Figure 1 From Remote Management Of Pacemaker Patients With Biennial In
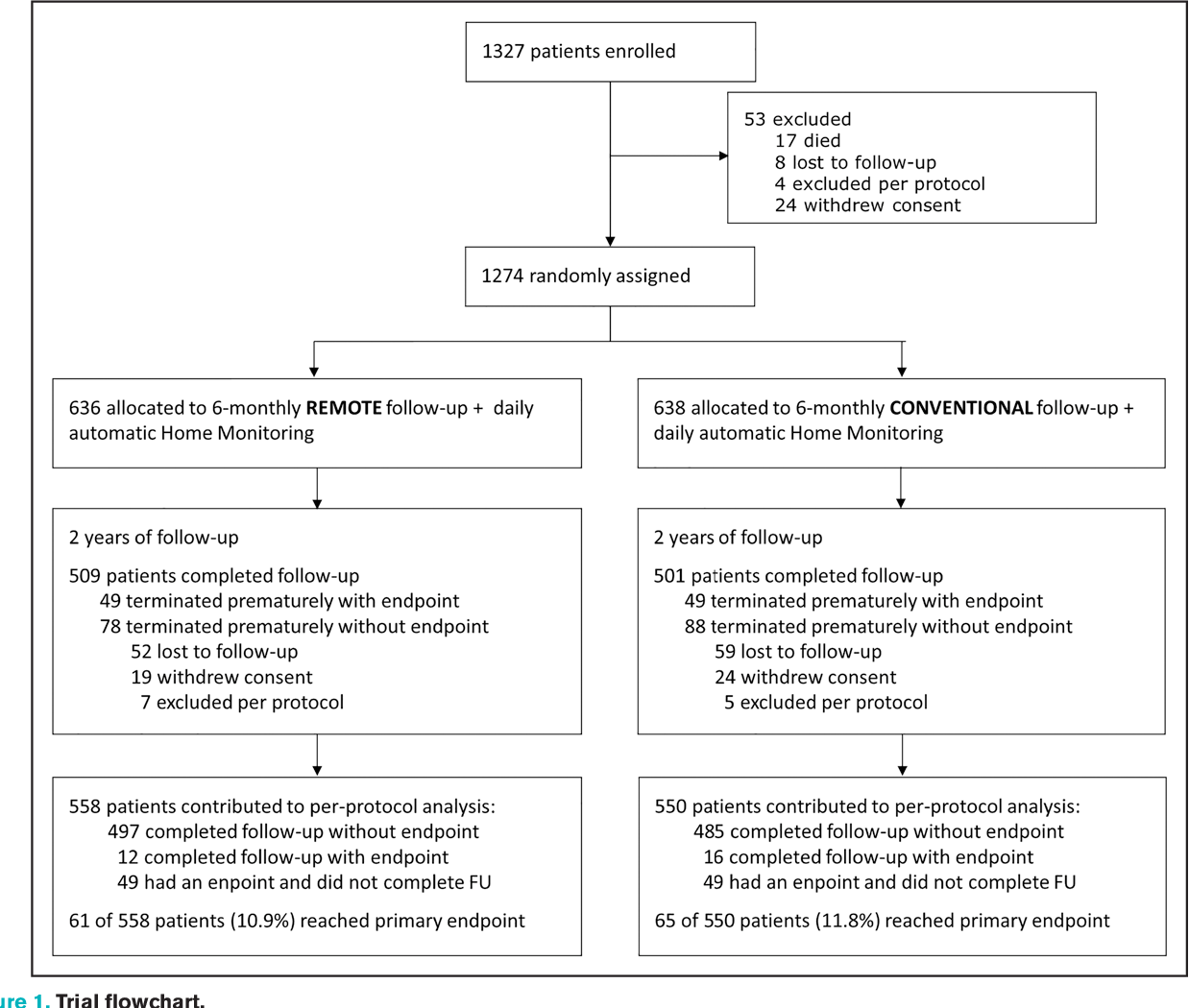
Figure 1 From Remote Management Of Pacemaker Patients With Biennial In Background: current expert consensus recommends remote monitoring for cardiac implantable electronic devices, with at least annual in office follow up. we studied safety and resource consumption of exclusive remote follow up (rfu) in pacemaker patients for 2 years. methods: in japan, consecutive pacemaker patients committed to remote monitoring were randomized to either rfu or conventional in. Only 1.5% of scheduled in office follow ups were considered actionable. conclusions: replacing periodic in office follow ups with remote follow ups for 2 years in pacemaker patients committed to remote monitoring does not increase the occurrence of major cardiovascular events and reduces resource consumption.

