Filament In Biology Definition Types Examples Lesson Study

Filament In Biology Definition Types Examples Lesson Study In biology, the term ''filament'' is widely used in many contexts and with different meanings. however, in the context of the cytoskeleton, three types of protein filaments make up its structure. Filaments are the structural proteins of the cell. there are three kinds of filaments: microtubules, intermediate filaments, and microfilaments. microtubules are the largest filament and act as.

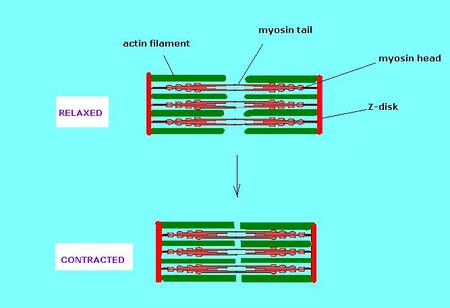
Filament In Biology Definition Types Examples Lesson Study Actin filaments are multipurpose proteins found in the vast majority of eukaryotic cells. actin is an important part of the cytoskeleton of certain types of eukaryotic cells. it is critical to. There are three types of fibers within the cytoskeleton: microfilaments, intermediate filaments, and microtubules (figure 4.5.1 4.5. 1). here, we will examine each. figure 4.5.1 4.5. 1: microfilaments thicken the cortex around the inner edge of a cell; like rubber bands, they resist tension. The anther is usually at the end of a thin tube like structure called the filament. filament: the filament is a stalk that holds up the anther, making the pollen accessible to pollinators or wind. female parts (pistil or carpel or gynoecium) stigma: this is the part of the pistil that receives. it is often sticky or feathery for trapping and. Cytoskeleton definition. the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus. it is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms. the cytoskeleton supports the cell, gives it shape.
Filament In Biology Definition Types Examples Lesson Study The anther is usually at the end of a thin tube like structure called the filament. filament: the filament is a stalk that holds up the anther, making the pollen accessible to pollinators or wind. female parts (pistil or carpel or gynoecium) stigma: this is the part of the pistil that receives. it is often sticky or feathery for trapping and. Cytoskeleton definition. the cytoskeleton is a network of filaments and tubules that extends throughout a cell, through the cytoplasm, which is all of the material within a cell except for the nucleus. it is found in all cells, though the proteins that it is made of vary between organisms. the cytoskeleton supports the cell, gives it shape. 2. intermediate filaments are composed of linear subunits that wrap around each other and interact very tightly. structurally, as mentioned previously, all intermediate laments start from a fibrous subunit (figure 12.2.2 12.2. 2). this then coils around another filamentous subunit to form a coiled coil dimer, or protofilament. Examples of intermediate filaments in cells example 1. the nuclear lamina. since all eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, the nuclear lamina is easily the most important example of intermediate filament function. we have already discussed this function back in chapter 3, when we examined the structure of the nucleus in detail. the nuclear lamina is.

Comments are closed.