Figure 3 Chronic Stress And Effect On Brain Development In Childhood

Figure 3 Chronic Stress And Effect On Brain Development In Childhood Background chronic and or extreme stress in early life, often referred to as early adversity, childhood trauma, or early life stress, has been associated with a wide range of adverse effects on development. however, while early life stress has been linked to negative effects on a number of neural systems, the specific mechanisms through which early life stress influences development and. Trauma in childhood is a grave psychosocial, medical, and public policy problem that has serious consequences for its victims and for society. chronic interpersonal violence in children is common worldwide. developmental traumatology, the systemic investigation of the psychiatric and psychobiological effects of chronic overwhelming stress on.
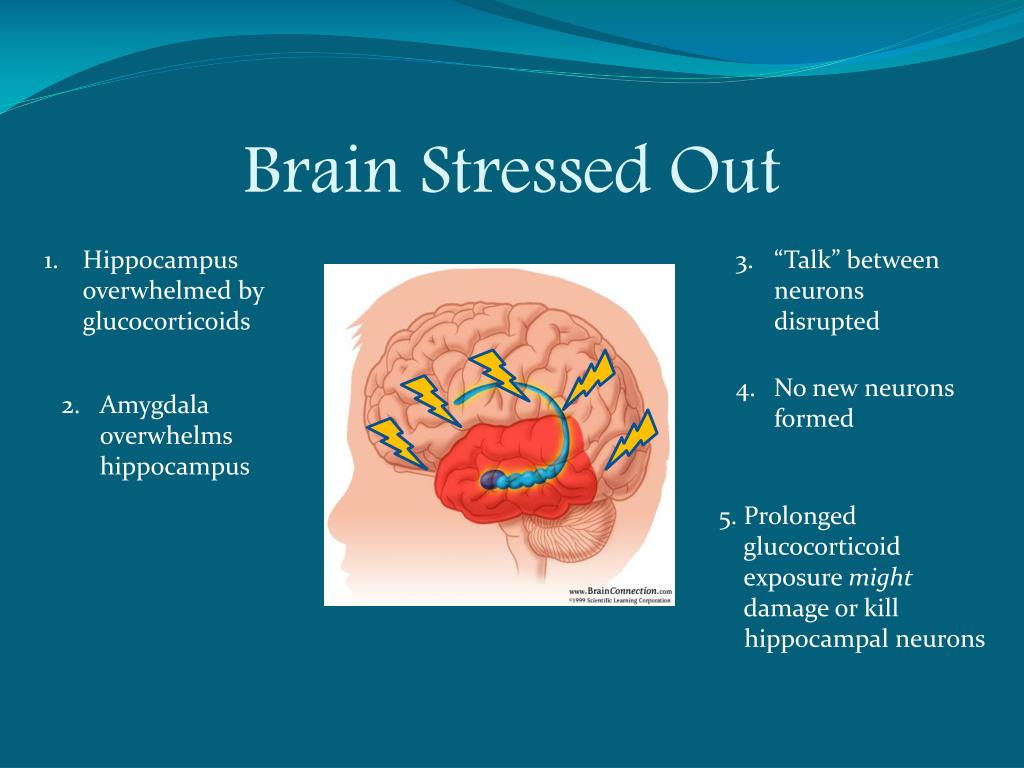
Ppt Childhood Trauma Chronic Stress Powerpoint Presentation Id Abstract. traumatic experiences early in life predispose animals and humans to later cognitive behavioral, emotional, and somatic problems. in humans, traumatic experiences are strong predictors of psychiatric illness. a growing body of research has emphasized alterations in neurological structure and function that underscore phenotypic changes. This type of prolonged stress exposure disrupts a child’s brain development and increases the risk for stress related disease and long term cognitive impairment, even well into the adult years. Discussion. traumatic stress has a broad range of effects on brain function and structure, as well as on neuropsychological components of memory. brain areas implicated in the stress response include the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex. neurochemical systems, including cortisol and norepinephrine, play a critical role in the stress. For example, human studies include temporally diverse types of stress: chronic stress throughout development, stress limited to infancy or childhood, or chronic stress during adolescence, each of which may have differential effects on brain development (figure 1). 189,243,244 further, difference in the nature of the stressor (e.g., abuse vs.

How Chronic Stress Affects Our Brain Back To Balance Discussion. traumatic stress has a broad range of effects on brain function and structure, as well as on neuropsychological components of memory. brain areas implicated in the stress response include the amygdala, hippocampus, and prefrontal cortex. neurochemical systems, including cortisol and norepinephrine, play a critical role in the stress. For example, human studies include temporally diverse types of stress: chronic stress throughout development, stress limited to infancy or childhood, or chronic stress during adolescence, each of which may have differential effects on brain development (figure 1). 189,243,244 further, difference in the nature of the stressor (e.g., abuse vs. For example, the brain develops in multiple stages throughout childhood, and its vulnerability to the effects of chronic stress varies over the course of development (andersen, 2003). thus, researchers must consider and further explore potentially sensitive periods in development in studies of chronic stress in children. Multiple consequences of early life stress. brain development goes through sensitive periods during which stressors and nurturing experiences can have lasting effects, as was shown in the center for disease control adverse childhood experiences study carried out on a middle class population in california. and a chart (see below) from a recent.

Early Brain And Child Development The Public Health For example, the brain develops in multiple stages throughout childhood, and its vulnerability to the effects of chronic stress varies over the course of development (andersen, 2003). thus, researchers must consider and further explore potentially sensitive periods in development in studies of chronic stress in children. Multiple consequences of early life stress. brain development goes through sensitive periods during which stressors and nurturing experiences can have lasting effects, as was shown in the center for disease control adverse childhood experiences study carried out on a middle class population in california. and a chart (see below) from a recent.

Stress And Early Brain Growth Infograph

Comments are closed.