Remote Management Of Pacemaker Patients With Biennial In Clinic In japan, consecutive pacemaker patients committed to remote monitoring were randomized to either rfu or conventional in office follow up (conventional follow up) at twice yearly intervals. rfu patients were only seen if indicated by remote monitoring. all returned to hospital after 2 years. Replacing periodic in office follow ups with remote follow ups for 2 years in pacemaker patients committed to remote monitoring does not increase the occurrence of major cardiovascular events and reduces resource consumption. registration: url: clinicaltrials.gov; unique identifier: nct01523 …. Reduced for pacemaker patients, thus significantly reducing the resource consumption related to management of pacemaker patients. patient surveillance purely based on home monitoring for 24 months (no scheduled in office visits in between) was safe for real world pacemaker patients*. patients at risk rfu:636 624 594608587 575513 403 549. From 1.76 to 0.54 per patient year) than in compas (36.2 % from 1.63 to 1.0 4 per patient year). apart from facilitat ing e fficient follow up , r m promises improved patient care. 13 our.
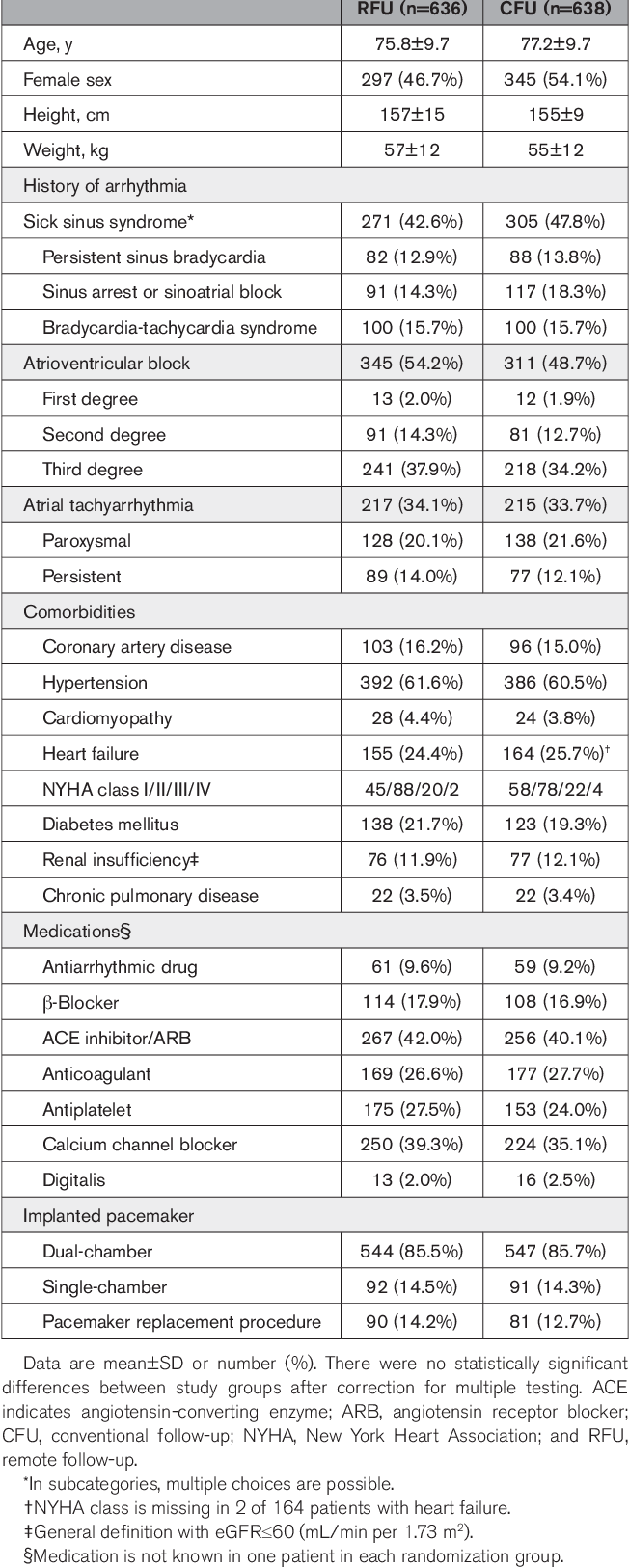
Table 1 From Remote Management Of Pacemaker Patients With Biennial In Reduced for pacemaker patients, thus significantly reducing the resource consumption related to management of pacemaker patients. patient surveillance purely based on home monitoring for 24 months (no scheduled in office visits in between) was safe for real world pacemaker patients*. patients at risk rfu:636 624 594608587 575513 403 549. From 1.76 to 0.54 per patient year) than in compas (36.2 % from 1.63 to 1.0 4 per patient year). apart from facilitat ing e fficient follow up , r m promises improved patient care. 13 our. Doi: 10.1161 circep.119.007734 corpus id: 216594364; remote management of pacemaker patients with biennial in clinic evaluation. Replacing periodic in office follow ups with remote follow up for 2 years in pacemaker patients committed to remote monitoring does not increase the occurrence of major cardiovascular events and reduces resource consumption. supplemental digital content is available in the text. background: current expert consensus recommends remote monitoring for cardiac implantable electronic devices, with.

Comments are closed.