. consider f(x) = x4 2x3 26x2 38x 145 = 0. starting with the factor x2 x 1, the next estimate is x2 1.960x 5.191, then the factor x2 2.000x 4.998, and then x2 2x 5. this gives the roots 1 ± 2i and the reduced polynomial is a quadratic with roots 2. About solving equations. a value c is said to be a root of a polynomial p x if p c =0. the largest exponent of x appearing in p x is called the degree of p. if p x has degree n, then it is well known that there are n roots, once one takes into account multiplicity. to understand what is meant by multiplicity, take, for example, x2 6x 9= x 3.

How To Find A Polynomial Of A Given Degree With Given Zeros Algebra

Comments are closed.